Abstract
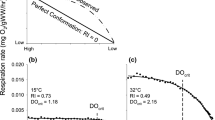
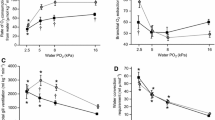
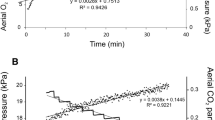
This study quantified the air-breathing frequency (ABf in breaths h−1) and gill ventilation frequency (Vf in ventilations min−1) of tarpon Megalops atlanticusas a function of PO2, temperature, pH, and sulphide concentration. Ten tarpon held at normoxia at 22–33°C without access to atmospheric oxygen survived for eight days, and seven survived for 14 days (at which point the experiment was terminated) suggesting that the species is a facultative, rather than an obligate, air breather. At temperatures of 29°C and below ABf was highest and Vf was lowest at low oxygen partial pressures. Tarpon appear to switch from aquatic respiration to air breathing at PO2levels of roughly 40 torr. The gills were the primary organ for oxygen uptake in normoxia, and the air-breathing organ the primary mechanism for oxygen uptake in hypoxia. At 33°C, both ABf and Vf were elevated but highly variable, regardless of PO2. There were no mortalities in tarpon exposed to total H2S concentrations of 0–232 µM (0–150.9 µM H2S); however, high sulfide concentrations resulted in very high ABf and Vf near zero. Vf was reduced when pH was acidic. We conclude that air breathing provides an effective means of coping with the environmental conditions that characterize the eutrophic ponds and sloughs that juvenile tarpon typically inhabit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Abel, D.C., C.C. Koenig & W.P. Davis. 1987. Emersion in the mangrove forest fish Rivulus marmoratus: a unique response to hydrogen sulfide. Env. Biol. Fish. 18: 67-72.
Babcock, L.L. 1936. The tarpon: a description of the fish together with some hints on its capture, 4th edition. Babcock, Buffalo. 175 pp.
Bagarinao, T. & R.D. Vetter. 1989. Sulfide tolerance and detoxification in shallow-water marine fishes. Mar. Biol. 103: 291-302.
Bicudo, J.E.P.W. & K. Johansen. 1979. Respiratory gas exchange in the airbreathing fish, Synbranchus marmoratus. Env. Biol. Fish. 4: 55-64.
Bone, Q., N.B. Marshall & J.H.S. Blaxter. 1995. Biology of fishes, 2nd ed. Chapman and Hall, London. 332 pp.
Chacón-Chaverri, D. & W.O. McLarney. 1992. Desarrollo temprano del sábalo, Megalops atlanticus(Pisces: Megalopidae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 40: 171-177.
Clark, L.C., R. Wolf, D. Granger & A. Taylor. 1956. Continuous recording of blood oxygen tensions by polarography. J. Appl. Physiol. 6: 189-193.
Cline, J.D. 1969. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 4: 454-458.
Crabtree, R.E. 1995. Relationship between lunar phase and spawning activity of tarpon, Megalops atlanticus, with notes on the distribution of larvae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 56: 895-899.
Crabtree, R.E., E.C. Cyr, R.E. Bishop, L.M. Faulkenstein & J.M. Dean. 1992. Age and growth of tarpon, Megalops atlanticus, larvae in the Gulf of Mexico, with notes on relative abundance and probable spawning areas. Env. Biol. Fish. 35: 361-370.
Durako, M.J., J.A. Browder, W.L. Kruczynski, C.B. Subrahmanyan & R.E. Turner. 1983. Salt marsh habitat and fishery resources of Florida. pp. 189-280. In: W. Seaman, Jr. (ed.) Florida Aquatic Habitat and Fishery Resources, Florida Chapter of the American Fisheries Society, Eustis.
Gee, J.H. & J.B. Graham. 1976. Respiratory and hydrostatic functions of the intestine of the catfishes Hoplosternum thoracatumand Brochis splendens. J. Exp. Biol. 74: 1-16.
Geiger, S.P. 1993. Respiratory physiology of juvenile tarpon, Megalops atlanticus. M.S. Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa. 96 pp.
Gibson, R.N. 1969. The biology and behavior of littoral fish. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 7: 367-410.
Graham, J.B. 1994. An evolutionary perspective for bimodal respiration: a biological synthesis of fish air breathing. Amer. Zool. 34: 229-237.
Graham, J.B. 1997. Air-breathing fishes-evolution, diversity and adaptation. Academic Press, San Diego. 299 pp.
Graham, J.B., D.L. Kramer & E. Pineda. 1977. Respiration of the air breathing fish Piabucina festae. J. Comp. Physiol. 122: 295-310.
Graham, J.B., D.L. Kramer & E. Pineda. 1978. Comparative respiration of an air-breathing and a non-air-breathing characoid fish and the evolution of aerial respiration in characins. Physiol. Zool. 51: 279-288.
Harrington, R.W., Jr. 1958. Morphometry and ecology of small tarpon, Megalops atlanticaValienciennes, from transitional stage through onset of scale formation. Copeia 1958: 1-10.
Hochachka, P.W. & G.N. Somero. 1984. Biochemical adaptation. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 538 pp.
Horn, M.H. & C.D. Riggs. 1973. Effects of temperature and light on the rate of air breathing of the bowfin, Amia calva. Copeia 1973: 653-657.
Johansen, K. 1966. Air-breathing fishes. Sci. Amer. 219: 102-111.
Johansen, K., D. Hanson & C. Lenfant. 1970. Respiration in a primitive air breather, Amia calva. Resp. Physiol. 9: 162-174.
Jordan, J. 1976. The influence of body weight on gas exchange in the air-breathing fish, Clarias batrachus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 53A: 305-310.
Kinkead, R. & S.F. Perry. 1990. An investigation of the role of circulating catecholamines in the control of ventilation during acute moderate hypoxia in rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss). J. Comp. Physiol. B 160: 441-448.
Kramer, D.L. 1983. Aquatic surface respiration in the fishes of Panama: distribution in relation to risk of hypoxia. Env. Biol. Fish. 8: 49-54.
Kramer, D.L. & M. McClure. 1980. Aerial respiration in the catfish Corydoras aenus(Callichthyidae). Can. J. Zool. 58: 1984-1991.
Lewis, R.R., III, R.G. Gilmore, Jr., D.W. Crewz & W.E. Odum. 1983. Mangrove habitat and fishery resources in Florida. pp. 281-336. In: W. Seaman, Jr. (ed.) Florida Aquatic Habitat and Fishery Resources, Florida Chapter of the American Fisheries Society, Eustis.
Liem, K.L. 1989. Respiratory gas bladders in teleosts: functional conservation and morphological diversity. Amer. Zool. 29: 333-352.
Liem, K.F., B. Eclancher & W.L. Fink. 1984. Aerial respiration in the banded knife fish Gymnotus carapo(Teleostei: Gymnotoidei). Physiol. Zool. 57: 185-195.
Luther, G.W. III, T.M. Church, J.R. Scudlark & M. Cosman. 1986. Inorganic and organic sulfur cycling in salt-marsh pore waters. Science 232: 746-749.
Magid, A.M.A. 1966. Breathing and function of the spiracles in Polypterus senegalus. Anim. Behav. 14: 530-533.
Martin, K.L.M. 1993. Aerial release of CO2and respiratory exchange ratio in intertidal fishes out of water. Env. Biol. Fish. 37: 189-196.
McKenzie, D., J.S. Aota & D.J. Randall. 1991. Ventilatory and cardiovascular responses to blood pH, plasma CO2, blood O2content, and catecholamines in an air-breathing fish, the bowfin (Amia calva). Physiol. Zool. 64: 432-450.
Millero, F.J. 1986. The thermodynamics and kinetics of the hydrogen sulfide system in natural waters. Mar. Chem. 18: 121-147.
Rickards, W.L. 1968. Ecology and growth of juvenile tarpon in a Georgia salt marsh. Bull. Mar. Sci. 18: 220-239.
Schlaifer, A. 1941. Additional social and physiological aspects of respiratory behavior of small tarpon. Zoologica 26: 55-60.
Schlaifer, A. & C.M. Breder. 1940. Social and respiratory behavior of small tarpon. Zoologica 25: 493-512.
Smatresk, N.J. 1986. Ventilatory and cardiac reflex responses and NaCN in Lepisosteus osseus, an air-breathing fish. Physiol. Zool. 59: 385-397.
Smith, D.G. 1980. Early larvae of the tarpon, Megalops atlanticaValenciennes (Pisces: Elopidae), with notes on spawning in the Gulf of Mexico and the Yucatan Channel. Bull. Mar. Sci. 30: 136-141.
Spjotvoll, E. & M.R. Stoline. 1973. An extension of the T-method of multiple comparison to include the cases with unequal sample sizes. J. Amer. Stat. Assoc. 68: 976-978.
Stevens, E.D. & G.F. Holeton. 1978. The partitioning of oxygen uptake from air and water by the large obligate air-breathing teleost pirarucu (Arapaima gigas). Can. J. Zool. 56: 974-976.
Todd, E.S. & A.W. Ebeling. 1966. Aerial respiration in the longjaw mudsucker Gillichthys mirabilis(Teleostei: Gobiidae). Biol. Bull. 130: 265-288.
Torres, J.J. & G.N. Somero. 1988. Metabolism, enzymic activities and cold adaptation in Antarctic mesopelagic fishes. Mar. Biol. 98: 169-180.
Tucker, J.W. & R.G. Hodson. 1976. Early and mid-metamorphic larvae of the tarpon Megalops atlanticus, from the Cape Fear River estuary, North Carolina, 1973-1974. Chesapeake Sci. 17: 123-125.
Wade, R.D. 1962. The biology of the tarpon, Megalops atlanticus, and the ox-eye, Megalops cyprinoides, with emphasis on larval development. Bull. Mar. Sci. Gulf Caribb. 12: 545-622.
Withers, P.C. 1992. Comparative animal physiology. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Publishers, Forth Worth. 1056 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geiger, S.P., Torres, J.J. & Crabtree, R.E. Air Breathing and Gill Ventilation Frequencies in Juvenile Tarpon, Megalops atlanticus: Responses to Changes in Dissolved Oxygen, Temperature, Hydrogen Sulfide, and PH. Environmental Biology of Fishes 59, 181–190 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007640132059
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007640132059