Abstract
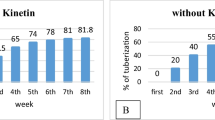
The effect of indole-3-acetic acid or kinetin on the weight and numberof microtubers formed was studied on single node cuttings of sevendifferent potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars as well astransgenic lines harbouring rolB or rolC genes undercontrol of the patatin class I (B33) promoter. Plants were cultivatedin vitro in the dark on solidified MS medium containing 1 to8% sucrose with or without phytohormones. Most of thenontransformed potato cultivars and transgenic lines responded tohormone application by an increase in tuber yield. Auxin and cytokininacted differently: IAA increased predominantly the tuber size whilekinetin increased the number of tubers. RolC transformantsdisplayed an altered response to sucrose and especially to auxin. Thedegree of phytohormone effect on tuberisation parameters depended onsucrose content of the medium and potato genotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chailakhyan MKh (1984) Photoperiodic and Hormonal Regulation of Tuber Formation in Plants (in Russian). Moscow: Nauka
Ewing EE (1995) The role of hormones in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tuberization. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant Hormones, Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 698-724
Harmey MA, Crowley MC and Clinch PEM (1966) The effect of growth regulators on tuberization of cultured stem pieces of Solanum tuberosum. Eur Potato J 9: 146-151
Palmer CE and Smith OE (1970) Effect of kinetin on tuber formation on isolated stolons of Solanum tuberosum L. cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Physiol 11: 303-311
McGrady JJ, Struik PC and Ewing EE (1986) Effects of exogenous applications of cytokinin on the development of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cuttings. Potato Res 29: 191-205
Xin X, van Lammeren AM, Vermer E and Vreugdenhil D (1998) The role of gibberellin, abscisic acid, and sucrose in the regulation of potato tuber formation in vitro. Plant Physiol 117: 575-584
Koda Y and Okazawa Y. (1983) Influences of environment, hormonal and nutritional factors on potato tuberization in vitro. Jap J Crop Sci 52: 582-591
Schmülling T, Schell J and Spena A (1988) Single genes from Agrobacterium rhizogenes influence plant development. EMBO J 7: 2621-2629
Gaudin V, Vrain T and Jouanin L (1994) Bacterial genes modifying hormonal balances in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 32: 11-29
Estruch JJ, Chriqui D, Grossmann K, Shell J and Spena A (1991) The plant oncogene rolC is responsible for the release of cytokinins from glucoside conjugates. EMBO J 10: 2889-2895
Estruch JJ, Shell J and Spena A (1991) The protein encoded by the rolB plant oncogene hydrolyzes indole glucosides. EMBO J 10: 3125-3128
Nilsson O, Crozier A, Schmülling T, Sandberg G and Olsson O (1993) Indole-3-acetic acid homeostasis in transgenic tobacco plants expressing the Agrobacterium rhizogenes rolB gene. Plant J 3: 681-689
Faiss M, Strnad M, Reding P, Dolezal K, Hanus J, van Onckelen H and Schmülling T (1996) Chemically induced expression of the rolC encoded β-glucosidase in transgenic tobacco plants and analysis of cytokinin metabolism: rolC does not hydrolyze endogenous cytokinin glucosides in planta. Plant J 10: 33-46
Maurel C, Barbier-Brygoo H, Spena A, Tempe J and Guern J (1991) Single rol genes from the Agrobacterium rhizogenes alter some of the cellular response to auxin in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Physiol 97: 212-216
Klee HJ and Lanahan MB (1995) Transgenic plants in hormone biology. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant Hormones, Physiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 340-353
Romanov GA, Konstantinova TN, Sergeeva LI, Golyanovskaya SA, Kossmann J, Willmitzer L, Schmülling T and Aksenova NP (1998) Morphology and tuber formation of in vitro-grown potato plants harboring the yeast invertase gene and/or the rolC gene. Plant Cell Rep 18: 318-324
Aksenova NP, Konstantinova TN, Golyanovskaya SA, Schmülling T, Kossmann J, Willmitzer L and Romanov GA (1999) In vitro growth and tuber formation by transgenic potato plants harboring rolC or rolB genes under control of the patatin promoter. Russian J Plant Physiol (Engl. version) 46: 513-519
Liu XL, Prat S, Willmitzer L and Frommer WB (1990) Cis regulatory elements directing tuber-specific and sucrose-inducible expression of a chimeric class I patatin promoter/GUS gene fusion. Mol Gen Genet 223: 401-406
Fladung M, Ballvora A and Schmülling T (1993) Constitutive or light regulated expression of the rolC gene in transgenic potato plants alters yield attributes and tuber carbohydrate composition. Plant Mol Biol 23: 749-757
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanov;, G., Aksenova, N., Konstantinova, T. et al. Effect of indole-3-acetic acid and kinetin on tuberisation parameters of different cultivars and transgenic lines of potato in vitro. Plant Growth Regulation 32, 245–251 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010771510526
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010771510526