Abstract
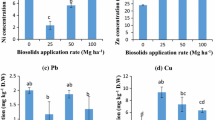
Generally, the potential for biosolids (digested or composted)to contribute heavy metals to the soil-plant system has beencompared with commercial fertilizers and other organic wastesbut not with biosolids-ash. An column study was conducted in agreenhouse to determine the availability, extractability andleachability of metals in a degraded, non-calcareous soilamended with different biosolids (200 Mg ha-1). Thebiosolids investigated were dewatered, anaerobically digestedbiosolids, composted biosolids and biosolids-ash. The columns(26 cm) were planted with wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cvMexa). The addition of digested biosolids decreased the drymatter yield of wheat. Treatments including organic biosolidsincreased Cu and Zn concentrations in wheat roots, straw andgrain, whereas the addition of biosolids-ash did not affect theconcentrations of these metals in wheat. Concentrations of Ni,Co, Pb, Cr and Cd in wheat were below reliable detection limits(0.06, 0.05, 0.1, 0.06 and 0.02 mg kg-1, respectively).After harvesting, total and AB-DTPA extractable Cu, Zn and Pbincreased in the upper layer of the soil amended with thedifferent biosolids studied, whereas levels of AB-DTPAextractable Ni and Co were affected only when the soil wasamended with digested or composted biosolids. Total chromiumincreased only in treatments including organic biosolids. TheAB-DTPA extractable Cu, Zn and Pb in the lower layer of thesoil in treatments including biosolids evidenced downwardmovement of these metals. However, absence of these metals incolumn leachates indicates that this movement was gradual.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C.: 1986, Trace Elements in the Terrestrial Environment, Springer-Verlag, New York, 533 pp.
Andersson, A.: 1976, Grundförbättring 27, 159.
Andersson, A. and Nilson, K. O.: 1976, Swedish J. Agric. Res. 6, 151.
A.O.A.C.: 1984, Official Methods of Analysis, 14th ed., Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, 1141 pp.
Balogh, H.: 1996, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 91, 249.
Bidwell, A. M. and Dowdy, R. H.: 1987, J. Environ. Qual. 16, 438.
Bierman, P. M. and Rosen, C. J.: 1994a, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 25, 2409.
Bierman, P. M. and Rosen, C. J.: 1994b, J. Environ. Qual. 23, 822.
Bierman, P. M., Rosen, C. J., Bloom, P. R. and Nater, E. A.: 1995, J. Environ. Qual. 24, 279.
C.I.I.: 1969, ‘Métodos de referencia para la determinación de elementos minerales en vegetales. I. N, P, K, Na, Ca y Mg’, Anal. Edaf. Agrobiol. 28, 409–430.
Chaney, R. L., Hundemann, P. T., Palmer, W. T., Small, R. J., White, M. C. and Decker, A. M.: 1978, ‘Plant accumulation of heavy metals and phytotoxicity resulting from utilization of sewage sludge and sludge composts on cropland’, Proceedings of the National Conference of Composting of Municipal Residues and Sludges, Information Transfer, Inc., Rockville, Md, pp. 86–97.
Chang, A. C., Warneke, J. E., Page, A. L. and Lund, L. J.: 1984, J. Environ. Qual. 13, 87.
Chromec, F. W. and Magdoff, F.: 1984, J Environ. Sci. Health A 19, 697.
Davis, R. D. and Beckett, P. H. T.: 1978, ‘Upper critical levels of toxic elements in plants. II. Critical levels of copper in young barley, wheat, rape, lettuce and ryegrass and of nickel and zinc in young barley and ryegrass’ New Phytol. 80, 23–32.
Furr, A. K., Parkinson, T. F., Elfving, D. C., Bache, C. A., Gutenman, W. H., Doss, G. J. and Lisk, D. J.: 1981, J. Agric. Food Chem. 29, 156.
Garcia, C., Hernandez, T., Costa, F. and Ceccanti, C.: 1994, Waste Manag. Res. 12, 457.
Gardiner, D. T., Miller, R.W., Badamchian, B., Azzari, A. S. and Sisson, D. R.: 1995, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 55, 1.
Giordano, P. M. and Mortvedt, J. J.: 1976, J. Environ Qual. 5, 165.
Guisquiani, P. L., Giglioti, G. and Businelli, D.: 1992, J. Environ. Qual. 21, 330.
Gupta, U. C.: 1971, Plant and Soil 34, 249.
Harris-Pierce, R. L., Redente, E. F. and Barbarick, K. A.: 1995, J. Environ. Qual. 24, 112.
Jakobsen, P. and Willett, I. R.: 1986, Fertilizer Res. 9, 187.
Kimber, R.W. L.: 1967, ‘Phytotoxicity from plant residues. I. The influence of rotted wheat straw on seedling growth’, Aust. J. Agric. Res. 18, 361.
Kimber, R. W. L.: 1973, ‘Phytotoxicity from plant residues, II. The effect of time of rotting of straw from some grasses and legumes on the growth of wheat seedlings’, Plant and Soil 38, 347–361.
Kirkham, M. B.: 1981, ‘Elemental composition of twelve plant species grown with irradiated municipal sludge’, Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 144, 205–214.
Kirkham, M. B.: 1983, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 9, 281.
Kubota, J., Welch, R. M. and Van Campen, D. R.: 1992, Environ. Geochem. Health 14, 91.
Leita, L. and De Nobili, M.: 1991, J. Environ. Qual. 20, 73.
Lerch, R. N., Barbarick, K. A., Westfall, D. G., Follet, R. H., McBride, T. M. and Owen, W. F.: 1990, ‘Sustainable rates of sewage sludge for dryland winter wheat production I. Soil nitrogen and heavy metals’, J. Prod. Agric. 3, 60–65.
Lester, J. N., Sterritt, R. M. and Kirk, P.W.W.: 1983, ‘Significance and behaviour of heavy metals in waste water treatment processes II. Sludge treatment and disposal’, Sci. Total Environ. 30, 45–83.
Lynch, J. M.: 1985, ‘Origin, Nature and Biological Activity of Aliphatic Substances and Growth Hormones Found in Soil’, in D. Vaughan and R. E. Malcolm (eds.), Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity, Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 151–174.
M.A.P.A.: 1986, Métodos oficiales de análisis. Tomo III. Plantas, productos orgánicos fertilizantes, suelos, agua, productos fitosanitarios y fertilizantes inorgánicos, Publicaciones del Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación, Madrid, 532 pp.
McBride, M. B.: 1995, J. Environ. Qual. 24, 5–18.
McGrath, S. P. and Cunliffe, C. H.: 1985, J. Sci. Food Agric. 36, 794.
Narwal, R. P., Singh, B. R. and Panhwar, A. R.: 1983, ‘Plant availability of heavy metals in a sludgetreated soil: I. Effect of sewage sludge and soil pH on the yield and chemical composition of rape’, J. Environ. Qual. 12, 358–365.
Nogales, R., Gallardo-Lara, F., Benítez, E., Soto, J., Hervas, D. and Polo, A.: 1997, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 94, 33.
Rappaport, B. D., Martens, D. C., Reneau Jr., R. B. and Simpson, T. W.: 1987, J. Environ. Qual. 16, 29.
Reddy, M. R., Lameck, D. and Rezania, M. E.: 1989, ‘Uptake and distribution of copper and zinc by soybean and corn from soil treated with sewage sludge’, Plant and Soil 113, 271–274.
Richards, B. K., Peverly, J. H., Steenhuis, T. S. and Liebowitz, B. N.: 1997 J. Environ. Qual. 26, 782–788.
Sheaffer, C. C., Decker, A. M., Chaney, R. L. and Douglass, L. W.: 1979, J. Environ. Qual. 8, 455.
Soil Survey Staff: 1983, Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, USDA Forest Service Staff, John Wiley & Sons Inc., 768 pp.
Soltanpour, P. N. and Schwab, A. P.: 1977, Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 8, 195.
Sposito, G., Lund, L. J. and Chang, A. C.: 1982, ‘Trace metal chemistry in arid-zone field soils amended with sewage sludge: I. Fractionation of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in solid phases’, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 260–264.
Takkar, P. N and Mann, M. S.: 1978, ‘Toxic levels of soil and plant zinc for maize and wheat’, Plant and Soil 49, 667–669.
Unger, M. and Fuller, W. H.: 1985, ‘Optimum utilization of sewage sludge of low and high metal content for grain production on arid lands’, Plant and Soil 88, 321–332.
Welch, J. E. and Lund, L. J.: 1987, J. Environ. Qual. 16, 403.
Wild, R. S. and Jones, K. C.: 1994, ‘The significance of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons applied to agricultural soils in sewage sludges in the U.K.’, Waste Manage. and Res. 12, 49–59.
Wilkins, E. S. and Wilkins, M. G.: 1983, ‘Review of pyrolysis and combustion products of municipal and industrial wastes’, J. Environ. Sci. Health, A 18, 747–772.
Wong, M. H.: 1985, ‘Heavy metal contamination of soils and crops from auto traffic, sewage sludge, pig manure and chemical fertilizer’, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 13, 139–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benítez, E., Romero, E., Gómez, M. et al. Biosolids and Biosolids-ash as Sources of Heavy Metals in a Plant-Soil System. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 132, 75–87 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012012924151
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012012924151