Abstract
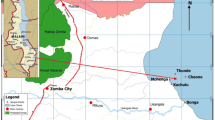
The concentrations of trace elements in water, sediment and fish samples from Tuskegee Lake located in Southeastern United States were investigated in this study. The Lake is utilized both as a source for municipal drinking water, and for recreational fishing. The water quality characteristics over two sampling periods, the speciation of metals in the Lake sediments, the risk to water column contamination and levels of heavy metals in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) samples from the Lake were evaluated. The Lake water quality characteristics were mostly below the recommended drinking water standards by the United StatesEnvironmental Protection Agency (US EPA) and the European Union (EU) except for aluminum, iron, manganese and thallium. In addition, the average values of Cr, As, Mn, Zn and Cl- in the water samples analyzed were higher than the respective reference values for fresh water. To study the speciation of metals in the Lake sediments, ten elements (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn) in four grain sizes (< 710 μm – 250 μm, < 250 μm – 75 μm, < 75 μm – 53μm, and < 53 μm) were subjected to sequential extractions. Irrespective of grain size, the elements analyzed were distributed in both the non-residual and residual phases except Ni that was found only in the residual fraction. The potential risk to Lake water contamination was highest downstream (Sites 1 and 2) based on the calculated global contamination factors. From the calculated individual contamination factors, Mn and Pb followed by Zn, Cu, Cr, Co and V posed the highest risk to water contamination. Based on this study, the human health risks for heavy metals in fish caught from Tuskegee Lake are low for now, and irrespective of the source of fish, concentrations of metals in muscle tissues were all below the recommended Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) maximum limits for Pb (0.5 mg Kg-1), Cd (0.5 mg Kg-1), Cu (30 mg Kg-1), and Zn (30 mg Kg-1) in fish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen-Gil, S. M. and Martynov, V. G.: 1995, ‘Heavy metal burdens in nine species of freshwater and anadromous fish from the Pechora River, northern Russia’, Sci. Total Environ. 160/161, 653-659.
Al-Yousuf, M. H., El-Shahawi, M. S. and Al-Ghais, S. M.: 2000, ‘Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex’, Sci. Total Environ. 256, 87-94.
APHA (American Public Health Association): 1998, Standard Methods for the Examination of Waters and Wastewaters, 20th ed. Washington, DC, pp. 1-1-10-161.
Aucoin, J., Blanchard, R., Billiot, C., Partridge, C., Schultz, D., Mandhare, K, Beck, M. J. and Beck, J. N.: 1999, ‘Trace metals in Fish and Sediments from Lake Boeuf, Southeastern Louisiana’, Microchemical Journal 62, 299-307.
Baruah, N. K, Kotoky, P., Bhattacharyya, K. G. and Borah, G. C.: 1996, ‘Metal speciation in Jhanji river sediments’, Sci. Total Environ. 193, 1-12.
Berk, J. N., Ramelow, G. J., Thompson, R. S., Mueller, C. S., Webre, C. L., Young, J. C. and Langley, M. P.: 1990, ‘Heavy metal content of sediments in the Calcasieu river/Lake complex, Louisiana. Hydrobiologia 192, 149-165.
Bortoli, A., Dell’Andrea, E., Gerotto, M., Marchiori, M., Palonta, M. and Troncon, A.: 1998, ‘Soluble and particulate metals in the Adige River’, Microchemical Journal 59, 19-31.
Byrne, C. J. and DeLeon, I. R.: 1986, ‘Trace metal residues in biota and sediments from Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 37, 151-158.
Chance, G. W. and Harmsen, E.: 1998, ‘Children are different: environmental contaminants and children’s health’, Can. J. Public Health 89, S10-S15.
CCFAC (Codex Committee on Food Additives and Contaminants): 2001, Comments Submitted on Draft Maximum Levels for Lead and Cadmium, Agenda 16c/16d, Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Thirty-third Session, The Hague, The Netherlands, 12-16 March 2001.
Dougherty, C. P., Henricks Holtz, S., Reinert, J. C., Panyacosit, L., Axelrad, D. A. and Woodruff, T. J.: 2000, ‘Dietary exposures to food contaminants across the United States’, Environmental Research 84, 170-185.
Elbaz-Poulichet, F., Garnier, J. M., Guan, D. M., Martin, J. M. and Thomas, A. J.: 1996, ‘The conservative behaviour of trace metals (Cd, Cu, Ni and Pb) and As in the surface plume of stratified estuaries: Example of the Rhone river (France)’, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 42, 289-310.
Evans, D. W., Doo, D. K. and Hanson, P.: 1993, ‘Trace element concentration in fish livers: implications of variations with fish size in pollution monitoring’, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 26, 329-334.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization): 1983, Compilation of Legal Limits for Hazardous Substances in Fish and Fishery Products, FAO Fishery Circular No. 464, pp. 5-100.
Federal Standards: 1989, Nature Protection Soils Classification of Chemical Species for Detection of Pollution, Federal Standards 174102-83. Moscow (in Russian).
Gauthreaux, K., Noble, C. O., Falgoust, T., Beck, M. J, Sneddon, J. and Beck, J. N.: 1998, ‘Reliability and Reproducibility of a Sequential Extraction Procedure for Trace Metal Determination in Marsh Sediments in Southwest Louisiana’, Microchem. J. 60, 175-183.
Gladyshev, M. I., Gribovskaya, I. V., Moskvicheva, A. V., Muchkina, E. Y., Chuprov, S. M. and Ivanova, E. A.: 2001, ‘Content of metals in compartments of ecosystem of a Siberian pond’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 157-162.
Govil, P. K, Reddy, G. L. N. and Gnaneswara Rao, T.: 1999, ‘Environmental Pollution in India: heavy metals and radiogenic elements in Nacharam Lake’, J. Environ. Health 61, 23-28.
Gray, J. E., Theodorakos, P. M., Elizabeth, A., Bailey, E. A. and Turner, R. R.: 2000, ‘Distribution, speciation, and transport of mercury in stream-sediment, stream-water, and fish collected near abandoned mercury mines in southwestern Alaska, U.S.A.’, Sci. Total Environ. 260, 21-33.
Grosheva, E. I., Voronskaya, G. N. and Pastukhove, M. V.: 2000, ‘Trace element bioavailability in Lake Baikal’, Aquat. Ecosys. Health Manage. 3, 229-234.
Hach.: 1998, DR/2010 Spectrophotometer: Procedures Manual, Hach Inc., Colorado, U.S.A., pp. 447-514.
Jenne, E. A.: 1968, ‘Trace inorganics in water’, Adv. Chem. Ser. 73, 337-387.
Johansson, K., Andersson, A. and Andersson, T.: 1995, ‘Regional accumulation of heavy metals in Lake sediments and forest soils in Sweden’, Sci. Total Environ. 160/161, 373-380.
Johnson, B. L, Hicks, H. E. and De Rosa, C. T.: 1999, ‘Key environmental human health issues in the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River basins’, Environ. Res. 80, S2-S12.
Khan, A. T., Forester, D. M. and Mielke, H. W.: 1995, ‘Heavy metal concentrations in two populations of crayfish’, Veterin. Human Toxicol. 37, 426-428.
Kirby, J., Maher, W. and Krikowa, F.: 2001, ‘Selenium, cadmium, and zinc concentrations in sediments and mullet (Mugil cephalus) from the Southern basin of LakeMacquarie, NSW,Australia’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 40, 246-256.
K¸lavi¸nš, M., Briede, A., Rodinov, V., Kokorite, I., Parele, E. and K¸lavi¸na, I.: 2000, ‘Heavy metals in rivers of Latvia’, Sci. Total Environ. 262, 175-184.
K¸lavi¸nš, M., Rodinov, V. and Vereskuns, G.: 1998, ‘Metals and organochlorine compounds in fish from Latvian Lakes’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 60, 538-545.
La Vecchia, C., Chatenoud, L., Altieri, A. and Tavani, A.: 2001, ‘Nutrition and health: epidemiology of diet, cancer and cardiovascular disease in Italy’, Nutr. Metabol. Cardiov. Dis. 11, 10-15.
Lewis, M. A., Scott, G. I., Bearden, D. W., Quarles, R. L, Moore, J., Strozier, E. D., Sivertsen, S. K., Dias, A. R. and Sanders, M.: 2002, ‘Fish tissue quality in near-coastal areas of the Gulf of Mexico receiving point source discharges’, Sci. Total Environ. 284, 249-261.
Lytle, T. F. and Lytle, J. S.: 1980, Pollution Impact in Mississippi Coastal Waters, Mississippi Alabama Sea Grant Consortium. MASGP-80-020, pp. 1-25.
MAFF: 1995, Monitoring and Surveillance of Non-Radioactive Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment and Activities Regulating the Disposal of Wastes at Sea, 1993, Aquatic Environment Monitoring Report No. 44. Directorate of Fisheries Research, Lowestoft; 1995.
Mannio, J., Järvinen, O., Tuominen, R. and Verta, M.: 1995, ‘Survey of trace elements in Lake waters of Finnish Lapland using the ICP-MS technique’, Sci. Tot. Environ. 160, 433-439.
Markert, B.: 1994, ‘Inorganic chemical fingerprinting of the environment; reference freshwater, a useful tool for comparison and harmonization of analytical data in freshwater chemistry’, Fresenius Z Anal. Chem. 349, 697-702.
McLean, E. O.: 1982, ‘Soil pH and Lime Requirement’, in A. L. Page et al. (eds), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Agronomy 9. Am. Soc. Agronomy, Inc., Madison, Wis., pp. 199-224.
Morgan, J. J. and Stumm, W.: 1991, ‘Chemical Processes in the Environment, Relevance of Chemical Speciation’, in E. Merien (ed.), Metals and Their Compounds in the Environment. Germany: VCH Publishers, pp. 67-103.
Northwest Florida Water Management District.: 1992, A Literature Based Review of the Physical Sedimentary and Water Quality Aspects of the Pensacola Bay System, Water Resources Special Report 92-5, Havana, FL.
Ontario Ministry of Environment: 1993, Guidelines for the Protection and Management of Aquatic Sediment Quality in Ontario, Ontario Ministry of Environment, Toronto, 32 pp.
Paul, T., Alicja, W., Harri, V. and Elisabete, W.: 2002, ‘Fatty fish consumption lowers the risk of endometrial cancer: a nationwide case-control study in Sweden’, Cancer Epidemiol. Biom. Prevent. 11, 143-145.
Rashed, M. N.: 2001, ‘Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser Lake’, Environ. Internat. 27, 27-33.
Rognerud, S. and Fjeld, E.: 2001, ‘Trace element contamination of Norwegian Lake sediments’, Ambio 30, 11-19.
Roméo, M., Siau, Y., Sidoumou, Z. and Gnassia-Barelli, M.: 1999, ‘Heavy metal distribution in different fish species from the Mauritania coast’, Sci. Total Environ. 232, 169-175.
Salomons, M.: 1980, ‘Biochemical processes affecting metal concentrations in Lake sediments (Ijsselmeer, The Netherlands)’, Sci. Total Environ. 16, 217-229.
Sager, M.: 1992, ‘Chemical Speciation and Environmental Mobility of Heavy Metals in Sediments and Soils’, in M. Stoeppler (ed.), Hazardous Metals in the Environment, Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., pp. 133-175.
Schoer, J.: 1985, ‘Iron-oxo-hydroxides and their significance to the behavior of heavy metals in estuaries, Environ. Technol. Lett. 6, 189.
Schleusner, C. J. and Maughan, O. E.: 1999, ‘Mobility of largemouth bass in a desert Lake in Arizona’, Fish. Res. 44, 175-178.
Sprenger, M., McIntosh, A. and Lewis, T.: 1987, ‘Variability in concentrations of selected trace elements in water and sediment of six acidic Lakes’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 383- 390.
Storelli, M. M. and Marcotrigiano, G. O.: 2001, ‘Heavy metal monitoring in fish, bivalve mollusks, water, and sediments from Varano Lagoon, Italy’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 66, 365-370.
Terry, P., Lichtenstein, P., Feychting, M., Ahlbom, A., and Wolk, A.: 2001, ‘Fatty fish consumption and risk of prostate cancer’, Lancet 357, 1764-1766.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C. and Bisson, M.: 1979, ‘Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals’, Anal. Chem. 51, 843-845.
Tuskegee News: 1947, Referendum Called on Proposed Municipal Lake, Tuskegee, AL, U.S.A. The Tuskegee News 83, No. 34: pp. 1
Tuskegee News: 1948, Construction Started on Municipal Lake Project, Tuskegee News Paper, Tuskegee, AL, U.S.A. The Tuskegee News 83, No. 34: 1.
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency): 2002, Source water, Office of water, Washington, D.C. 20460. Internet address: http://www.epa.gov/safewater/protect.html
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency): 2001, Fact sheet. Update: National Listing of Fish and Wildlife Advisories, EPA-823-F-010. Office of water, Cincinnati, Ohio. Internet address: http://www.epa.gov/ost/fish/advisories/factsheet.pdf
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency).: 1983, Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Waste, EPA Report 600/4-79-020, Office of water, Cincinnati, Ohio.
Von Gunten, H. R., Sturm, M. and Moser, R. N.: 1997, ‘200 year record of metals in Lake sediments and natural background concentrations’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2193-2197.
Yang, H, Rose, N. L. and Battarbee, R. W.: 2002, ‘Distribution of some trace metals in Lochnagar, a Scottish mountain Lake ecosystem and its catchment’, Sci. Total Environ. 285, 197-208.
Zhou, H. Y, Cheung, R. Y. H., Chan, K. M. and Wong, M. H.: 1998, ‘Metal concentrations in sediments and Tilapia collected from inland waters of Hong Kong’, Wat. Res. 32, 3331-3340.
Zoumis, T., Schmidt, A., Grigorova, L. and Calmano, W.: 2001, ‘Contaminants in sediments: remobilization and demobilisation’, Sci. Total Environ. 266, 195-202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikem, A., Egiebor, N.O. & Nyavor, K. Trace Elements In Water, Fish and Sediment from Tuskegee Lake, Southeastern Usa. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 149, 51–75 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025694315763
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025694315763