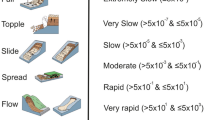
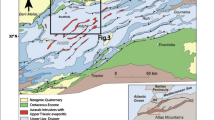
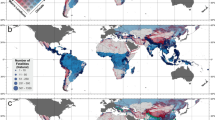
Abstract
Post-earthquake field investigations of landslide occurrence have provided a basis for understanding, evaluating, and mapping the hazard and risk associated withearthquake-induced landslides. This paper traces thehistorical development of knowledge derived from these investigations. Before 1783, historical accounts of the occurrence of landslides in earthquakes are typically so incomplete and vague that conclusions based on these accounts are of limited usefulness. For example, the number of landslides triggered by a given event is almost always greatly underestimated. The first formal, scientific post-earthquake investigation that included systematic documentation of the landslides was undertaken in the Calabria region of Italy after the 1783 earthquake swarm. From then until the mid-twentieth century, the best information on earthquake-induced landslides came from a succession ofpost-earthquake investigations largely carried out by formal commissions that undertook extensive ground-based field studies. Beginning in the mid-twentieth century, when the use of aerial photography became widespread, comprehensive inventories of landslide occurrence have been made for several earthquakes in the United States, Peru, Guatemala, Italy, El Salvador, Japan, and Taiwan. Techniques have also been developed for performing ``retrospective'' analyses years or decades after an earthquake that attempt to reconstruct the distribution of landslides triggered by the event. The additional use of Geographic Information System (GIS) processing and digital mapping since about 1989 has greatly facilitated the level of analysis that can applied to mapped distributions of landslides. Beginning in 1984, syntheses of worldwide and national data on earthquake-induced landslides have defined their general characteristics and relations between their occurrence and various geologic and seismic parameters. However, the number of comprehensive post-earthquake studies of landslides is still relatively small, and one of the most pressing needs in this area of research is for the complete documentation of landslides triggered by many more earthquakes in a wider variety of environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.: 1980, Contemporary Uplift and Erosion of the Southern Alps, New Zealand, Geological Society of America Bulletin 91(1), 2–4 and (2), 1-114.
Agnesi, V., Carrara, A., Macaluso, T., Monteleone, S., Pipitone, G., and Sorriso-Valvo, M.: 1983, Elementi Tipologici e Morfologici dei Fenomeni di Instabilità dei Versanti Indotti dal Sisma del 1980 (Alta Valle del Sele), Geologia Applicata e Idrogeologia 18(1), 309–341.
Ambraseys, N.N.: 1976, The Gemona di Friuli Earthquake of 6 May 1976, UNESCO Restricted Technical Report RP/1975-76/2.222.3, Part II.
Arias, A.: 1970, A Measure of Earthquake Intensity, in R.J. Hansen (ed.), Seismic Design for Nuclear Power Plants, Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, pp. 438–483.
Bonilla, M.G.: 1960, Landslides in the San Francisco South Quadrangle, California, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report.
Bozzano, F., Gambino, P., Prestininzi, A., Scarascia Mugnozza, G., and Valentini, G.: 1998, Ground Effects Induced by the Umbria-Marche Earthquakes of September-October 1997, Central Italy, Proceedings of the 8th International Congress of the International Association for Engineering Geology and the Environment, Vancouver, Canada, 21-25 September, 1998, A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 825–830.
Carrara, A., Agnesi, V., Macaluso, T., Monteleone, S., and Pipitone, G.: 1986, Slope Movements Induced by the Southern Italy Earthquake of November 1980, Geologia Applicata e Idrogeologia 21(2), 237–250.
Case, W.F.: 1988, Geologic Effects of the 14 and 18 August, 1988 Earthquakes in Emery County, Utah, Utah Geological and Mineral Survey, Survey Notes 22, pp. 8–14.
Cheng, J.D., Chen, B.K., Su, R.R., and Yeh, C.L.: 2000, Landslides Induced by the Disastrous Earthquake on September 21, 1999 in Central Taiwan (Abs.), European Geophysical Society 25th General Assembly, Nice, France, 2000, Geophysical Research Abstracts.
Collins, J.L. and Foster, H.L.: 1949, The Fukui Earthquake Hokuriku Region, Japan, 28 June 1948, Volume I, Geology, U.S.Army Office of the Engineer, General Headquarters, Far East Command.
Cotecchia, V.: 1986, Ground Deformations and Slope Instability Produced by the Earthquake of 23 November 1980 in Campania and Basilicata, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Geology Problems in Seismic Areas, Bari, Italy vol. 5, pp. 31–100.
Cotecchia, V. and Del Prete, M.: 1984, The Reactivation of Large Flows in the Parts of Southern Italy Affected by the Earthquake of November 1980, with Reference to the Evolutive Mechanism, Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Landslides, Toronto, vol. 2, pp. 33–37.
Cotecchia, V., Guerricchio, A., and Melidoro, G.: 1986, The Geomorphogenetic Crisis Triggered by the 1783 Earthquake in Calabria (Southern Italy), Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Geology Problems in Seismic Areas, Bari, Italy, vol. 6, pp. 245–304.
Cotecchia, C. and Melidoro, G.: 1974, Some Principal Aspects of the Landslides of Southern Italy, Bulletin of the International Association of Engineering Geology 9, 23–32.
Davison, C.: 1936, Great Earthquakes, Thomas Murby & Co., London.
Del Gaudio, V., Trizzino, R., Calcagnile, G., Calvaruso, D., and Pierri, P.: 2000, Landsliding in Seismic Areas: The Case of the Acquara-Vadoncello Landslide (Southern Italy), Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 59, 23–37.
D'Elia, B., Esu, F., Pellegrino, A., and Pescatore, T.: 1985, Some Effects on Natural Slope Stability Induced by the 1980 Italian Earthquake, Proceedings of the Eleventh International Society of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Conference, San Francisco.
Dutton, C.E.: 1889, The Charleston Earthquake of August 31, 1886, U.S. Geological Survey Ninth Annual Report 1887-1888, pp. 203–528.
Esposito, E., Porfido, S., Simonelli, A.L., Mastrolorenzo, G., and Iaccarino, G.: 2000, Landslides and Other Surface Effects Induced by the 1997 Umbria-Marche Seismic Sequence, Engineering Geology 58, 353–376.
Fukuoka, H., Sassa, K., and Scarascia-Mugnozza, G.: 1997, Distribution of Landslides Triggered by the 1995 Hyogo-ken Nanbu Earthquake and Long Runout Mechanism of the Takarazuka Golf Course Landslide, Journal of Physics of the Earth 45, 83–90.
Fuller, M.L.: 1912, The New Madrid Earthquake, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 394, reprint edition.
Geological Survey of India: 1939, The Bihar-Nepal Earthquake of 1934, Memoirs of the Geological Survey of India 73.
Govi, M.: 1977a, Carta delle Frane Prodotte dal Terremoto (Map Showing the Landslides Triggered by the Earthquake), Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia 83, Plate 1.
Govi, M.: 1977b, Photo-interpretation and Mapping of the Landslides Triggered by the Friuli Earthquake (1976), International Association of Engineering Geology Bulletin 15, 67–72.
Govi, M. and Sorzana, P.F.: 1977, Effetti Geologici del Terremoto, Frane, Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia 83, 329–368.
Hadley, J.B.: 1964, Landslides and Related Phenomena Accompanying the Hebgen Lake Earthquake of August 17, 1959, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 435, pp. 107–138.
Hall, J.F. (ed.): 1994, The Northridge Earthquake January 17, 1994 - Preliminary Reconnaissance Report, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute Publication 94-01.
Hancox, G.T., Perrin, N.D., and Dellow, G.D.: 1997, Earthquake-induced Landsliding in New Zealand and Implications for MM Intensity and Seismic Hazard Assessment, Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences, Ltd., GNS Client Report 43601B.
Hancox, G.T., Perrin, N.D., and Dellow, G.D.: 2002, Recent Studies of Historical Earthquake-Induced Landsliding, Ground Damage, and MM Intensity in New Zealand, Bulletin of the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 59–94.
Hansen, A. and Franks, C.A.M.: 1991, Characterisation and Mapping of Earthquake Triggered Landslides for Seismic Zonation, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Seismic Zonation, Stanford, California, vol. 1, pp. 149–195.
Harp, E.L. and Jibson, R.W.: 1995, Inventory of Landslides Triggered by the 1994 Northridge, California Earthquake, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-213.
Harp, E.L. and Jibson, R.W.: 1996, Landslides Triggered by the 1994 Northridge, California, Earthquake, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 86(1B), S319–S332.
Harp, E.L., Jibson, R.W., and Keefer, D.K.: 1993, Seismically-induced Landslides Triggered at Extraordinary Distances: Evidence from the Springdale, Utah, Landslide, Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 25, no. 6, p. A32.
Harp. E.L. and Keefer, D.K.: 1990, Landslides Triggered by the Earthquake, in M.J. Rymer and W. L. Ellsworth (eds.), The Coalinga, California, Earthquake of May 2, 1983, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1487, pp. 335–347.
Harp, E. L., Tanaka, K., Sarmiento, J., and Keefer, D. K.: 1984, Landslides from the May 25-27, 1980, Mammoth Lakes, California, Earthquake Sequence, U.S.Geological Survey Miscellaneous Investigations Series Map I-1612.
Harp, E.L. and Wilson, R.C.: 1995, Shaking Intensity Thresholds for Rock Falls and Slides: Evidence from 1987 Whittier Narrows and Superstition Hills Earthquake Strong-motion Records, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 85, 1739–1757.
Harp, E.L., Wilson, R.C., and Wieczorek, G.F., 1981, Landslides from the February 4, 1976, Guatemala Earthquake, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1204-A.
Hecker, S., Ponti, D.J., Garvin, C.D., and Hamilton, J.C.: 1995, Characteristics and Origin of Ground Deformation Produced in Granada Hills and Mission Hills During the January 17, 1994 Northridge, California, Earthquake, California Department of Conservation, Division of Mines and Geology Special Publication 116, pp. 111–131.
Holzer, T.L. (ed.): 1998, The Loma Prieta, California, Earthquake of October 17, 1989 - Liquefaction, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1551-B.
Japan Geotechnical Society, 1996, Special Issue on Geotechnical Aspects of the January 17, 1995 Hyogoken-Nambu Earthquake, Soils and Foundations, The Japanese Geotechnical Society, Tokyo.
Jibson, R.W.: 1985, Landslides Caused by the 1811-12 NewMadrid Earthquakes, Ph.D. Dissertation, Stanford University.
Jibson, R.W. and Harp, E.L.: 1996, The Springdale, Utah, Landslide: An Extraordinary Event, Environmental & Engineering Geoscience 2, 137–150.
Jibson, R.W., Harp, E.L., and Michael, J.A.: 1998, A Method for Producing Digital Probabilistic Seismic Landslide Hazard Maps: An Example from the Los Angeles, California, Area, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 98-113.
Jibson, R.W., Harp, E.L., and Michael, J.A.: 2000, A Method for Producing Digital Probabilistic Seismic Landslide Hazard Maps, Engineering Geology 58, 271–289.
Jibson, R.W. and Keefer, D.K.: 1988, Landslides Triggered by Earthquakes in the Central Mississippi Valley, Tennessee and Kentucky, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1336-C.
Jibson, R.W. and Keefer, D.K.: 1989, Statistical Analysis of Factors Affecting Landslide Distribution in the New Madrid Seismic Zone, Tennessee and Kentucky, Engineering Geology 27, 509–542.
Jibson, R.W. and Keefer, D.K.: 1993, Analysis of the Seismic Origin of Landslides: Examples from the New Madid Seismic Zone, Geological Society of America Bulletin 105, 521–536.
Jibson, R.W., Prentice, C.S., Borissoff, B.A., Rogozhin, E.A., and Langer, C.J.: 1994, Some Observations of Landslides Triggered by the 29 April 1991 Racha Earthquake, Republic of Georgia, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 84, 963–973.
Johnston, A.: 1996, Seismic Moment Assessment of Earthquakes in Stable Contiental Regions - III. New Madrid 1811-1812, Charleston 1886, and Lisbon 1755, Geophysical Journal International 126, 314–344.
Kamai, T.: 1995, Landslides in the Hanshin Urban Region Caused by the 1995 Hygoken-Nanbu Earthquake, Japan, Landslide News 9, 12–13.
Kamai, T., Wang, W.N., and Shuzui, H.: 2000, The Landslide Disaster Induced by the Taiwan Chi-Chi Earthquake of 21 September 1999, Landslide News 13, 8–12.
Keefer, D.K.: 1984, Landslides Caused by Earthquakes, Geological Society of America Bulletin 95, 406–421.
Keefer, D. K. (ed.): 1998, The Loma Prieta, California, Earthquake of October 17, 1989 - Landslides: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1551-C.
Keefer, D.K.: 1999, Earthquake-induced Landslides and Their Effects on Alluvial Fans, Journal of Sedimentary Research 69, 84–104.
Keefer, D.K.: 2000, Statistical Analysis of an Earthquake-induced Landslide Distribution - the 1989 Loma Prieta, California Event, Engineering Geology 58, 213–249.
Keefer, D.K. and Manson, M.W.: 1998, Regional Distribution and Characteristics of Landslides Generated by the Earthquake, in D.K. Keefer (ed.), The Loma Prieta, California, Earthquake of October 17, 1989-Landslides, U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1551-C, pp. 7–32.
Keefer, D.K. and Tannaci, N.E.: 1981, Bibliography on Landslides, Soil Liquefaction, and Related Ground Failures in Selected Historic Earthquakes, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 81-572.
Keefer, D.K. and Wilson, R.C.: 1989, Predicting Earthquake-induced Landslides, with Emphasis on Arid and Semi-arid Enviroments, in P.M. Sadler, and D.M. Morton (eds.), Landslides in a Semiarid Environment, Inland Geological Society of Southern California Publications, Riverside, California, vol. 2, part 1, pp. 118–149.
Keefer, D.K., Wilson, R.C., Harp, E.L., and Lips, E.W.: 1985, The Borah Peak, Idaho Earthquake of October 28, 1983 - Landslides, Earthquake Spectra 2, 91–125.
Lawson, A.C. (ed.): 1908, The California Earthquake of April 18, 1906: Report of the California State Earthquake Investigation Commission, Carnegie Institution,Washington, D.C., Publication 87, reprint edition.
Lee, K.L., Marcuson, W.F. III, Stokoe, K.H. II, and Yokel, F.Y. (eds.): 1977, Research Needs and Priorities for Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering Applications, Report of Workshop at University of Texas, Austin, National Science Foundation Grant No. AEN77-09861.
Lee, W.H.K.: 2001, Strong-motion Instrumentation and Data, in J. Uzarski and C. Arnold, (eds.), Chi-Chi, Taiwan, Earthquake of September 21, 1999 Reconnaissance Report, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute Publication 2001-02, Earthquake Spectra, Supplement A to Vol. 17, pp. 5–18.
Liao, H.W. and Lee, C.T.: 2000, Landslides Triggered by the Chi-Chi Earthquake, Asian Association on Remote Sensing, Asian Conference on Remote Sensing ACRS 2000, http://www.gisdevelopment.net/aars/acrs/2000/ts8/hami0007.htm.
Lin, J.C., Jen, C.H., and Jou, T.C.: 2001, Earthquake Landslide Hazard: Case Study of Chi-Chi Earthquake, Taiwan, Paper Presented at International Conference on Geomorphology, Tokyo, (Abs.), p. 471.
Lin, M.L., Wang, K.L., and Chen, C.T.: 2000, Characteristics of the Slope Failure Caused by the Chi-Chi Earthquake, International Workshop on Annual Commemoration of the Chi-Chi Earthquake, September 18-20, 2000, vol. 3, pp. 199–209.
Lyell, C.: 1874, Principles of Geology, D. Appleton, New York, 11th edition, vol. 2, pp. 113–144.
Manson, M.W., Keefer, D.K., and McKittrick, M.A., (eds.): 1992, Landslides and Other Geologic Features in the Santa Cruz Mountains, California, Resulting from the Loma Prieta Earthquake of October 17, 1989, State of California Division of Mines and Geology Open-File Report 91-05.
Matthews, W.H.: 1979, Landslides of Central Vancouver Island and the 1946 Earthquake, Seismological Society of America Bulletin 69, 445–450.
Mitchill, S.L.: 1815, A Detailed Narrative of the Earthquake which Occurred on the 16th Day of December, 1811, Literary and Philosophical Society of New York, Transactions 1, 281–307.
Morton, D.M.: 1971, Seismically Triggered Landslides in the Area Above the San Fernando Valley, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 733, pp. 99–104.
Morton, D.M.: 1975, Seismically Triggered Landslides in the Area Above the San Fernando Valley, State of California Division of Mines and Geology Bulletin 196, pp. 145–154.
National Research Council Committee on the Alaska Earthquake: 1968-1973, The Great Alaska Earthquake of 1964, National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., National Research Council Publication 1603.
Newmark, N.M.: 1965, Effects of Earthquakes on Dams and Embankments, Geotechnique 15, 139–160.
Oldham, R.D.: 1899, Report on the Great Earthquake of 12th June 1897, Memoirs of the Geological Survey of India, vol. 29.
Ochiai, H., Kitahara, H., Sammori, T., and Abe, K.: 1996, Landslides Triggered by the 1995 Hyogen-Ken Nanbu Earthquake in the Rokko Mountains, in K. Senneset (ed.), Landslides, Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Landslides, Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 1007–1012.
Okimura, T. and Torii, N.: 1999, A Study on Slope Failures due to Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake and Post-earthquake Rainfalls, Sino-Japan Second Workshop on Seismic Hazard and Mitigation, Taiwan National University, Taipei, Taiwan, pp. 62–65.
O'Rourke, T.D. (ed.): 1992, The Loma Prieta, California, Earthquake of October 17, 1989 - Marina District: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1551-F.
Papadopoulos, G.A. and Plessa, A.: 2000, Magnitude-Distance Relations for Earthquake-induced Landslides in Greece, Engineering Geology 58, 377–386.
Parise, M. and Jibson, R.W.: 2000, A Seismic Landslide Susceptibility Rating of Geologic Units Based on Analysis of Characteristics of Landslides Triggered by the 17 January, 1994 Northridge, California Earthquake, Engineering Geology 58, 251–270.
Pearce, A.J., and O'Loughlin, C.L.: 1985, Landsliding During a M 7.7 Earthquake: Influence of Geology and Topography, Geology 13, 855–858.
Penick, J. L., Jr.: 1981, The New Madrid Earthquakes of 1811-1812, University of Missouri Press, Columbia and London.
Plafker, G. and Ericksen, G.E.: 1978, Nevados Huascarán Avalanches, Peru, in B. Voight (ed.), Rockslides and Avalanches, 1 Natural Phenomena, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 277–314.
Plafker, G., Ericksen, G.E., and Fernández Concha, J.: 1971, Geological Aspects of the May 31, 1970, Perú Earthquake, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 61, 543–578.
Plafker, G., Kachadoorian, R., Eckel, E.B., and Mayo, L.R.: 1969, Effects of the Earthquake of March 27, 1964 on Various Communities, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 542-G.
Plant, N. and Griggs, G.B.: 1990, Coastal Landslides Caused by the October 17, 1989 Earthquake Santa Cruz County, California, California Geology 43, 75–84.
Prestininzi, A. and Romeo, R.: 2000, Earthquake-induced Ground Failures in Italy, Engineering Geology 58, 387–397.
Rodríguez, C.E., Bommer, J.J., and Chandler, R.J.: 1999, Earthquake-induced Landslides: 1980- 1997, Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 18, 325–346.
Rogers, G.C.: 1980, A Documentation of Soil Failure During the British Columbia Earthquake of 23 June, 1946, Canadian Geotechnical Journal 17, 122–127.
Rymer, M.J.: 1987, The San Salvador Earthquake of October 10, 1986 - Geologic Aspects, Earthquake Spectra 3, 435–463.
Rymer, M.J. and White, R.A.: 1989, Hazards in El Salvador from Earthquake-induced Landslides, in E.E. Brabb and B.L. Harrod (eds.), Landslides: Extent and Economic Significance, Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 105–109.
Sassa, K., Fukuoka, H., Scarascia-Mugnozza, G., Irikura, K., and Okimura, T.: 1995, Landslides Triggered by the Hyogoken-Nanbu Earthquake, Landslide News 9, 2–5.
Sarconi, M.: 1784, Osservazioni Fatte Nelle Calabrie e Nella Frontiera di Valdemone sui Fenomeni del Tramoto del 1783 e Sulla Geografia Fisica di Quelle Regioni, Reali Accademia delle Scienze e Belle Lettere. Napoli.
Seed, H.B.: 1968, Landslides During Earthquakes Due to Soil Liquefaction, American Society of Civil Engineers, Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division 94, 1053–1122.
Simonett, D.S.: 1967, Landslide Distribution and Earthquakes in the Bewani and Torricelli Mountains, New Guinea - a Statistical Analysis, in J.N. Jennings and J.A. Mabbutt (eds.), Landform Studies from Australia and New Guinea, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, pp. 64–84.
Sitar, N. and Bardet, J.P.: 2001, Landslides, in J. Uzarski and C. Arnold (eds.), Chi-Chi, Taiwan, Earthquake of September 21, 1999 Reconnaissance Report, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute Publication 2001-2002, Earthquake Spectra, Supplement A to Vol. 17, pp. 61–76.
Spittler, T. E. and Harp, E.L.: 1990, Preliminary Map of Landslide Features and Coseismic Fissures, in the Summit Road Area of the Santa Cruz Mountains, Triggered by the Loma Prieta Earthquake of October 17, 1989, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 90-688.
Stewart, J.P.: 2001, Soil Liquefaction, in J. Uzarski and C. Arnold, (eds.), Chi-Chi, Taiwan, Earthquake of September 21, 1999 Reconnaissance Report, Earthquake Engineering Research Institute Publication 2001-2002, Earthquake Spectra, Supplement A to Vol. 17, pp. 37–60.
Stewart, J.P., Seed, R.B., and Bray, J.D.: 1996, Incidents of Ground Failure from the 1994 Northridge Earthquake, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 86(1B), S300–S318.
Varnes, D.J.: 1978, Slope Movement Types and Processes, in R.L. Schuster and R.J. Krizek (eds.), Landslides - Analysis and Control, National Academy of Sciences Transportation Research Board Special Report 176, pp. 11–33.
Vivenzio, G.: 1788, Istoria de' Tremouti Avvenuti Nella Provincia della Calabria Ulteriore, e Nella Città di Messina Nell'anno 1783. E di Quanto Nella Calabria Fu Fatto per lo Suo Risorgimento Fino al 1787. Preceduta da una Teoria ed Istoria Generale dei Tremouti. II Edizione, Stamperia Reale, Napoli.
Wang, G. and Xu, B: 1984, Brief Introduction of Landslides in Loess in China, Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Landslides, Toronto, vol. 1, pp. 197–207.
Wasowski, J., Del Gaudio, V., Pierri, P., and Capolongo, D.: 2002, Factors Controlling Seismic Susceptibility of the Sele Valley Slopes: The Case of the 1980 Irpinia Earthquake Re-examined, Surveys in Geophysics (this volume).
Weber, G.E. and Nolan, J.M., 1989, Landslides and Associated Ground Failure in the Epicentral Region of the October 17, 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake, Final Technical Report to U.S. Geological Survey under Contract 14-08-0001-G1861.
Wieczorek, G.F. and Jäger, S.: 1996, Triggering Mechanisms and Depositional Rates of Postglacial Slope-movement Processes in the Yosemite Valley, California, Geomorphology 15, 17–31.
Wilson, R.C.: 1993, Relation of Arias Intensity to Magnitude and Distance in California, U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 93-556.
Wilson, R.C. and Keefer, D.K.: 1985, Predicting Areal Limits of Earthquake-induced Landsliding, in J.I. Ziony, (ed.), Earthquake Hazards in the Los Angeles Region - An Earth-science Perspective, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1360, pp. 317–345.
Wilson, R. C., Wieczorek, G. F., Keefer, D. K., Harp, E. L., and Tannaci, N.E.: 1985, Map Showing Ground Failures from the Greenville/Mount Diablo Earthquake Sequence of January 1980, Northern California, U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Field Studies Map MF 1711.
Wood, S.H., Wurts, C., Lane, T., Ballenger, N., Shaleen, M., and Totorica, D.: 1985, The Borah Peak, Idaho Earthquake of October 28, 1983 - Hydrologic Effects, Earthquake Spectra 2, 127–150.
Youd, T.L. and Hoose, S.N.: 1978, Historic Ground Failures in Northern California Associated with Earthquakes, U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keefer, D.K. Investigating Landslides Caused by Earthquakes – A Historical Review. Surveys in Geophysics 23, 473–510 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021274710840
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021274710840