Abstract
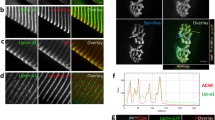
Matrix metalloproteinases are important regulators of extracellular matrix molecules and cell-cell signaling. Antibodies to matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3) recognize molecules at the frog neuromuscular junction, and MMP3 can remove agrin from synaptic basal lamina (VanSaun & Werle, 2000). To gain insight into the possible roles of MMP3 at the neuromuscular junction, detailed observations were made on the structure and function of the neuromuscular junctions in MMP3 null mutant mice. Striking differences were found in the appearance of the postsynaptic apparatus of MMP3 null mutant mice. Endplates had an increased volume of AChR stained regions within the endplate structure, leaving only small regions devoid of AChRs. Individual postsynaptic gutters were wider, containing prominent lines that represent the AChRs concentrated at the tops of the junctional folds. Electron microscopy revealed a dramatic increase in the number and size of the junctional folds, in addition to ectopically located junctional folds. Electrophysiological recordings revealed no change in quantal content or MEPP frequency, but there was an increase in MEPP rise time in a subset of endplates. No differences were observed in the rate or extent of developmental synapse elimination. In vitro cleavage experiments revealed that MMP3 directly cleaves agrin. Increased agrin immunofluorescence was observed at the neuromuscular junctions of MMP3 null mutant mice. These results provide strong evidence that MMP3 is involved in the control of synaptic structure at the neuromuscular junction and they support the hypothesis that MMP3 is involved in the regulation of agrin at the neuromuscular junction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AKAABOUNE, M., HANTAI, D., SMIRNOVA, I., LACHKAR, S., KAPSIMALI, M., VERDIERESAHUQUE, M. & FESTOFF, B. W. (1998) Developmental regulation of the serpin, protease nexin I, localization during activity-dependent polyneuronal synapse elimination in mouse skeletal muscle. Journal of Comparative Neurology 397, 572–579.
ALLAN, J. A., HEMBRY, R. M., ANGAL, S., REYNOLDS, J. J. & MURPHY, G. (1991) Binding of latent and high Mr active forms of stromelysin to collagen is mediated by the C-terminal domain. Journal Cell Science 99, 789–795.
BARBER, A. J. & LIETH, E. (1997) Agrin accumulates in the brain microvascular basal lamina during development of the blood-brain barrier. Developmental Dynamics 208, 62–74.
BURGESS, R. W., NGUYEN, Q. T., SON, Y. J., LICHTMAN, J. W. & SANES, J. R. (1999) Alternatively spliced isoforms of nerve-and muscle-derived agrin: Their roles at the neuromuscular junction. Neuron 23, 33–44.
COHEN, I., RIMER, M., LOMO, T. & MCMAHAN, U. J. (1997) Agrin-induced postsynaptic-like apparatus in skeletal muscle fibers in vivo. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 9, 237–253.
CONNOLD, A. L., EVERS, J. V. & VRBOVA, G. (1986) Effect of low calcium and protease inhibitors on synapse elimination during postnatal development in the rat soleus muscle. Brain Research 393, 99–107.
DECHIARA, T. M., BOWEN, D. C., VALENZUELA, D. M., SIMMONS, M. V., POUEYMIROU, W. T., THOMAS, S., KINETZ, E., COMPTON, D. L., ROJAS, E., PARK, J. S., SMITH, C., DISTEFANO, P. S., GLASS, D. J., BURDEN, S. J. & YANCOPOULOS, G. D. (1996) The receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK is required for neuromuscular junction formation in vivo. Cell 85, 501–512.
DONAHUE, J. E., BERZIN, T. M., RAFII, M. S., GLASS, D. J., YANCOPOULOS, G. D., FALLON, J. R. & STOPA, E. G. (1999) Agrin in Alzheimer's disease: Altered solubility and abnormal distribution within microvasculature and brain parenchyma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96, 6468–6472.
FAHIM, M. A. & ROBBINS, N. (1982) Ultrastructural studies of young and old mouse neuromuscular junctions. Journal of Neurocytology 11, 641–656.
FESTOFF, B. W., HANTAI, D., SORIA, J., THOMAIDIS, A. & SORIA, C. (1986) Plasminogen activator in mammalian skeletal muscle: Characteristics of effect of denervation on urokinase-like and tissue activator. Journal of Cell Biology 103, 1415–1421.
GAUTAM, M., NOAKES, P. G., MOSCOSO, L., RUPP, F., SCHELLER, R. H., MERLIE, J. P. & SANES J. R. (1996) Defective neuromuscular synaptogenesis in agrindeficient mutant mice. Cell 85, 525–535.
GLASS, D. J., BOWEN, D. C., STITT, T. N., RADZIEJEWSKI, C., BRUNO, J., RYAN, T. E., GIES, D. R., SHAH, S., MATTSSON, K., BURDEN, S. J., DISTEFANO, P. S., VALENZUELA, D. M., DECHIARA, T. M. & YANCOPOULOS, G. D. (1996) Agrin acts via a MuSK receptor complex. Cell 85, 513–523.
GODFREY, E. W., DIETZ, M. E., MORSTAD, A. L., WALLSKOG, P. A. & YORDE, D. E. (1988) Acetylcholine receptor-aggregating proteins are associated with the extracellular matrix of many tissues in Torpedo. Journal of Cell Biology 106, 1263–1272.
GOMIS-RUTH, F. X., MASKOS, K., BETZ, M., BERGNER, A., HUBER, R., SUZUKI, K., YOSHIDA, N., NAGASE, H., BREW, K., BOURENKOV, G. P., BARTUNIK, H. & BODE, W. (1997) Mechanism of inhibition of the human matrix metalloproteinase stromelysin-1 by TIMP-1. Nature 389, 77–81.
GROFFEN, A. J., BUSKENS, C. A., VAN KUPPEVELT, T. H., VEERKAMP, J. H., MONNENS, L. A. & VAN DEN HEUVEL, L. P. (1998) Primary structure and high expression of human agrin in basement membranes of adult lung and kidney. European Journal of Biochemistry 254, 123–128. ÑHERRERA, A. A., BANNER, L. R. & NAGAYA, N. (1990) Repeated, in vivo observation of frog neuromuscular junctions: Remodelling involves concurrent growth and retraction. Journal of Neurocytology 19, 85–99.
HUGHES, P. M., WELLS, G. M., PERRY, V. H., BROWN, M. C. & MILLER, K. M. (2002) Comparison of matrix metalloproteinase expression duringWallerian degeneration in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neuroscience 113, 273–287.
KAMMERER, R. A., SCHULTHESS, T., LANDWEHR, R., SCHUMACHER, B., LUSTIG, A., YURCHENCO, P. D., RUEGG, M. A., ENGEL, J. & DENZER, A. J. (1999) Interaction of agrin with laminin requires a coiled-coil conformation of the agrin-binding site within the laminin gamma1 chain. EMBO Journal 18, 6762– 6770.
KHERIF, S., DEHAUPAS, M., LAFUMA, C., FARDEAU, M. & ALAMEDDINE, H. S. (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 in denervated muscle and injured nerve. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology 24, 309–319.
KO, C. P. (1985) Formation of the active zone at developing neuromuscular junctions in larval and adult bullfrogs. Journal of Neurocytology 14, 487–512.
LA FLEUR, M., UNDERWOOD, J. L., RAPPOLEE, D. A. & WERB, Z. (1996) Basement membrane and repair of injury to peripheral nerve: Defining a potential role for macrophages, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1. Journal of Experimental Medicine 184, 2311–2326.
MCMAHAN, U. J. (1990) The agrin hypothesis. Cold Spring Harbour Symp. Quant. Biology 55, 407–418.
MUDGETT, J. S., HUTCHINSON, N. I., CHARTRAIN, N. A., FORSYTH, A. J., MCDONNELL, J., SINGER, I. I., BAYNE, E. K., FLANAGAN, J., KAWKA, D., SHEN, C. F., STEVENS, K., CHEN, H., TRUMBAUER, M. & VISCO, D. M. (1998) Susceptibility of stromelysin 1-deficient mice to collagen-induced arthritis and cartilage destruction. Arthritis and Rheumatism 41, 110–121.
MURPHY, G., WILLENBROCK, F., CRABBE, T., O'SHEA, M., WARD, R., ATKINSON, S., O'CONNELL, J. & DOCHERTY, A. (1994) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 732, 31–41.
NAGASE, H. & BREW, K. (2002) Engineering of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases mutants as potential therapeutics. Arthritis Research 4(Suppl 3), S51–S61.
NAGASE, H. & WOESSNER, J. F. JR. (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 21491–21494.
O'BRIEN, R. A., OSTBERG, A. J. & VRBOVA, G. (1978) Observations on the elimination of polyneuronal innervation in developing mammalian skeletal muscle. Journal of Physiology (London) 282, 571–582.
O'BRIEN, R. A., OSTBERG, A. J. & VRBOVA, G. (1984) Protease inhibitors reduce the loss of nerve terminals induced by activity and calcium in developing rat soleus muscles in vitro. Neuroscience 12, 637–646.
REIST, N. E., WERLE, M. J. & MCMAHAN, U. J. (1992) Agrin released by motor neurons induces the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions. Neuron 8, 865–868.
REYNOLDS, J. J. (1986) Inhibition of production and action of tissue metalloproteinases. Annual Biological Clinic (Paris) 44, 188–194.
RICH, M. & LICHTMAN, J. W. (1989) In vivo visualization of pre-and postsynaptic changes during synapse elimination in reinnervated mouse muscle. Journal of Neuroscience 9, 1781–1805.
RUEGG, M. A., TSIM, K. W., HORTON, S. E., KROGER, S., ESCHER, G., GENSCH, E. M. & MCMAHAN, U. J. (1992) The agrin gene codes for a family of basal lamina proteins that differ in function and distribution. Neuron 8, 691–699.
SHI, Y. & SANG, Q. A. (1998). Stromelysin 1. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes (edited by BARRETT, A. J., RAWLINGS, N. D. & WOESSNER, J. F.) pp. 1172–1178. San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
SLATER, C. R., LYONS, P. R., WALLS, T. J., FAWCETT, P. R. W. & YOUNG, C. (1992) Structure and function of neuromuscular junctions in the vastus lateralis of man. Brain 115, 451–478.
STERNLICHT, M. D. & WERB, Z. (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 17, 463–516.
TURK, B. E., HUANG, L. L., PIRO, E. T. & CANTLEY, L. C. (2001) Determination of protease cleavage site motifs using mixture-based oriented peptide libraries. Nature Biotechnology 19, 661–667.
VANSAUN, M. & WERLE, M. J. (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-3 removes agrin from synaptic basal lamina. Journal of Neurobiology 43, 140–149.
VAN WART, H. E. & BIRKEDAL-HANSEN, H. (1990) The cysteine switch: A principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 87, 5578–5582.
WALLACE, B. G. (1988) Regulation of agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor aggregation by Ca++ and phorbol ester. Journal of Cell Biology 107, 267–278.
WALLACE, B. G. (1989) Agrin-induced specializations contain cytoplasmic, membrane, and extracellular matrixassociated components of the postsynaptic apparatus. Journal of Neuroscience 9, 1294–1302.
WALSH, M. K. & LICHTMAN, J. W. (2003) In vivo timelapse imaging of synaptic takeover associated with naturally occurring synapse elimination. Neuron 37, 67–73.
WERLE, M. J., JONES, M. A. & STANCO, A. M. (1999) Agrin produced by Schwann cells does not induce the aggregation of AChRs at the frog neuromuscular junction. Journal of Neurobiology 40, 45–54.
YANG, J. F., CAO, G., KOIRALA, S., REDDY, L. V. & KO, C. P. (2001) Schwann cells express active agrin and enhance aggregation of acetylcholine receptors on muscle fibers. Journal of Neuroscience 21, 9572– 9584.
ZOUBINE, M. N., MA, J. Y., SMIRNOVA, I. V., CITRON, B. A. & FESTOFF, B. W. (1996) Amolecular mechanism for synapse elimination: Novel inhibition of locally generated thrombin delays synapse loss in neonatal mouse muscle. Developmental Biology 179, 447–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VanSaun, M., Herrera, A.A. & Werle, M.J. Structural alterations at the neuromuscular junctions of matrix metalloproteinase 3 null mutant mice. J Neurocytol 32, 1129–1142 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000021907.68461.9c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEUR.0000021907.68461.9c