Abstract
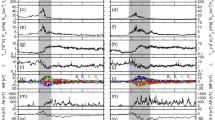
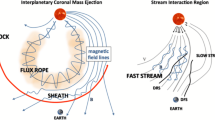
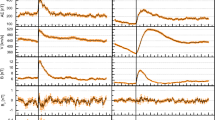
Corotating interaction regions are a consequence of spatial variability in the coronal expansion and solar rotation, which cause solar wind flows of different speeds to become radially aligned. Compressive interaction regions are produced where high-speed wind runs into slower plasma ahead. When the flow pattern emanating from the Sun is roughly time-stationary these compression regions form spirals in the solar equatorial plane that corotate with the Sun, hence the name corotating interaction regions, or CIRs. The leading edge of a CIR is a forward pressure wave that propagates into the slower plasma ahead, while the trailing edge is a reverse pressure wave that propagates back into the trailing high-speed flow. At large heliocentric distances the pressure waves bounding a CIR commonly steepen into forward and reverse shocks. Spatial variation in the solar wind outflow from the Sun is a consequence of the solar magnetic field, which modulates the coronal expansion. Because the magnetic equator of the Sun is commonly both warped and tilted with respect to the heliographic equator, CIRs commonly have substantial north-south tilts that are opposed in the northern and southern hemispheres. Thus, with increasing heliocentric distance the forward waves in both hemispheres propagate toward and eventually across the solar equatorial plane, while the reverse shocks propagate poleward to higher latitudes. This paper provides an overview of observations and numerical models that describe the physical origin and radial evolution of these complex three-dimensional (3-D) heliospheric structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bame, S. J., Goldstein, B. E., Gosling, J. T., Harvey, J.W., McComas, D. J., Neugebauer, M., and Phillips, J. L.: 1993, ‘Ulysses Observations of a Recurrent High Speed Stream and the Heliomagnetic Streamer Belt’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 2323–2326.
Belcher, J.W., and Davis, L.:1971, ‘Large-Amplitude Alfvén Waves in the Interplanetary Medium-II.’, J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3,534–3,563.
Borrini, G., Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., Feldman,W.C., and Wilcox, J. M.: 1981, ‘SolarWind Helium and Hydrogen Structure near the Heliospheric Current Sheet-A Signal of Coronal Streamers at 1AU’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4,565–4,573.
Bruno, R., Villante, U., Bavassano, B., Schwenn, R., and Mariani F.: 1986, ‘In-situ Observations of the Latitudinal Gradients of the Solar Wind Parameters during 1976 and 1977’, Sol. Phys. 104, 431–445.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1974, ‘Interplanetary Stream Interfaces’, J. Geophys. Res. 79, 3,717–3,725.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1983, ‘Corotating Pressure Waves without Fast Streams in the Solar Wind’, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 6,085–6,094.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1984, ‘MHD Processes in the Outer Heliosphere’, Space Sci. Rev. 39, 255–316.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1994, ‘Shocks in the Outer Heliosphere: Voyager 2 Observations from 18.9AU to 30.2 AU (1986–1989)’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 4,161–4,171.
Burlaga, L. F., Ness, N. F., Belcher, J.W., and Whang, Y. C.: 1996, ‘Pickup Protons and Pressure-Balanced Structures from 39 to 43 AU: Voyager 2 Observations during 1993 and 1994’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 15,523–15,532.
Burlaga, L. F., Ness, N. F., and Belcher, J.W.: 1997, ‘Radial Evolution of Corotating Merged Interaction Regions and Flows between _14AU and _43AU’, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 4,661–4,671.
Burton, M. E., Smith, E. J., Balogh, A., Forsyth, R. J., Bame, S. J., Phillips, J. L., and Goldstein, B. E.: 1996, ‘Ulysses out-of-Ecliptic Observations of Interplanetary Shocks’, Astron. Astrophys. 316, 313–322.
Carovillano, R. L., and Siscoe, G. L.: 1969, ‘Corotating Structure in the Solar Wind’, Sol. Phys. 8, 401–414.
Coles, W. A.: 1995, ‘Interplanetary Scintillation Observations of the High-Latitude Solar Wind’, Space Sci. Rev. 72, 211–222.
Dryer, M., Smith, Z.K., Smith, E. J., Mihalov, J. D., Wolfe, J.H., Steinolfson, R. S., and Wu, S.T.: 1978, ‘MHD Modeling of Solar Wind Corotating Stream Interaction Regions Observed by Pioneer 10 and 11’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 4,347–4,352.
Feldman, W.C., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S. J., Fenimore, E. E., and Gosling, J. T.: 1981, ‘The Solar Origin of Solar Wind Interstream Flows: Near Equatorial Coronal Streamers’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5,408–5,416.
Fisk, L.A.: 1996, ‘Motion of the Footpoints of Heliospheric Magnetic Field Lines at the Sun: Implications for Recurrent Energetic Particle Events at High Heliographic Latitudes’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 15,547-15,553.
Gazis, P. R., Mihalov, J.D., Barnes, A., Lazarus, A. J., and Smith, E. J.: 1989, ‘Pioneer and Voyager Observations of the Solar Wind at Large Heliocentric Distances and Latitudes’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 16, 223–226.
Gloeckler, G., Geiss, J., Roelof, E. C., Fisk, L. A., Ipavich, F.M., Ogilvie, K.W., Lanzerotti, L. J., von Steiger, R., and Wilken, B.: 1994, ‘Acceleration of Interstellar Pickup Ions in the Disturbed Solar Wind Observed on Ulysses’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 17,637–17,643.
Gosling, J. T.: 1986, ‘Global Aspects of Stream Evolution in the Solar Wind’, in R. I. Epstein and W. C. Feldman(eds.), Magnetospheric Phenomena in Astrophysics, AIP Conf. Proceed.144, New York, pp. 124–144.
Gosling, J. T.: 1996, ‘Corotating and Transient Solar Wind Flows in Three Dimensions’, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 34, 35–73.
Gosling, J. T., Hundhausen, A. J., Pizzo, V., and Asbridge, J.R.: 1972, ‘Compressions and Rarefactions in the Solar Wind: Vela 3’, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 5,442–5,454.
Gosling, J. T., Hundhausen, A. J., and Bame, S. J.: 1976, ‘Solar wind Stream Evolution at Large Heliocentric Distances: Experimental Demonstration and Test of a Model’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 2,111–2,122.
Gosling, J. T., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., and Feldman,W.C.: 1978, ‘SolarWind Stream Interfaces’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1,401–1,412.
Gosling, J. T., Borrini, G., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., Feldman, W.C., and Hansen, R. F.: 1981, ‘Coronal Streamers in the Solar Wind at 1AU’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5,438–5,448.
Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., McComas, D. J., Phillips, J. L., Pizzo, V. J., Goldstein, B. E., and Neugebauer, M.: 1993, ‘Latitudinal Variation of Solar Wind Corotating Stream Interaction Regions: Ulysses’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 2789–2792.
Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., McComas, D. J., Phillips, J. L., Pizzo, V. J., Goldstein, B. E., and Neugebauer, M.: 1995a, ‘SolarWind Corotating Interaction Regions out of the Ecliptic Plane: Ulysses’, Space Sci. Rev. 72, 99–104.
Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., Feldman, W.C., McComas, D. J., Phillips, J. L., Goldstein, B. E., Neugebauer, M., Burkepile, J., Hundhausen, A. J., and Acton, L.: 1995b, ‘The Band of Solar Wind Variability at Low Heliographic Latitudes near Solar Activity Minimum: Plasma Results from the Ulysses Rapid Latitude Scan’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 3329–3332.
Gosling, J. T., Feldman, W.C., McComas, D. J., Phillips, J. L., Pizzo, V. J., and Forsyth, R. J.: 1995c, ‘Ulysses Observations of Opposed Tilts of Solar Wind Corotating Interaction Regions in the Northern and Southern Solar Hemispheres’, J. Geophys. Res. 22, 3,333–3,336.
Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., Feldman, W.C., McComas, D. J., Riley, P., Goldstein, B. E., and Neugebauer, M.: 1997, ‘The Northern Edge of the Band of SolarWind Variability, Ulysses at_4.5AU’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 309–312.
Hoeksema, J. T.: 1995, ‘The Large-Scale Structure of the Heliospheric Current Sheet during the Ulysses Epoch’, Space Sci. Rev. 72, 137–148.
Hundhausen, A. J.: 1972, Coronal Expansion and Solar Wind, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Hundhausen, A. J.: 1973, ‘Nonlinear Model of High-Speed Solar Wind Streams’, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 1,528–1,542.
Hundhausen, A. J.: 1977, ‘An Interplanetary View of Coronal Holes’, in J. B. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams, Colorado Assoc. Univ. Press., Boulder, pp. 225–329.
Hundhausen, A. J., and Gosling, J. T.: 1976, ‘Solar Wind Structure at Large Heliocentric Distances: An Interpretation of Pioneer 10 Observations’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 1,436–1,440.
Jokipii, J.R., and Davis, L. Jr.: 1969, ‘Long-Wavelength Turbulence and the Heating of the Solar Wind’, Astrophys. J. 156, 1101–1106.
Jokipii, R. J., and Thomas, B.: 1981, ‘Effects of Drift on the Transport of Cosmic-Rays-IV. Modulation by a Wavy Current Sheet’, Astrophys. J. 243, 1115–1122.
Kóta, J.: 1992, ‘A Numerical Model of the Large-Scale Solar Wind in the Outer Heliosphere’, in E. Marsch and R. Schwenn(eds.), Solar Wind Seven, Pergamon, New York, pp. 205–208.
Krieger, A. S., Timothy, A. F., and Roelof, E.C.: 1973, ‘A Coronal Hole and its Identification as the Source of a High Velocity Solar Wind Stream’, Sol. Phys. 29, 505–525.
Lallement, R., Bertaux, J. L., and Kurt, V.G.: 1985, ‘Solar Wind Decrease at High Heliocentric Latitudes Detected from Prognoz Interplanetary Lyman-??Mapping’, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 1,413–1,423.
McNutt, R. L., Jr.: 1988, ‘Possible Explanations of North-South Plasma Flow in the Outer Heliosphere and Meridional Transport of Magnetic Flux’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 15, 1523–1526.
Ogilvie, K.W.: 1972, ‘Corotating Shock Structures’, in P. J. Coleman, C. P. Sonett, and J.M. Wilcox (eds.), Solar Wind, NASA SP 308, Washington DC, pp. 430–434.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, John Wiley, New York.
Phillips, J. L., Balogh, A., Bame, S. J., Goldstein, B. E., Gosling, J. T., Hoeksema, J. T., McComas, D. J., Neugebauer, M., Sheeley, N.R., and Wang, Y.-M.: 1994, ‘Ulysses at 50_ South: Constant Immersion in the High-Speed Solar Wind’, J. Geophys. Res. 21, 1,105–1,108.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1978, ‘A Three-Dimensional Model of Corotating Streams in the Solar Wind-I. Theoretical Foundations’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 5,563–5,572.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1980, ‘A Three-Dimensional Model of Corotating Streams in the Solar Wind-II. Hydrodynamic Streams’, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 727–743.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1982, ‘A Three-Dimensional Model of Corotating Streams in the Solar Wind-III. Magnetohydrodynamic Streams’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 4,374–4,394.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1991, ‘The Evolution of Corotating Stream Fronts near the Ecliptic Plane in the Inner Solar System-II. Three-Dimensional Tilted-Dipole Fronts’, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 5,405–5,420.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1994a, ‘Global, Quasi-Steady Dynamics of the Distant Solar Wind-I. Origins of North-South Flows in the Outer Heliosphere’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 4,173–4,183.
Pizzo, V. J.: 1994b, ‘Global, Quasi-Steady Dynamics of the Distant Solar Wind-II. Deformation of the Heliospheric Current Sheet’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 4,185–4,191.
Pizzo, V. J., and Gosling, J. T.: 1994, ‘Three-dimensional Simulation of High-Latitude Interaction Regions: Comparison with Ulysses Results’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 2063–2066.
Pizzo, V. J., Intriligator, D. S., and Siscoe, G. L.: 1995, ‘Two-dimensional Radial-Alignment Simulation of Solar Wind Streams Observed by Pioneer 10 and 11 in 1974’, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 12,251–12,260.
Pneuman, G.W., and Kopp, R. A.: 1971, ‘Gas-Magnetic Field Interactions in the Solar Corona’, Sol. Phys. 18, 258–270.
Richter, A. K., and Luttrell, A. H.: 1986, ‘Superposed Epoch Analysis of Corotating Interaction Regions at 0.3 and 1.0AU: A Comparative Study’, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 5,873–5,878.
Riley, P., Gosling, J. T., Weiss, L. A., and Pizzo, V. J.: 1996, ‘The Tilts of Corotating Interaction Regions at Mid-Heliograhic Latitudes’, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 24,349-24,357.
Sarabhai, V.: 1963, ‘Some Consequences of Nonuniformity of Solar-Wind Velocity’, J. Geophys. Res. 68, 1,555–1,557.
Schwenn, R.: 1990, ‘Large-Scale Structure of the Interplanetary Medium’, in R. Schwenn and E. Marsch(eds.), Physics of the Inner Heliosphere, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 99–181.
Sime, D.G.: 1983, ‘Interplanetary Scintillation Observations of the Solar Wind Close to the Sun and out of the Ecliptic’, in M. Neugebauer (ed.), Solar Wind Five, NASA CP 2280, pp. 453–467.
Siscoe, G. L.: 1972, ‘Structure and Orientation of Solar Wind Interaction Fronts: Pioneer 6’, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 27–34.
Siscoe, G. L.: 1976, ‘Three-Dimensional Aspects of Interplanetary Shock Waves’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 6,235–6,241.
Siscoe, G. L., Goldstein, B., and Lazarus, A. J.: 1969, ‘An East-West Asymmetry in the Solar-Wind Velocity’, J. Geophys. Res. 74, 1,759–1,762.
Smith, E. J., and Wolfe, J.H.: 1976, ‘Observations of Interaction Regions and Corotating Shocks between One and Five AU: Pioneers 10 and 11’, J. Geophys. Res. 3, 137-140.
Suess, S. T., Hundhausen, A. J., and Pizzo, V.: 1975, ‘Latitude-Dependent Nonlinear High-Speed Solar Wind Streams’, J. Geophys. Res. 80, 2,023–2,029.
Whang, Y.C., and Burlaga, L. F.: 1988, ‘Evolution of Recurrent Solar Wind Structures between 14 AU and the Termination Shock’, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 5,446–5,460.
Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. F., von Steiger, R., and Paerli, R.: 1997, ‘SolarWind Stream Interfaces in Corotating Interaction Regions: SWICS/Ulysses Results’, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 17,404-17,417.
Zhao, X. P., and Hundhausen, A. J.: 1981, ‘Organization of SolarWind Plasma Properties in a Tilted, Heliomagnetic Coordinate System’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5,423–5,430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gosling, J., Pizzo, V. Formation and Evolution of Corotating Interaction Regions and their Three Dimensional Structure. Space Science Reviews 89, 21–52 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005291711900
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005291711900