Abstract
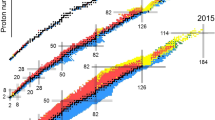
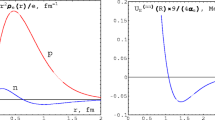
Systematic properties of heavy nuclides reveal a fine structure in Coulomb energy that parallels variations in mass arising from n-n interactions between neutrons. These results confirm an earlier suggestion that n-n interactions in the nucleus are repulsive. Neutron emission may release up to 1.1%–2.4% of the nuclear rest mass as energy. By comparison, 0.8% of the rest mass is converted to energy in hydrogen fusion and 0.1% is converted to energy in fission. Neutron emission in the core of the Sun may trigger a series of reactions that collectively produce the Sun's luminosity and an outpouring of protons and neutrinos from its surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
O. Manuel, C. Bolon, A. Katragada, and M. Insall, J. Fusion Energy 19, 93-98 (2000).
O. Manuel, in Origin of Elements in the Solar System: Implications of Post-1957 Observations, Proceedings of the 1999 ACS Symposium organized by Glenn T. Seaborg and Oliver K. Manuel, edited by O. Manuel (Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, NY, 2000) pp. 589-643.
O. Manuel, C. Bolon, M. Zhong, and P. Jangam, Abstract 1041, Lunar Planetary Science Conference XXXII, LPI Contribution No. 1080, ISSN No. 0161-5297 (2001).
O. Manuel, C. Bolon, and A. Katragada, Meteoritics and Planet. Sci. 37, A92 (2002).
O. Manuel, in Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Beyond Standard Model Physics-BEYOND 2002, Oulu, Finland (IOP, Bristol, England, in press, 2002).
O. Manuel and A. Katragada, in Proceedings of the Conference on Asteroids, Comets and Meteros, Berlin, Germany (ESA SP-500, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, in press, 2002).
O. Manuel and S. Friberg, in Proceedings of SOHO 12/GONG1 Conference, Big Bear Lake, CA (ESA SP-517 SOHO/GONG, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, in press, 2003).
J. K. Tuli, Nuclear Wallet Cards, 6th ed. (Bookhaven National Laboratory, National Nuclear Data Center, Upton, NY, 2000) 74 pp.
C. F. v. Weizäcker, “Zur Theorie der Kernmassen,” Z. Physik 96, 431-458 (1935).
R. D. Evans, The Atomic Nucleus (McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc., New York, NY, 1955) p. 33.
O. Manuel, C. Bolon, and M. Zhong, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 252, 3-7 (2002).
O. Manuel and D. Sabu, Trans. Mo. Acad. Sci. 9, 104-122 (1975).
O. Manuel and D. Sabu, Science 195, 208-209 (1977).
R. Davis Jr., D. S. Harmer and K. C. Hoffman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 20, 1205-1209 (1968).
J. R. Cronin and S. Pizzarello, Science 274, 951-955 (1997).
A. A. Penzias and R. W. Wilson, Ap. J. 142, 419-421 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manuel, O., Miller, E. & Katragada, A. Neutron Repulsion Confirmed as Energy Source. Journal of Fusion Energy 20, 197–201 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023485018692
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023485018692