Abstract
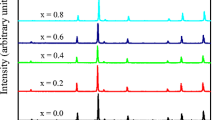
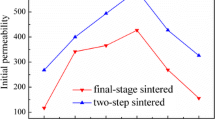
Ni–Zn ferrites were prepared in air by using the conventional ceramic powder methodology. The compositions analysed belong to the type NixZn1−xFe2O4 ferrites, with x ranging from 0.3–0.4. Copper wire was coiled round the specimens, previously pressed to a toroidal shape, to characterize their magnetic properties as a function of the frequency of the applied electric field. Powder X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and microanalysis, and the magnetic susceptibility of the ferrites, were studied, indicating that the highest permeability is achieved at the composition x = 0.3, a result which is correlated to the microstructural characterization. The Curie temperature was also determined to range from 60–130 °C, depending on the specific composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Y. Tseng and J. C. Lin, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 8 (1989) 261.
Idem., IEEE Trans. Mag. 25 (1989) 4405.
U. Varshney and R. K. Puri, ibid. 25 (1989) 3109.
U. Varshney, R. K. Puri, K. H. Rao and R. G. Mendiratta, in “Ferrites, Proceedings of ICF-3” (1981) p. 207.
R. K. Puri and U. Varshney, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 44 (1983) 655.
S. Fischer, C. Michalk, W. ToÖpelmann and H. Scheler, Ceram. Int. 18 (1992) 317.
F. G. Stickland, J. Phys. Chem. 67 (1963) 2504.
V. V. Zaporozhets and V. V. Oleynik, Fiz. Metal Metalloved, 61 (1986) 192.
J. Gieraltowski and A. Globus, IEEE Trans. Mag. MAG-13 (1977) 1357.
M. I. Rosales, PhD Progress Report, UNAM, Mexico City (1995).
Y. Yamato and A. Makino, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 133 (1994) 500.
M. I. Rosales, A. M. Plata, M. E. Nicho, A. Brito, M. A. Ponce and V. M. CastaÑo, J. Mater. Sci. 30 (1995) 4446.
A. Makino, Y. Yamato and N. Sakatsume, J. Jpn Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 39 (1992) 129.
S. Komarneni, E. Fregeau, E. Breval and R. Roy, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 71 (1988) C-26.
E. Cedillo, J. Ocampo, V. Rivera and R. Valenzuela, J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 13 (1980) 383.
A. Globus, Proc. J. Phys. Coll. C1-38 (1977).
M. Guyot and V. Cagan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 27 (1982) 202.
V. G. Harris, M. C. Koon, C. M. Williams, Q. Zhang, M. Abe and J. P. Kirkland, IEEE Trans. Mag. 31 (1995) pp. 3473.
E. Schloemann, R. J. Maher and J. A. Weiss, ibid. 31 (1995) 3470.
R. Valenzuela, J. Mater. Sci. 15 (1980) 3173.
G. Aguilar-SahagÚn, P. Quintana, E. Amano, J. T. S. Irvine and R. Valenzuela, J. Appl. Phys. 75 (1994) 7000.
J. T. S. Irvine, A. R. West, E. Amano, A. Huanosta and R. Valenzuela, Sol. State Ionics 40 (1990) 220.
M. I. Rosales, E. Amano, M. P. Cuautle and R. Valenzuela, J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 49 (1997) 221.
C. G. Oliver, IEEE Trans. Mag. (1995) 3982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosales, M.I., Cuautle, M.P. & Castano, V.M. Microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. Journal of Materials Science 33, 3665–3669 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004671732746
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004671732746