Abstract
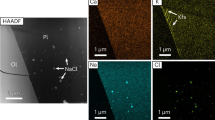
The SNC (Shergotty-Nakhla-Chassigny) meteorites have recorded interactions between martian crustal fluids and the parent igneous rocks. The resultant secondary minerals — which comprise up to ∼1 vol.% of the meteorites — provide information about the timing and nature of hydrous activity and atmospheric processes on Mars. We suggest that the most plausible models for secondary mineral formation involve the evaporation of low temperature (25 – 150 °C) brines. This is consistent with the simple mineralogy of these assemblages — Fe-Mg-Ca carbonates, anhydrite, gypsum, halite, clays — and the chemical fractionation of Ca-to Mg-rich carbonate in ALH84001 "rosettes". Longer-lived, and higher temperature, hydrothermal systems would have caused more silicate alteration than is seen and probably more complex mineral assemblages. Experimental and phase equilibria data on carbonate compositions similar to those present in the SNCs imply low temperatures of formation with cooling taking place over a short period of time (e.g. days). The ALH84001 carbonate also probably shows the effects of partial vapourisation and dehydration related to an impact event post-dating the initial precipitation. This shock event may have led to the formation of sulphide and some magnetite in the Fe-rich outer parts of the rosettes.
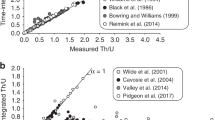
Radiometric dating (K-Ar, Rb-Sr) of the secondary mineral assemblages in one of the nakhlites (Lafayette) suggests that they formed between 0 and 670 Myr, and certainly long after the crystallisation of the host igneous rocks. Crystallisation of ALH84001 carbonate took place 0.5 Gyr after the parent rock. These age ranges and the other research on these assemblages suggest that environmental conditions conducive to near-surface liquid water have been present on Mars periodically over the last ∼1 Gyr. This fluid activity cannot have been continuous over geological time because in that case much more silicate alteration would have taken place in the meteorite parent rocks and the soluble salts would probably not have been preserved.
The secondary minerals could have been precipitated from brines with seawater-like composition, high bicarbonate contents and a weakly acidic nature. The co-existence of siderite (Fe-carbonate) and clays in the nakhlites suggests that the pCO2 level in equilibrium with the parent brine may have been 50 mbar or more. The brines could have originated as flood waters which percolated through the top few hundred meters of the crust, releasing cations from the surrounding parent rocks. The high sulphur and chlorine concentrations of the martian soil have most likely resulted from aeolian redistribution of such aqueously-deposited salts and from reaction of the martian surface with volcanic acid volatiles.
The volume of carbonates in meteorites provides a minimum crustal abundance and is equivalent to 50–250 mbar of CO2 being trapped in the uppermost 200–1000 m of the martian crust. Large fractionations in δ18O between igneous silicate in the meteorites and the secondary minerals (≤30‰) require formation of the latter below temperatures at which silicate-carbonate equilibration could have taken place (∼400°C) and have been taken to suggest low temperatures (e.g. ≤150°C) of precipitation from a hydrous fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anovitz, L.M., and Essene, E.J.: 1987, 'Phase Equilibria in the System CaCO3-MgCO3-FeCO3', J. Petrology 28, 389-414.
Baker, V.R., Carr, M.H., Gulick, V.C., Williams, C.R., Marley, M.S.: 1992, 'Channels and Valley Networks', in H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder and M.S. Matthews (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 493-522.
Baker, L.L., Agenbroad, D.J., and Wood, S.J.: 2000, 'Experimental Hydrothermal Alteration of a Martian Analog Basalt:Implications for Martian Meteorites', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 31-38.
Banin, A., Clark, B.C. and Wänke, H.: 1992, 'Surface Chemistry and Mineralogy', in H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder and M.S. Matthews (Eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 594-625.
Banin, A., Han, F.X., Kan, I. and Cicelsky A.: 1997, 'Acidic Volatiles in the Mars Soil', J. Geophys.Res. 102, 13,341-13, 356.
Bell, J.F. III, et al.: 2000, 'Mineralogic and Compositional Properties of Martian Soil and Dust: Results from Pathfinder', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 1721-1755.
Bibring, J.-P., and Erard, S.: 2001, 'The Martian Surface Composition', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Bills, B.G.: 1990, 'The Rigid Obliquity History of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14, 137-14, 153.
Boctor, N.Z., Wang, J., Alexander, C.M.O'D., Hauri, E., Bertka, C.M. and Fei, Y.: 1998, 'Hydrogen Isotope Studies of Carbonate and Phosphate in Martian Meteorite Allan Hills 84001' Met. Planet.Sci. 33, A18 (abstract).
Bogard, D.D., and Garrison, D.H.: 1999, 'Argon-39-argon-40 “Ages” and Trapped Argon in Martian Shergottites, Chassigny, and Allan Hills 84001', Met. Planet. Sci. 34, 451-473.
Bogard, D.D., Clayton, R.N., Marti, K., Owen, T., and Turner, G.: 'Martian Volatiles:Isotopic Composition, Origin, and Evolution', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Borg, L.E., Connelly, J.N., Nyquist, L.E., Shih, C.-Y., Wiesmann, H., and Reese, Y.: 1999, 'The Age of the Carbonates in Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Science 286, 90-94.
Bradley, J.P., McSween, H.P., and Harvey, R.P.: 1998, 'Epitaxial Growth of Nanophase Magnetite in Martian Meteorite Allan Hills 84001:Implications for Biogenic Mineralization', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, 765-773.
Brass, G.W.: 1980, 'Stability of Brines on Mars', Icarus 42, 20-28.
Brearley, A.J.: 2000, 'Hydrous Phases in ALH84001:Further Evidence for Preterrestrial Alteration and a Shock-induced Thermal Overprint', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1203 (CD-ROM).
Bridges, J.C., and Grady, M.M.: 1999, 'A Halite-siderite-anhydrite-chlorapatite Assemblage in Nakhla:Mineralogical Evidence for Evaporites on Mars', Met. Planet. Sci. 34, 407-416.
Bridges, J.C., and Grady, M.M.: 2000, 'Evaporite Mineral Assemblages in the Nakhlite (Martian) Meteorites', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 176, 267-279.
Carr, M.H.: 1996, 'Water on Mars', Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 229 pp.
Carr, R.H., Grady, M.M., Wright, I.P., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1985, 'Martian Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide and Weathering-products in SNC Meteorites', Nature 314, 248-250.
Catling, D.C.: 1999, 'A Chemical Model for Evaporites on Early Mars: Possible Sedimentary Tracers of the Early Climate and Implications for Exploration', J. Geophys. Res. 104,16,453-16,469.
Chatzitheodoridis, E., and Turner, G.: 1990, 'Secondary Minerals in the Nakhla Meteorite' Meteoritics 25, 354 (abstract).
Christensen, P.R., and Moore, H.J.: 1992, 'The Martian Surface Layer', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 686-729.
Christensen, P.R., et al.: 1998, 'Results from the Mars Global Surveyor Thermal Emission Spectrometer', Science 279, 1692-1698.
Clayton, R.N., and Mayeda, T.K.: 1988, 'Isotopic Composition of Carbonate in EETA 79001 and its Relation to Parent Body Volatiles', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 925-927.
Dong, H., Hall, C.M., Halliday, A.N., and Peacor, D.R.: 1997, 'Laser 40Ar-39Ar Dating of Microgram-size Illite Samples and Implications for Thin Section Dating', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 3803-3808.
Douglas, C., Wright, I.P., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1994, 'A Search for Further Concentrations of Organic Materials in EETA79001', Proc. 25 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 339 (abstract).
Drever, J.I.: 1997, 'The Geochemistry of Natural Waters', Prentice-Hall, London. 436 pp.
Eiler, J.M., Valley, J.W., Graham, C.M., and Fournelle, J.: 1998, 'Geochemistry of Carbonates and Glass in ALH84001', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, A4 (abstract).
Farquhar, J., and Thiemens, M.H.: 2000, 'Oxygen Cycle of the Martian Atmosphere-regolith System: Δ 17O of Secondary Phases in Nakhla and Lafayette', J. Geophys. Res. 105,11,991-11,997.
Farquhar, J., Thiemens, M.H., and Jackson, T.: 1998, 'Atmosphere-surface Interactions on Mars: Δ 17O Measurements of Carbonate from ALH84001', Science 275, 1580-1582.
Farquhar, J., Savarino, J., Jackson, T.I., and Thiemens, M.H.: 2000, 'Evidence of Atmospheric Sulphur in the Martian Regolith from Sulphur Isotopes in Meteorites.', Nature 404, 50-52.
Floran, R.J., Prinz, M., Hlava, P.F., Keil, K., Nehru, C.E., and Hinthorne, J.R.: 1978, 'The Chassigny Meteorite:a Cumulate Dunite with Hydrous Amphibole-bearing Melt Inclusions', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 42, 1213-1230.
Forget, F., and Pierrehumbert, R.T.: 1997, 'Warming Early Mars with Carbon Dioxide Clouds that Scatter Infrared Radiation', Science 278, 1273.
Forsythe, R.D., and Zimbelman, J.R.: 1995, 'A Case for Ancient Evaporite Basins on Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 100, 5553-5563.
Forsythe, R.D., and Blackwelder, C.R.: 1998, 'Closed Drainage Crater Basins of the Martian Highlands: Constraints on the Early Martian Hydrologic Cycle', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 31, 421-31, 431.
Franchi, I.A., Wright, I.P., Sexton, A.S., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1999, 'The Oxygen-isotopic Composition of Earth and Mars', Met. Planet. Sci. 34, 657-661.
Friedman, Lentz, R.C., Taylor, G.J., and Treiman, A.H.: 1999, 'Formation of a Martian Pyroxenite: A Comparative Study of the Nakhlite Meteorites and Theo's Flow', Met. Planet. Sci. 34, 919-932.
Garrels, R.M.: 1967, 'Genesis of Some Ground Waters from Igneous Rocks', in P.H. Abelson (ed.), Researches in Geochemistry Vol. 2, John Wiley, New York, pp. 405-420.
Golden, D.C., Ming, W., Schwandt, C.S., Morris, R.V., Yang, S.V., and Lofgren, G.E.: 2000, 'An Experimental Study on Kinetically-driven Precipitation of Calcium-magnesium-iron Carbonates from Solution: Implications for the Low-temperature Formation of Carbonates in Martian Meteorite Allan Hills 84001.' Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 457-465.
Gooding, J.L.: 1978, 'Chemical Weathering on Mars: Thermodynamic Stabilities of Primary Minerals and Their Alteration Products from Mafic Igneous Rocks', Icarus 33, 483-513.
Gooding, J.L., and Muenow, D.W.: 1986, 'Martian Volatiles in Shergottite EETA79001: New Evidence from Oxidised Sulfur and Sulfur-rich Alumino-silicates', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1049-1059.
Gooding, J.L., Wentworth, S.J. and Zolensky, M.E.: 1988, 'Calcium Carbonate and Sulfate of Possible Extraterrestrial Origin in the EETA79001 Meteorite', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 909-916.
Gooding, J.L, Wentworth, S.J., and Zolensky, M.E.: 1991, 'Aqueous Alteration of the Nakhla Meteorite', Meteoritics 26, 135-143.
Grady, M.M., Wright, I.P., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1995, 'A Search for Nitrates in Martian Meteorites', J. Geophys. Res. 100, 5449-5455.
Grady, M.M., Wright, I.P., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1997, 'A Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Study of Zagami', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 9165-9173.
Greenwood, J.P., Riciputi, L.R., and McSween, H.Y.: 1997, 'Sulfide Isotopic Compositions in Shergottites and ALH84001, and Possible Implications for Life on Mars', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 4449-4453.
Greenwood, J.P., Riciputi, L.R., McSween, H.Y., and Taylor, L.A.: 2000, 'Modified Sulfur Isotopic Compositions of Sulfides in the Nakhlites and Chassigny', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 1121-1131.
Gulick, V.C.: 1998, 'Magmatic Intrusions and a Hydrothermal Origin for Fluvial Valleys on Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 19, 365-19, 388.
Haberle, R.M., McKay, C.P., Schaeffer, J., Joshi, M., Cabrol, N.A. and Grin, E.A.: 2000, 'Meteorological Control on the Formation of Martian Paleolakes', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1509 (CD-ROM).
Hartmann, W.K.: 2001, 'Martian Seeps and Their Relation to Youthful Geothermal Activity', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Harvey, R.P., and McSween, H.Y., Jr.: 1996, 'A Possible High-temperature Origin for the Carbonates in the Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Nature 382, 49-51.
Head et al.: 2001, 'Geological Processes and Evolution', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Herut, B., Starinsky, A., Katz, A., and Bein, A.: 1990, 'The Role of Seawater Freezing in the Formation of Subsurface Brines', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 54, 13-21.
Holland, H.D.: 1978, 'The Chemistry of the Atmosphere and Oceans', John Wiley, New York, pp. 190-200.
Holland, G., Lyon, I.C., Saxton, J.M., and Turner, G.: 2000, 'Very Low Oxygen-isotopic Ratios in Allan Hills 84001 Carbonates: A Possible Meteoric Component?', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, A76-77 (abstract).
Ilg, S., Jessberger, E.K., and El Goresy, A.: 1997, '40Ar/39Ar Laser Extraction Dating of Individual Maskelynites in SNC Pyroxenite Allan Hills 84001', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, A65 (abstract).
Jakosky, B.M.: 1993, 'Mars Volatile Evolution: Implications of the Recent Measurement of 17O in Water from SNC Meteorites', Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1591-1594.
Jull, A.J.T., Eastoe, C.J., Xue, S., and Herzog, G.F.: 1995, 'Isotopic Composition of Carbonates in the SNC Meteorites ALH84001 and Nakhla', Meteoritics 30, 311-318.
Jull, A.J.T., Eastoe, C.J., and Cloudt, S.: 1997, 'Isotopic Composition of Carbonates in the SNC Meteorites, Allan Hills 84001 and Zagami', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 1663-1669.
Karlsson, H.R., Clayton, R.N., Gibson, E.K., Jr., and Mayeda, T.K.: 1992, 'Water in SNC Meteorites: Evidence for a Martian Hydrosphere', Science 255, 1409-1411.
Kathie, L., Thomas-Keptra, D.A., Bazylinski, D.A., Kirschvink, J.L., Clemett, S.J., McKay, D.S., Wentworth, S.J., Hojatollah, V., Gibson, E.K., Jr., and Romanek, C.S.: 2000, 'Elongated Prismatic Magnetite Crystals in ALH84001 Carbonate Globules:P otential Martian Magnetofossils', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 3933-4096.
Knott, S.F., Ash, R.D., and Turner, G.: 1997, 40Ar-39Ar Dating of ALH84001: Evidence for the Early Bombardment of Mars', Proc. 27 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 765-766 (abstract).
Kring, D.A., Swindle, T.D., Gleason, J.D., and Grier, J.A.: 1998, 'Formation and Relative Ages of Maskelynite and Carbonate in ALH84001', Geochim Cosmochim. Acta 62, 2155-2166.
Leshin, L.A., Epstein, S., and Stolper, E.M.: 1996, 'Hydrogen Isotope Geochemistry of SNC Meteorites', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 2635-2650.
Leshin, L.A., McKeegan, K.D., Carpenter, P.K. and Harvey, R.P.: 1998, 'Oxygen Isotope Constraints on the Genesis of Carbonates from Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62,3-13.
Lloyd, R.M.: 1966, 'Oxygen Isotope Enrichment of Seawater by Evaporation', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 30, 801-814.
Malin, M.C., and Edgett, K.S.:2000a, 'Evidence for Recent Groundwater Seepage and Surface Runoff on Mars', Science 288, 2330-2335.
Malin, M.C., and Edgett, K.S.:2000b, 'Sedimentary Rocks of Early Mars', Science 290, 1927-1937.
McKay, D.S., Gibson, E.K., Jr., Thomas-Keptra, K.L., Vali, H., Romanek, C.S., Clemett, S.J., Chiller, X.D.F., Maechling, C.R., and Zare, R.N.: 1996, 'Search for Past Life on Mars: Possible Biogenic Activity in Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Science 273, 924-930.
McSween, H.Y., and Harvey, R.P.: 1998, 'An Evaporation Model for the Formation of Carbonates in the ALH84001 Martian Meteorite', Intern. Geol. Rev. 40, 774-783.
Melosh, H.J., and Vickery, A.M.: 1989, 'Impact Erosion of the Primordial Atmosphere of Mars', Nature 338, 487-489.
Mittlefehldt, D.W.: 1994, 'ALH84001, a Cumulate Orthopyroxenite Member of the Martian Meteorite Clan', Meteoritics 29, 214-221.
Moersch, J.E., Farmer, J., and Hook, S.J.: 2000, 'Detectability of Martian Evaporites Terrestrial Analog Studies with MASTER Data', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #2054 (CDROM).
Moore, H.J., Bickler, D.B., Crisp, J.A., Eisen, H.J., Gensler, A., Haldemann, A.F.C., Matijevic, J.R., Reid, L.K. and Pavlics, F.: 1999, 'Soil-like Deposits Observed by Sojourner, and Pathfinder Rover', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 8729-8746.
Morris, R.V., et al.: 2000, 'Mineralogy, Composition, and Alteration of Mars Pathfinder Rocks and Soils:E vidence from Multispectral, Elemental, and Magnetic Data on Terrestrial Analogue, SNC Meteorite, and Pathfinder Samples', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 1757-1817.
Newsom, H.E., Hagerty, J.J., and Goff, F.: 1999, 'Mixed Hydrothermal Fluids and the Origin of the Martian Soil', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 8717-8728.
Nyquist, L.E., Bogard, D.D., Shih, C.Y., Greshake, A., Stöffler, D., and Eugster, O.: 2001, 'Ages and Geologic Histories of Martian Meteorites', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Owen, T.: 1992, The Composition and Early History of the Atmosphere of Mars, in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 818-834.
Reid, A.M., and Bunch, T.E.: 1975, The Nakhlites, Part II.Where,When and How?', Meteoritics 10, 317-324.
Romanek, C.S., Grady, M.M., Wright, I.P., Mittlefehldt, D.W., Socki, R.A., Pillinger, C.T., and Gibson, E.K., Jr.: 1994, 'Record of Fluid-rock Interactions on Mars from the Meteorite ALH84001', Nature 372, 655-657.
Romanek, C.S., Perry, E.C., Treiman, A.H., Sockim, R.A., Jones, J.H., and Gibson, E.K.: 1998, 'Oxygen Isotopic Record of Silicate Alteration in the Shergotty-Nakhla-Chassigny Meteorite Lafayette', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, 775-784.
Ruff, S.W., et al.: 2000, 'Mars “White Rock” Feature Lacks Evidence of an Aqueous Origin', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1945 (CD-ROM).
Russell, M.J., Ingham, J.K., Zadef, V., Maktav, D., Sunar, F., Hall, A.J., and Fallick, A.E.: 1999, 'Search for Signs of Ancient Life on Mars: Expectations from Hydromagnesite Microbialites, Salda Lake, Turkey', J. Geol. Soc. 156, 869-888.
Rye, R., Kuo, P.H., and Holland, H.D.: 1995, 'Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentration Before 2.2 billion Years Ago', Nature 378, 603-605.
Sawyer, D.J., McGehee, M.D., Canepa, J., and Moore, C.B.: 2000, 'Water Soluble Ions in the Nakhla Martian Meteorite', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 743-747.
Saxton, J.M., Lyon, I.C., and Turner, G.: 1998, 'Correlated Chemical and Isotopic Zoning in Carbonates in the Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 160, 811-822.
Saxton, J.M., Lyon, I.C., and Turner, G.:2000a, 'Ion Probe Studies of Deuterium/hydrogen in the Nakhlite Meteorites', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, A142-A143.
Saxton, J.M., Lyon, I.C., Chatzitheodoridis, E., and Turner, G.:2000b, 'Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Carbonate in the Nakhla Meteorite: Implications for the Hydrosphere and Atmosphere of Mars', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 1299-1309.
Scott, E.R.D.: 1999, 'Origin of Carbonate-magnetite-sulfide Assemblages in Martian Meteorite ALH84001', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 3803-3813.
Scott, E.R.D., Yamaguchi, A., and Krot, A.N.: 1997, 'Petrological Evidence for Shock Melting of Carbonates in the Martian Meteorite ALH84001', Nature 387, 377-379.
Shih, C.-Y., Nyquist, L.E., Reese, Y., and Wiesmann, H.: 1998, 'The Chronology of the Nakhlite, Lafayette: Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd Isotopic Ages', Proc. 29th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1145 (CD-ROM).
Steele, A., Goddard, D.T., Stapleton, D., Toporski, J.K.W., Peters, V., Bassinger, V., Sharples, G., Wynn-Williams, D.D., and McKay, D.S.: 2000, 'Investigations Into an Unknown Organism on the Martian Meteorite Allan Hills 84001', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 237-242.
Stöffler, D., Ostertag, R., Jammes, C., Pfannschmidt, G., Sen Gupta, P.R., Simon, S.B., Papike, J.J., and Beauchamp, R.H.: 1986, 'Shock Metamorphism and Petrography of the Shergotty Achondrite', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 889-903.
Sugiura, N., and Hoshino, H.: 2000, 'Hydrogen Isotopic Composition of Allan Hills 84001 and the Evolution of the Martian Atmosphere', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 373-380.
Swindle, T.D., Treiman, A.H., Lindstrom, D.J., Burkland, M.K., Cohen, B.A., Grier, J.A., Li, B., and Olson, E.K.: 2000, 'Noble Gases in Iddingsite from the Lafayette Meteorite: Evidence for Liquid Water on Mars in the Last Few Hundred Million Years', Met. Planet. Sci. 35, 107-115.
Treiman, A.H.: 1985, 'Amphibole and Hercynite Spinel in Shergotty and Zagami: Magmatic Water, Depth of Crystallization, and Metasomatism', Meteoritics 20, 229-243.
Treiman, A.H.: 1995, 'A Petrographic History of Martian Meteorite ALH84001: Two Shocks and an Ancient Age', Meteoritics 30, 294-302.
Treiman, A.H.:1998a, 'The History of Allan Hills 84001 Revised: Multiple shock events', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, 753-764.
Treiman, A.H.:1998b, 'Amphiboles in More Martian Meteorites: Elephant Moraine 79001B, Elephant Moraine 79001X, and Lewis Cliff 88516', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, A156 (abstract).
Treiman, A.H., Barrett, R.A., and Gooding, J.L.: 1993, 'Preterrestrial Alteration of the Lafayette (SNC) Meteorite', Meteoritics 28, 86-97.
Turner, G., Knott, S.F., Ash, R.D., and Gilmour, J.D.: 1997, 'Ar-Ar Chronology of the Martian Meteorite ALH84001:Evidence for the Timing of the Early Bombardment of Mars', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 3835-3850.
Valley, J.W., Eiler, J.M., Graham, C.M., Gibson, E.K., Romanek, C.S., and Stolper, E.M.: 1997, 'Low-temperature Carbonate Concretions in the Martian Meteorite ALH84001:Evidence from Stable Isotopes and Mineralogy', Science 275, 1633-1637.
Vicenzi, E.P., and Eiler, J.: 1998, 'Oxygen-isotopic Composition and High Resolution Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Martian Carbonate in Lafayette Meteorite', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, A159-A160 (abstract).
Wadhwa, M., and Crozaz, G.: 1995, 'Constraints on the Rare Earth Element Characteristics of Metasomatizing Fluids in the Martian Meteorite ALH84001' Proc. 26 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 1451-1452 (abstract).
Wadhwa, M., and Lugmair, G.W.: 1996, 'The Formation Age of Carbonates in ALH84001', Met. Planet. Sci. vn 31, A145 (abstract).
Wadhwa, M., Lentz, R.C.F., McSween, H.Y., and Crozaz, G.: 2000, 'Dar al Gani 476 and Dar al Gani 489, Twin Shergottites from Mars', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1413 (CD-ROM).
Wänke, H., Brückner, J., Dreibus, G., Rieder, R., and Ryabchikov, I.: 2001, 'Chemical Composition of Rocks and Soils at the Pathfinder Site', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Warren, P.H.: 1998, 'Petrologic Evidence for Low-temperature, Possibly Flood Evaporitic Origin of Carbonates in the ALH84001 Meteorite', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 16, 759-16, 773.
Watson, L.L., Hutcheon, I.D., Epstein, S. and Stolper, E.M.: 1994, 'Water on Mars:Clues from D/H and Water Contents of Hydrous Phases in SNC Meteorites', Science 265, 85-90.
Wentworth, S.J., and Gooding, J.L.: 1994, 'Carbonates and Sulfates in the Chassigny Meteorite: Further Evidence for Aqueous Chemistry on the SNC Parent Planet', Meteoritics 29, 861-863.
Wentworth, S.J., and Gooding, J.L.: 2000, 'Weathering and Secondary Minerals in the Martian Meteorite Shergotty', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., abstract #1888 (CD-ROM).
Woods, T.L., and Garrels, R.M.: 1992, 'Calculated Aqueous Solution Solid-solution Relations in the Low Temperature System CaO-MgO-FeO-CO2-H2O', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 3031-3043.
Wright, I.P., Grady, M.M., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1988, 'Carbon, Oxygen and Nitrogen Isotopic Compositions of Possible Martian Weathering Products in EETA79001' Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 917-924.
Wright, I.P., Grady, M.M., and Pillinger, C.T.: 1992, 'Chassigny and the Nakhlites:Carbon Bearing Components and Their Relationship to Martian Environmental Conditions', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 817-826.
Zahnle, K., Kasting, J.F., and Pollack, J.B.: 1990, 'Mass Fraction of Noble Gases in Diffusion-limited Hydrodynamic Escape', Icarus 84, 502-527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bridges, J., Catling, D., Saxton, J. et al. Alteration Assemblages in Martian Meteorites: Implications for Near-Surface Processes. Space Science Reviews 96, 365–392 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011965826553
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011965826553