Abstract
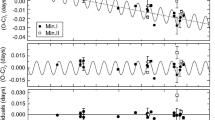
Many available published times of light minima of the late-type binary system ER Vul have been compiled and analyzed using a new method proposed by Kalimeris et al. (1994). It was shown that the orbital period of the system oscillation with a period of about 30.6 years and an amplitude of 3.2×10-6 days while it undergoes a constant period decrease of about dP /P=7.84× 10-8 day / year. The prospective physical mechanisms that could have modulated the orbital period behaviour (periodic or non-periodic), have been studied. We found that a combination of a magnetic activity cycle mechanism and an enhanced stellar wind could explain satisfactorily the period change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrami, A. and Cester, B.: 1963, Publ. Trieste 320, 7.
Al-Naimiy, H.M.: 1978, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 1418.
Applegate, J.H.: 1992, Astrophys. J. 385, 621.
Arévalo, M.J., Lázaro, C. and Fuensalída, J.D.: 1988, Astron. J. 96, 1061.
Barden, S.C.: 1985, Astrophys. J. 295, 162.
Battistini, P., Bonifazi, A. and Guarnieri, A.: 1974, ibid 951.
Fernández-Figueroa, M.J., Montes, D., De Castro, E. and Cornide, M.: 1994, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 90, 433.
Gunn, A.G. and Doyle, J.G.: 1996, Astron. Astrophys. (in press).
Hall, D.S.: 1976, Proc. IAU Coll., No. 29, Budapest, Part 1, p. 287.
Íbanoğlu, C., Akan, M.C. and Evren, S.: 1985, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 2782.
Íbanoğlu, C., Evren, S., et al.: 1993, Astron. Astrophys. 269, 310.
Kalimeris, A., Rovithis-Livaniou, H. and Rovithis, P.: 1994, Astron. Astrophys. 282, 775.
Kalimeris, A., Mitrou, C.K., et al.: 1995, Astron. Astrophys. 293, 371.
Lázaro, C. and Arévalo, M.G.: 1994, in: J.P. Caillault (ed.), Cool Stars, Stellar System, and the Sun, Eighth Cambridge Workshop, ASP Conference Series 64, 435.
Mclean, B.J.: 1982, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 201, 421.
Milano, L., Mancuso, S., et al.: 1986, Astrophys. Space Sci. 124, 83.
Mochnacki, S.W.: 1984, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 55, 551.
Montes, D., Fernández-Figueroa, M.J., Cornide, M. and De Castro, E.: 1996, Astron. Astrophys. 312, 221.
Northcott, R.J. and Bakos, G.A.: 1956, Astron. J. 61, 188.
Northcott, R.J. and Bakos, G.A.: 1967, Astron. J. 72, 89.
Oláh, K., Buddingf, E., Kim, H.-I. and Etzel, P.B.: 1994, Astron. Astrophys. 291, 110.
Pohl, E., Tunca, Z., et al.: 1985, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 2793.
Pohl, E., et al.: 1987, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 3078.
Srivastava, R.K., Padalia, T.D. and Srivastava, J.B.: 1991, Astrophys. Space Sci. 182, 281.
Tout, C.A. and Eggleton, P.P.: 1988, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 231, 823.
Tout, C.A. and Hall, D.S.: 1991, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 253, 9.
Wunder, E., et al.: 1992, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 3760.
Zeinali, F., Edalati, M.T. and Mirtorahi, M.T.: 1995, Inf. Bull. Variable Stars 4190.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shengbang, Q., Qingyao, L. & Yulan, Y. A Period Study of the Rs CVn-Type Binary ER Vulpeculae. Astrophysics and Space Science 257, 1–10 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000448104322
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000448104322