Abstract
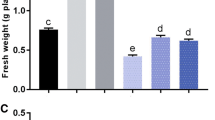
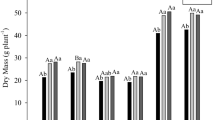
Pot experiments were conducted to evaluate the possible interaction of salinity (osmotic potential -0.3, -0.9 and -1.2 MPa) and occurrence of Azospirillum lipoferum or exogenous gibberellic acid (GA3) (100 µg g-1) on growth and some physiological parameters of maize. 15N-uptake as well as the percentage of nitrogen derived from 15N-fertilizer were decreased by increasing the NaCl concentrations and completely inhibited at concentrations corresponding to osmotic potentials -0.9 and -1.2 MPa. The percentage of nitrogen originating from N2 fixation was significantly correlated to the total counts of Azospirillum cells that colonized the histosphere. At high NaCl concentrations although no significant changes in N % in shoot dry mass either in inoculated or uninoculated plants were observed, the total N-yield [mg(N) pot-1] was decreased. Fresh and dry shoot mass significantly increased by Azospirillum inoculation. Azospirillum and GA3 treatments were positively correlated with most of the parameters analysed. Azospirillum inoculation or GA3 application at NaCl concentrations up to -1.2 MPa significantly increased the chlorophyll, K, Ca, soluble saccharides and protein contents as compared with control plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Wahab, A.M., Zahran, H.H.: Effects of salt stress on nitrogenase activity and growth of four legumes.-Biol. Plant. 23:16-23, 1981.
Abdul-Kadir, S.M., Paulsen, G.M.: Effect of salinity on nitrogen metabolism in wheat.-J. Plant Nutr. 5: 1141-1151, 1982.
Al-Rawahy, S.A., Stroehlein, J.L., Pessarrakli, M.: Dry matter yield and nitrogen-15, Na, Cl, and K content of tomatoes under sodium chloride stress.-J. Plant Nutr. 15: 341-358, 1992.
Barnett, N.M., Naylor, A.W.: Amino acids and protein metabolism in Bermuda grass during water stress.-Plant Pysiol. 41: 1222-1230, 1986.
Bashan, Y., Harrison, S.K., Whitmayer, R.E.: Enhanced growth of wheat and soybean plants inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense is not due to general enhanced of mineral uptake.-Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 769-775, 1990.
Bejaoui, M.: Interactions between NaCl and some phytohormones on soybean growth.-J. Plant Physiol. 120: 95-110, 1985.
Bekki, A., Trinchant, J. C., Rigaud, J.: Nitrogen fixation (C2H2 reduction) by Medicago nodules and bacteriods under sodium chloride stress.-Physiol. Plant. 71: 61-67, 1987.
Bernstein, L., Francois, L.E., Clark, R.A.: Interactive effects of salinity and fertility on yields of grain and vegetables.-Agron. J. 66: 412-421, 1974.
Boddey, R.M., Victoria, R.L.: Estimation of biological nitrogen fixation associated with Brachiaria and Paspalum grasses using 15N labeled organic matter and fertilizer.-Plant Soil 90: 265-292, 1986.
Boucaud, J., Unger, I.A.: Influence of hormonal treatments on the growth of two halophytic species of Suaeda.-Amer. J. Bot. 63: 694-699, 1976.
Caballero-Mellado, G., Carcano Mantiel, M.G., Mascaarua-Esparza, M.A.: Field inoculation of wheat (Triticum aestivum) with Azospirillum brasilense under temperate climate.-Symbiosis 13: 243-253, 1992.
Cochram, W. G.: Estimation of bacterial densities by means of most probable number.-Biometric 6: 105-116, 1950.
Cordovilla, M.P., Ligero, F., Lluch, C.: The effect of salinity on nitrogen fixation and assimilation in Vicia faba.-J. exp. Bot. 45: 1483-1488, 1994.
Devitt, D. A., Stolzy, L., Labonauskas, C.K.: Impact of potassium, sodium and salinity on the protein and free amino acids content of wheat grain.-Plant Soil 103: 101-109, 1987.
Dobereiner, J.: The Brazilian program in biological nitrogen fixation.-In: Graham, P.H., Harris, S.C. (ed.): BNF Technology for Tropical Agriculture. Pp. 687-688. CIAT, Cali 1982.
Dobereiner, J., Day, J. M.: Physiological aspects of N2 fixation by Azospirillum from Digitaria roots.-Soil Biol. Biochem. 8: 45-50, 1976.
El-Komy, H.M.: Ecological and physiological studies on the genus Azospirillum from the rhizosphere of maize and rice plants.-Ph.D. Thesis. Institute of Agricultural Microbiology, Russian Acad. Agr. Sci., Sankt Peterburg 1992.
El-Rewainy, H. M.: Studies on use of azospirilla for improving growth and yield of some non-leguminous plants.-Ph.D. Thesis. Dept. of Soils and Water, Fac. Agr., Assiut Univ., Assiut 1994.
Fales, F.W.: The assimilation and degradation of carbohydrates of yeast cells.-J. biol. Chem. 193: 113-118, 1951.
Fried, M., Middleboe, V.: Measurement of amount of nitrogen fixed by a legume crop.-Plant Soil 47: 713-715, 1977.
Frota, J.N.E., Tucker, T.C.: Absorption rates of ammonia and nitrate by red kidney beans under salt and water stress.-Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 42: 753-756, 1978.
Giller, K.E., Day, J.M.: Nitrogen fixation in the rhizosphere: significance in nature and agricultural systems.-In: Filter, A.H., Atkinson, D., Read, D.J., Usher, M.B. (ed.): Ecological Interaction in Soil. Pp. 127-147. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford 1985.
Hamdia, H.A.: Physiological studies of some plants to salinity injury.-Ph.D. Thesis, Minia University, Minia 1991.
Handa, S., Bressan, R.A., Handa, A.K., Carpita, N.C., Hasegawa, P.M.: Solutes contributing to osmotic adjustment in cultured plant cells adapted to water stress.-Plant Physiol. 73: 834-843, 1983.
Hegazi, N.A.: Contribution of Azospirillum spp. a symbiotic N2-fixation in Egypt.-In: Klingmuller, W. (ed.): Azospirillum II — Genetics, Physiology, Ecology. Pp. 171-189. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1983.
Ishac, Y.Z., El-Haddad, M.E., El-Borollosy, M.A., Eweda, W.E., Giris, M.G.Z.: Studies on Azospirillum in Egypt. I — Densities as affected by some ecological factors.-In: Proc. 2nd AABNF Conference. Pp. 450-468. Cairo 1988.
Itai, C., Wayers, J.D.B., Hillman, J.R., Meidner, H., Willmer, C. M.: Abscisic acid and guard cells of Commelina communis L.-Nature 271: 652-654, 1978.
Lin, W., Okon, Y., Hardy, R.W.F.: Enhanced mineral uptake by Zea mays and Sorghum bicolor roots inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense.-Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1175-1779, 1983.
Lowry, O.H., Roserbrogh, N.J., Farr, A.L., Ramadall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.-J. biol. Chem. 193: 265-275, 1951.
Makboul, H.E., Fayez, N., Eman, N.F., El-Shahawy, R.: Nitrogen-fixing azospirilla in some soils of Egypt.-In: Proc. V. Conference of Microbiology. Vol. II. Soils and Water Microbiology. Cairo 1983.
Martin, A.E., Burgess, B.K., Ismaa, S.E., Smart, C.T., Dean, D.R.: Construction and characterization of an Azotobacter vinelandii strain with mutations in the genes encoding flavodoxin and ferredoxin.-J. Bacteriol. 171: 3162-3167, 1989.
Metzner, H., Rau, H., Senger, H.: Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbarkeit einzelner Pigment-Mangel Mutanten von Chlorella.-Planta 65: 186-194, 1965.
Mohammad, M., Campbell, W.F., Rumbaugh, M.D.: Variation in salt tolerance of alfalfa.-Arid Soil Rehabil. 3: 11-20, 1989.
Moore, S., Stein, W.: Photometric Ninhydrine Method for Use in the Chromatography of Amino Acids.-Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York 1948.
Omay, S.H., Schmidt, W.A., Martin, P.: Indole acetic acid production by the rhizosphere bacterium Azospirillum brasilense Cd. under in vitro conditions.-Can. J. Microbiol. 39: 187-192, 1993.
Pessarakli, M., Tucker, T.C.: Dry matter yield and nitrogen-15 uptake by tomato under NaCl stress.-Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 52: 698-700, 1988.
Picconi, P., Bottini, R.: Effect of C/N ratio, N content, pH and inoculation time on growth and gibberelin production by Azospirillum lipoferum.-Symbiosis 17: 229-236, 1994.
Rao, A.V., Venkateswarlu, B.: Salt tolerance of Azospirillum brasilense.-Acta microbiol. hung. 32: 221-224, 1985.
Reinhold, B., Hurek, T., Fendrik, I., Pot, B., Gillis, M., Kertsers, K., Thielemans, D., De Ley, J.: Azospirillum halopreaferans sp. nov., a nitrogen fixing organism associated with roots of kallar grasses (Leptochloa fusca L. Kunth).-Int. J. system. Bacteriol. 37: 43-51, 1987.
Rennie, R.J.: 15N-isotope dilution as a measure of dinitrogen fixation by Azospirillum brasilense associated with maize.-Can. J. Bot. 58: 21-24, 1980.
Rennie, R.J.: Defreitas, J.R., Ruschel, A.P., Vose, P.B.: 15N-isotope dilution to quantify nitrogen fixation associated with Canadian and Brazilian wheat.-Can. J. Bot. 61: 1667-1671, 1983.
Rice, I.: Utility of phyllosphere N2-fixing microorganisms in the improvement of crop growth.-Plant Soil 68: 55-67, 1982.
Schwarzenbach, G., Biedermann, W.: Complexons X. Alkaline earth complexes of O,O-dihydroxyazodyes.-Helv. chim. Acta 31: 678-687, 1948.
Singleton, P.W.: A split-root growth system for evaluating the effect of salinity on components of the soybean Rhizobium japonicum symbiosis.-Crop Sci. 23: 259-262, 1983.
Starck, Z., Karwowska, R.: Effect of salt stress on the hormonal regulation of growth, photosynthesis and distribution of 14C-assimilates in bean plants.-Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 47: 245-267, 1978.
Steel, R.G., Torrie, J.H.: Principles and Procedures of Statistics.-McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York 1960.
Shaddad, M.A., El-Tayeb, M.A.: Interactive effects of soil moisture content and hormonal treatments on dry matter and pigment contents of some crop plants.-Acta agron. hung. 39: 49-57, 1990.
Walker, A.M., Dumbroff, B.E.: Effect of salt stress on abscisic and cytokinin levels in tomato.-Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 101: 461-470, 1981.
Wallace, A., Berry, W.L.: Toxicity — the concept and relationship to the dose response curve.-J. Plant Nutr. 3: 13-19, 1981.
Weil, R.R., Khalil, N.A.: Salinity tolerance of winged beans as compared to that of soybean.-J. Agron. 78: 67-70, 1986.
Williams, V., Twine, S.: Flame photometric methods for sodium, potassium, and calcium.-In: Paech, K., Tracey, M.V. (ed.): Modern Methods of Plants Analysis. Vol. V. Pp. 3-5. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1960.
Zahran, H.H.: Conditions for successful Rhizobium-legume in saline environments.-Biol. Fertil. Soils 12: 73-80, 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdia, M., El-Komy, H. Effect of salinity, gibberellic acid and Azospirillum inoculation on growth and nitrogen uptake of Zea mays. Biologia Plantarum 40, 109–120 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000904819841
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000904819841