Abstract
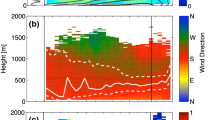
Characteristics and evolution of the low-level jet (LLJ)over southeastern Kansas were investigated during the 1999 Cooperative Surface-AtmosphereExchange Study (CASES–99) field campaign with an instrument complement consisting of ahigh-resolution Doppler lidar (HRDL), a 60 m instrumented tower, and a triangle of Dopplermini-sodar/profiler combinations. Using this collection of instrumentation we determined thespeed UX, height ZX and direction DX of the LLJ. We investigate here the frequencyof occurrence, the spatial distribution, and the evolution through the night, of these LLJcharacteristics. The jet of interest in this study was that which generates the shear and turbulencebelow the jet and near the surface. This was represented by the lowest wind maximum.We found that this wind maximum, which was most often between 7 and 10 m s‐1,was often at or just below 100 m above ground level as measured by HRDL at the CASEScentral site. Over the 60 km profiler–sodararray, the topography varied by ∼100 m. The wind speed anddirection were relatively constant over this distance (with some tendency for strongerwinds at the highest site), but ZX was more variable. ZX was occasionally about equal at allthree sites, indicating that the jet was following the terrain, but more often it seemed to berelatively level, i.e., at about the same height above sea level. ZX was also more variable thanUX in the behaviour of the LLJ with time through the night, and on some nights $UX wasremarkably steady. Examples of two nights with strong turbulence below jet level were furtherinvestigated using the 60 m tower at the main CASES–99 site. Evidence of TKE increasing withheight and downward turbulent transport of TKE indicates that turbulence was primarilygenerated aloft and mixed downward, supporting the upside–down boundary layer notion in thestable boundary layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas, E. L., Claffey, K. J., and Makshtas, A. P.: 2000, 'Low-Level Atmospheric Jets and Inversions over the Western Weddell Sea', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 459-486.
Banta, R. M., Senff, C. J., White, A. B., Trainer, M., McNider, R. T., Valente, R. J., Mayor, S. D., Alvarez, R. J., Hardesty, R. M., Parish, D. D., and Fehsenfeld, F. C.: 1998, 'Daytime Buildup and Nighttime Transport of Urban Ozone in the Boundary Layer during a Stagnation Episode', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 22,519-22,544.
Blackadar, A. K.: 1957, 'Boundary Layer Wind Maxima and their Significance for the Growth of Nocturnal Inversions', Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 38, 283-290.
Blumen, W., Banta, R. M., Burns, S. P., Fritts, D. C., Newsom, R. K., Poulos, G. S., and Sun, J.: 2001, 'Turbulence Statistics of a Kelvin-Helmholtz Billow Event Observed in the Nighttime Boundary Layer during the CASES-99 Field Program', Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 34, 189-204.
Bonner, W. D.: 1968, 'Climatology of the Low Level Jet', Mon. Wea. Rev. 96, 833-850.
Bowen, B. M.,:1996, 'Example of Reduced Turbulence during Thunderstorm Outflows', J. Appl. Meteorol. 35, 1028-1032.
Browning, K. A. and Wexler. R.: 1968, 'The Determination of Kinematic Properties of a Wind Field Using Doppler Radar', J. Appl. Meteorol. 7, 105-113.
Coulter, R. L, and Kallistratova, M. A.: 1999, 'The Role of Acoustic Sounding in a High-Technology Era', Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 71, 3-13.
Coulter, R. L., Klazura, G., Lesht, B. M., Martin, T. J., Shannon, J. D., Sisterson, D. L., and Wesely, M. L.: 1999, 'The Argonne Boundary Layer Experiments Facility: Using Minisodars to Complement a Wind Profiler Network', Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 71, 53-59.
Cuxart, J., Morales, G., Terradellas, E., and Yagüe, C.: 2002, 'Study of Coherent Structures and Estimation of the Pressure Transport Terms for the Nocturnal Stable Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105, 305-328.
Darby, L. S., Banta, R. M., Brewer, W. A., Neff, W. D., Marchbanks, R. D., McCarty, B. J., Senff, C. J., White, A. B., Angevine, W. M., and Williams, E. J.: 2002, 'Vertical Variations in O3 Concentrations before and after a Gust Front Passage', J. Geophys. Res., in press.
Droegemeier, K. K. and Wilhelmson, R. B.: 1987, 'Numerical Simulation of Thunderstorm Outflow Dynamics, Part I: Outflow Sensitivity Experiments and Turbulence Dynamics', J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 1180-1210.
Eklund, W. L., Carter, D. A., and Balsley, B. B.: 1988, 'A UHFWind Profiler for the Boundary Layer: Brief Description and Initial Results', J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 5, 432-441.
Frisch, A. S., Orr, B.W., and Martner, B. E.: 1992, 'Doppler Radar Observations of the Development of a Boundary-Layer Nocturnal Jet', Mon. Wea. Rev. 120, 3-16.
Grund, C. J., Banta, R.M., George, J. L., Howell, J. N., Post, M. J., Richter, R. A., and Weickmann, A. M.: 2001, 'High-Resolution Doppler Lidar for Boundary-Layer and Cloud Research', J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 18, 376-393.
Hoecker, W. L.: 1963, 'Three Southerly Low-Level Jet Systems Delineated by the Weather Bureau Special Pibal Network of 1961', Mon. Wea. Rev. 91, 573-582.
LeMone, M. A., Grossman, R. L., Coulter, R. L., Wesley, M. L., Klazura, G. E., Poulos, G. S., Blumen, W., Lundquist, J. K., Cuenca, R. H., Kelly, S. F., Brandes, E. A., Oncley, S. P., McMillen, R. T., and Hicks, B. B.: 2000, 'Land-Atmosphere Interaction Research, Early Results, and Opportunities in the Walnut River Watershed in Southeast Kansas: CASES and ABLE', Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 757-779.
Lundquist, J. K.: 2000, The Evening Transition of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer: Inertial Oscillations, and Boundary-Layer Dynamics, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Colorado at Boulder, 180 pp.
Mahrt, L.: 1998, 'Stratified Atmospheric Boundary Layers and Breakdown of Models', J. Theor. Comp. Fluid Dyn. 11, 263-280.
Mahrt, L.: 1999, 'Stratified Atmospheric Boundary Layers', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 90, 375-396.
Mahrt, L. and Vickers, D.: 2002, 'Contrasting Vertical Structures of Nocturnal Boundary Layers', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105, 351-363.
Mitchell, M. J., Arritt, R. W., and Labas, K.: 1995, 'A Climatology of the Warm Season Great Plains Low-Level Jet Using Wind Profiler Observations', Wea. Forecast. 10, 576-591.
Newsom, R. K. and Banta, R. M.: 2002, 'Shear-Flow Instability in the Stable Nocturnal Boundary Layer as Observed by Doppler Lidar during CASES-99', J. Atmos. Sci., in press.
Poulos, G. S., Blumen, W., Fritts, D. C., Lundquist, J. K., Sun, J., Burns, S. P., Nappo, C., Banta, R. M., Newsom, R. K., Cuxart, J., Terradellas, E., Balsley, B., and Jensen, M.: 2002, 'CASES-99, A Comprehensive Investigation of the Stable Nocturnal Boundary Layer', Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 83, 555-581.
Smedman, A. S.: 1988, 'Observations of a Multi-Level Turbulence Structure in a Very Stable Atmospheric Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 44, 231-253.
Stensrud, D. J.: 1996, 'Importance of Low-Level Jets to Climate: A Review', J. Climate 9, 1698-1711.
Sun, J., Burns, S. P., Lenschow, D. H., Banta, R., Newsom, R., Coulter, R., Frasier, S., Ince, T., Nappo, C., Cuxart, J., Blumen,W., Lee, X., and Hu, X.-Z.: 2002, 'Intermittent Turbulence Associated with a Density Current Passage in the Stable Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 105, 199-219.
Thorpe, A. J. and Guymer, T. H.: 1977, 'The Nocturnal Jet', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 103, 633-653.
Whiteman, C. D., Bian, X., and Zhong, S.: 1997, 'Low-Level Jet Climatology from Enhanced Rawinsonde Observations at a Site in the Southern Great Plains', J. Appl. Meteorol. 36, 1363-1376.
Wulfmeyer, V. O., Randall, M., Brewer, W. A., and Hardesty R. M.: 2000, '2 µm Doppler Lidar Transmitter with High Frequency Stability and Low Chirp', Opt. Lett. 25, 1228-1230.
Zhong, S., Fast, J. D., and Bian, X.: 1996, 'A Case Study of the Great Plains Low-Level Jet Using Wind Profiler Network Data and a High-Resolution Mesoscale Model', Mon. Wea. Rev. 124, 785-806.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banta, R., Newsom, R.K., Lundquist, J.K. et al. Nocturnal Low-Level Jet Characteristics Over Kansas During Cases-99. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 105, 221–252 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019992330866
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019992330866