Abstract
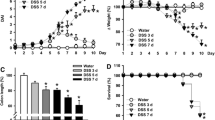
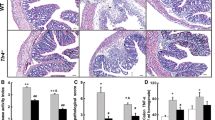
Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in micehas been recognized as a model for human ulcerativecolitis. Using this model, we carried out a study on thepreventive effect of Icatibant, a bradykinin B receptor antagonist previously called HOE 140,on the development of colitis. Subcutaneousadministration of Icatibant (0.3 or 1.5 mg/kg)significantly suppressed shortening of the largeintestine and worsening of the general health. Oraladministration of Icatibant (50 mg/kg) significantlysuppressed shortening of the large intestine, the onsetof diarrhea, and worsening of the general health. Inaddition, the oral treatment significantly inhibited thedevelopment of colitis that was observedhistopathologically. These results indicate a role of BKin the development of dextran sulfate sodiuminducedcolitis in mice, and suggest that BK could be importantin human ulcerative colitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kraft SC, Kirsner JB: Ulcerative colitis. In Immunological Disease. DW Talmage, B Rose, WB Sherman, JH Vaughan (eds). Boston, Little, Brown and Company, 1971, pp 1346-1366
Sharon P, Ligumsky M, Rachmilewitz D, Zor U: Role of prostaglandins in ulcerative colitis. Enhanced production during active disease and inhibition by sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology 75:638-640, 1978
Ligumsky M, Karmeli F, Sharon P, Zor U, Cohen F, Rachmilewitz D: Enhanced thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin production by cultured rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis and its inhibition by steroid and sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology 81:444-449, 1981
Boughton-Smith NK, Hawkey CJ, Whittle BJR: Biosynthesis of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase products from [14C]arachidonic acid by human colonic mucosa. Gut 24:1176-1182, 1983
Bhoola KD, Figueroa CD, Worthy K: Bioregulation of kinins: Kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol Rev 44:1-80, 1992
Gaginella TS, Kachur JF: Kinins as mediators of intestinal secretion. Am J Physiol 19:G1-G15, 1989
Cuthbert AW, Halushka PV, Margolius HS, Spayne JA: Role of calciumions in kinin-induced chloride secretion. Br J Pharmacol 82:587-595, 1984
Miller DH, Baird AW, Bennet S, Halushka M, Sasaguri M, Schomer H, Margolius HS: Regulation of bradykinin induced chloride secretion in a human epithelial cell line. AAS 38:81-86, 1992
Chapman V, Dickenson AH: The spinal and peripheral roles of bradykinin and prostaglandins in nociceptive processing in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 219:427-433, 1992
Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB, Cunha FQ, Poole S: Bradykinin release of TNF-alpha plays a key role in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Agents Actions 38:C7-C9, 1993
Ferreira SH, Lorenzetti BB, Poole S: Bradykinin initiates cytokine-mediated inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br J Pharmacol 110:1227-1231, 1993
Zeitlin IJ, Smith AN: Mobilization of tissue kallikrein in inflammatory disease of the colon. Gut 14:133-138, 1973
Hasler WL, Kurosawa S, Takahashi T, Feng H, Gaginella TS, Owyang C: Bradykinin acting on B2 receptors contracts colon circular muscle cells by IP3 generation and adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:344-350, 1995
Cominelli F, Nast CC, Dinarello CA, Gentilini P, Zipser RD: Regulation of eicosanoid production in rabbit colon by interleukin-1. Gastroenterology 97:1400-1405, 1989
Hojvat SA, Musch MW, Miller RJ: Stimulation of prostaglandin production in rabbit ileal mucosa by bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:749-755, 1983
Wardle TD, Hall L, Turnberg LA: Inter-relationships between inflammatory mediators released from colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis and their effects on colonic secretion. Gut 34:503-508, 1993
Burch RM, Connor JR, Tiffany CW: The kallikrein-kininogen-kinin system in chronic inflammation. Agents Actions 27:258-260, 1989
Paegelow I, Werner H, Reismann S: Effects of bradykinin and bradykinin analogues on spleen cells of mice. Eur J Pharmacol 279:211-216, 1995
Pan ZK, Zuraw BL, Lung CC, Prossnitz ER, Browning DD, Ye RD: Bradykinin stimulates NK-κB activation and interleukin 1β gene expression in cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 98:2042-2049, 1996
Sartor RB, DeLa Cadena RA, Green KD, Stadnicki A, Davis SW, Schwab JH, Adam AA, Raymond P, Colman RW: Selective kallikrein-kinin system activation in inbred rats differentially susceptible to granulomatous enterocolitis. Gastroenterology 110:1467-1481, 1996
Stadnicki A, DeLa Cadena RA, Sartor RB, Bender D, Kettner CA, Rath HC, Adam AA, Colman RW: Selective plasma kallikrein inhibitor attenuates acute intestinal inflammation in Lewis rat. Dig Dis Sci 41:912-920, 1996
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Ohkusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R: A novel method in the induction of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694-702, 1990
Murthy SNS, Cooper HS, Shim H, Shah RS, Ibrahim SA, Sedergran DJ: Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis Sci 37:1722-1734, 1993
Dieleman LA, Ridwan BU, Tennyson GS, Beagley KW, Bucy RP, Elson CO: Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis occurs in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Gastroenterology 107:1643-1652, 1994
Wirth K, Heitsch H, Schölkens BA: Kinin receptor antagonists: Unique probes in basic and clinical research. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 73:797-804, 1995
Rhaleb N, Rouissi N, Jukic D, Regoli D, Henke S, Breipohl G, Knolle J: Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (Hoe-140: D-Arg0[Hyp3,Thi5,DTic7,Oic8]-bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol 210:115-120, 1992
Hock FJ, Wirth K, Albus U, Linz W, Gerhards HJ, Wiemer G, Henke ST, Breipohl G, König W, Knolle J, Schölkens BA: Hoe 140, a new potent and long acting bradykinin antagonist: In vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:769-773, 1991
Wirth K, Hoch FJ, Albus U, Linz W, Alpermann HG, Anagnostopoulos H, Henke ST, Breipohl G, König W, Knolle J, Schölkens BA: Hoe140, a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: In vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:774-777, 1991
Allgayer H: Sulfasalazine and 5-ASA compounds. Gastrointest Pharmacol 21:643-658, 1992
Wiggins RC, Glatfelter A, Campbell AM, Kunkel RG, Ulevitch RJ: Acute hypotension due to platelet serotonin-induced chemore flexes after intravenous injection of dextran sulfate in the rabbit. Circ Res 57:262-277, 1985
Silverberg M, Diehl SV: The autoactivation of factor XII (Hageman factor) induced by low-Mr heparin and dextran sulphate. Biochem J 248:716-720, 1987
Siebeck M, Cheronis JC, Fink E, Kohl J, Spies B, Spannagl M, Jochum M, Fritz H: Dextran sulfate activates contact system and mediates arterial hypotension via B2 kinin receptors. J Appl Physiol 77:2675-2680, 1994
Mahida YR, Wu K, Jewell DP: Enhanced production of interleukin 1-γ by mononuclear cells isolated from mucosa with active ulcerative colitis of Crohn's disease. Gut 30:835-838, 1989
Ligumsky M, Simon PL, Karmeli F, Rachmilewitz D: Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease enhanced production during active disease. Gut 31:686-689, 1990
Youngman KR, Simon PL, West GA, Cominelli F, Rachmilewitz D, Klein JS, Fiocchi C: Localization of intestinal interleukin 1 activity and protein and gene expression to lamina propria cells. Gastroenterology 104:749-758, 1993
Wardle TD, Turnberg LA: Potential role for interleukin-1 in the pathophysiology of ulcerative colitis. Clin Sci 86:619-626, 1994
Woywodt A, Neustock P, Kruse A, Schwarting K, Lugwig D, Stange EF, Kirchner H: Cytokine expression in intestinal mucosal biopsies. In situ hybridisation of the mRNA for interleukin-1β, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur Cytokine Netw 5:387-395, 1994
Arai Y, Takanashi H, Kitagawa H, Okayasu I: Involvement of interleukin-1 in the development of ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium in mice. Cytokine 10:890-896, 1998
Marceau F: Kinin B1 receptors. Immunopharmacology 30:1-26, 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, Y., Takanashi, H., Kitagawa, H. et al. Effect of Icatibant, a Bradykinin B2 Receptor Antagonist, on the Development of Experimental Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Dig Dis Sci 44, 845–851 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026694732602
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026694732602