Abstract
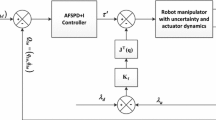
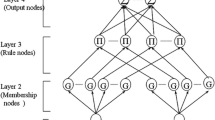
The key feature of this paper is the application of a robotic control concept – Active Force Control (AFC). In this type of control, the unknown friction effect of the robotic arm may be compensated by the AFC method. AFC involves the direct measurement of the acceleration and force quantities and therefore, the process of estimating the system ‘disturbance’ due to friction becomes instantaneous and purely algebraic. However, the AFC strategy is very practical provided a good estimation of the inertia matrix of articulated robot arm is acquired. A dynamic structure neural network – Growing Multi-experts Network (GMN) is developed to estimate the robot inertia matrix. The growing and pruning mechanism of GMN ensures the optimum size of the network that results in an excellent generalization capability of the network. Active Force Control (AFC) in conjunction with GMN successfully reduces the velocity and position tracking errors in spite of robot joint friction. The embedded GMN is capable of coupling the inertia matrix estimation on-line that clearly enhances the performance of AFC controller. The robustness and effectiveness of the new hybrid neural network-based AFC scheme are demonstrated clearly with regard to two link articulated robot and a simulated two-degree of freedom Puma 560 robot.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loo, C.K., Mandava, R. & Rao, M.V.C. A Hybrid Intelligent Active Force Controller for Articulated Robot Arms Using Dynamic Structure Neural Network. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems 40, 113–145 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JINT.0000039014.41797.dc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JINT.0000039014.41797.dc