Abstract
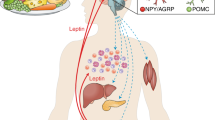
Leptin, the product of the obesity gene, is a cytokine-like circulating protein acting as a peripheral satiety signal to the hypothalamus. It was initially described as a secreted product of white adipose cells, but more recent data have demonstrated its expression by endocrine and neuroendocrine tissues like the ovary and the hypothalamus, as well as several anterior pituitary cell types. The effects of leptin on body weight homeostasis are mediated via different hypothalamic neurotransmitters regulating appetite and energy expenditure. In addition, leptin participates to the modulation of the activity of the neuroendocrine thyrotrope, somatotrope, corticotrope and gonadotrope axes. These endocrine effects of leptin have progressively emerged as important physiological functions of this molecule. Its role as a permissive factor for puberty and normal reproductive function in adulthood is becoming widely recognized. In addition, leptin participates in the fine tuning of the corticotrope axis. Thus, by signalling body fat stores to the hypothalamus and other endocrine organs, leptin serves as a metabolic integrator of several neuroendocrine functions. The precise site of action and mode of regulation of the gonadotrope and somatotrope axes by leptin are reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994;372:425-432.
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: Evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural network. Science 1995;269:546-549.
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, Lallone RL, Burley SK, Friedman JM.Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 1995;269:543-546.
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 1995;269: 540-543.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Sagawa N, Hosoda K, Matsumoto T, Mise H, Nishimura H, Yoshimasa Y, Tanaka I, Mori T, Nakao K. Nonadipose tissue production of leptin: Leptin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. Nat Med 1997;3:1029-1033.
Cioffi JA, Van Blerkom J, Antczak M, Schafer A, Wittmer S, Snodgrass HR. The expression of leptin and its receptors in pre-ovulatory human follicles. Mol Hum Reprod 1997;3:467-472.
Morash B, Li A, Murphy PR, Wilkinson M, Ur E. Leptin gene expression in the brain and pituitary gland. Endocrinology 1999;140:5995-5998.
Iqbal J, Pompolo S, Considine RV, Clarke IJ. Localization of leptin receptor-like immunoreactivity in the corticotropes, somatotropes, and gonadotropes in the ovine anterior pituitary. Endocrinology 2000;141:1515-1520.
Dieterich KD, Lehnert H. Expression of leptin receptor mRNA and the long form splice variant in human anterior pituitary and pituitary adenoma. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1998;106:522-525.
Shimon I, Yan X, Magoffin DA, Friedman TC, Melmed S. Intact leptin receptor is selectively expressed in human fetal pituitary and pituitary adenomas and signals human fetal pituitary growth hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:4059-4064.
Jin L, Zhang S, Burguera_BG, Couce ME, Osamura RY, Kulig E, Lloyd RV. Leptin and leptin receptor expression in rat and mouse pituitary cells. Endocrinology 2000;141:333-339.
Jin L, Burguera BG, Couce ME, Scheithauer BW, Lamsan J, Eberhardt NL, Kulig E, Lloyd RV. Leptin and leptin receptor expression in normal and neoplastic human pituitary: Evidence of a regulatory role for leptin on pituitary cell proliferation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:2903-2911.
Vidal S, Cohen SM, Horvath E, Kovacs K, Scheithauer BW, Burguera BG, Lloyd RV. Subcellular localization of leptin in non-tumorous and adenomatous human pituitaries: An immuno-ultrastructural study. J Histochem Cytochem 2000;48: 1147-1152.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. New Engl J Med 1996;334:292-295.
Montague CT, Sadaf Farooqi I, Whitehead JP, Soos MA, Rau H, Wareham NJ, Sewter CP, Digby JE, Mohammed SN, Hurst JA, Cheetham CH, Earley AR, Barnett AH, Prins JB, O'Rahilly S. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe, early-onset obesity in humans. Nature 1997; 387:903-908.
Strobel A, Issad T, Camoin L, Ozata M, Strosberg AD. A leptin missense mutation associated with hypogonadism and morbid obesity. Nature Genetics 1998;18:213-215.
Clément K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambyz J, Lacorte J-M, Basdevant A, Bougnères P, Lebouc Y, Froguel P, Guy-Grand B. A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 1998;392:398-401.
Kalra SP, Crowley WR. Norepinephrine-like effects of neuropeptide Y in the rat. Life Sci 1984;35:1173-1176.
Wahlestedt C, Skagerberg G, Ekman R, Heilig M, Sundler F, Hakanson R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the area of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus activates the pituitaryadrenocortical axis in the rat. Brain Res 1987;417:33-38.
McDonald JK, Lumpkin MD, Samson WK, McCann SM. Neuropeptide Y affects secretion of luteinizing hormone and growth hormone in ovariectomized rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1985;82:561-564.
Haas DA, George SR. Neuropeptide Y administration acutely increases hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity: Lack of effect in other rat brain regions. Life Sci 1987;41:2725-2731.
Harfstrand A, Eneroth P, Agnati L, Fuxe K. Further studies on the effects of central administration of neuropeptide Y on neuroendocrine function in the male rat: Relationship to hypothalamic catecholamines. Regul Pept 1987;17:167-179.
Levine AS, Morley JE. Neuropeptide Y: A potent inducer of consummatory behavior in rats. Peptides 1984;5:1025-1029.
Clark JT, Kalra PS, Crowley WR, Kalra SP. Neuropeptide Y and human pancreatic polypeptide stimulate feeding behavior in rats. Endocrinology 1984;115:427-429.
Gruaz NM, Pierroz DD, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Sizonenko PC, Aubert ML. Evidence that neuropeptide Y could represent a neuroendocrine inhibitor of sexual maturation in unfavorable metabolic conditions in the rat. Endocrinology 1993;133:1891-1894.
Catzeflis C, Pierroz DD, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Rivier JE, Sizonenko PC, Aubert ML. Neuropeptide Y administered chronically into the lateral ventricle profoundly inhibits both the gonadotropic and the somatotropic axis in intact adult female rats. Endocrinology 1993;132:224-234.
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 1996;382:250-252.
Wang Q, Bing C, Al-Barazanji K, Mossakowaska DE, Wang XM, McBay DL, Neville WA, Taddayon M, Pickavance L, Dryden S, Thomas ME, McHale MT, Gloyer IS, Wilson S, Buckingham R, Arch JR, Trayhurn P, Williams G. Interactions between leptin and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y neurons in the control of food intake and energy homeostasis in the rat. Diabetes 1997;46:335-341.
Stephens TW, Basinski M, Bristow PK, Bue-Valleskey JM, Burgett SG, Craft L, Hale J, Hoffmann J, Hsiung HM, Kriauciunas A, MacKellar W, Rosteck PR, Jr., Schoner B, Smith D, Tinsley FC, Zhang X-Y, Heiman M. The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obese gene product. Nature 1995;377:530-532.
Schwartz MW, Baskin DG, Bukowski TR, Kuijper JL, Foster D, Lasser G, Prunkard DE, Porte D, Jr., Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Weigle DS. Specificity of leptin action on elevated blood glucose levels and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 1996;45:531-535.
Zachow RJ, Magoffin DA. Direct intraovarian effects of leptin: impairment of the synergistic action of insulin-like growth factor-I on follicle-stimulating hormone-dependent estradiol-17 beta production by rat ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology 1997;138:847-850.
Spicer LJ, Francisco CC. The adipose obese gene product, leptin: Evidence of a direct inhibitory role in ovarian function. Endocrinology 1997;138:3374-3379.
Pralong FP, Roduit R, Waeber G, Castillo E, Mosimann F, Thorens B, Gaillard RC. Leptin inhibits directly glucocorticoid secretion by normal human and rat adrenal gland. Endocrinology 1998; 139: 4264-4268.
Bornstein RS, Uhlmann K, Haidan A, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Scherbaum WA. Evidence for a novel peripheral action of leptin as a metabolic signal to the adrenal gland. Leptin inhibits cortisol release directly. Diabetes 1997;46:1235-1238.
Malendowicz LK, Nussdorfer GG, Markowska A. Effects of recombinant murine leptin on steroid secretion of dispersed rat adrenocortical cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1997;63: 123-125.
Malendowicz LK, Tortorella C, Nowak KW, Nussdorfer GG, Hochol A, Majchrzak M. Leptin prolonged administration inhibits the growth and glucocorticoid secretion of rat adrenal cortex. Endocr Res 2000;26:141-152.
Bornstein SR. Is leptin a stress related peptide? Nature Medicine 1997;3:937.
Licino J, Mantzoros C, Negrao AB, Cizza G, Wong ML, Bongiorno PB, Chrousos GP, Karp B, Allen C, Flier JS, Gold PW. Human leptin levels are pulsatile and inversely related to pituitary-adrenal function. Nature Med 1997;3:575-579.
De Vos P, Saladin R, Auwerx J, Staels B. Induction of Obgene expression by corticosteroids is accompanied by body weight loss and reduced food intake. J Biol Chem 1995; 270:15958-15961.
Slieker LJ, Sloop KW, Surface PL, Kriauciunas A, LaQuier F, Manetta J, Bue-Valleskey J, Stephens TW. Regulation of expression of ObmRNA and protein by glucocorticoids and cAMP.J Biol Chem 1996;271:5301-5304.
Spinedi E, Gaillard RC. A regulatory loop between the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and circulating leptin: A physiological role of ACTH. Endocrinology 1998;139: 4016-4020.
Kruse M, Bornstein SR, Uhlmann K, Paeth G, Scherbaum WA. Leptin down-regulates the steroid producing system in the adrenal. Endocr Res 1998;24:587-590.
Tena-Sempere M, Pinilla L, Gonzalez LC, Casanueva FF, Dieguez C, Aguilar E. Homologous and heterologous downregulation of leptin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in rat adrenal gland. J Endocrinol 2000;167:479-486.
Garthwaite TL, Martinson DR, Tseng LF, Hagen TC, Menahan LA. A longitudinal hormonal pro~le of the genetically obese mouse. Endocrinology 1980;107:671-676.
Edwardson JA, Hough CA. The pituitary-adrenal system of the genetically obese (ob/ob) mouse.J Endocrinol 1975;65: 99-107.
Heiman ML, Ahima RS, Craft LS, Schoner B, Stephens TW, Flier JS. Leptin inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in response to stress.Endocrinology 1997;138: 3859-3863.
Giovambattista A, Chisari AN, Gaillard RC, Spinedi E. Food intake-induced leptin secretion modulates hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis response and hypothalamic Ob-Rb expression of insulin administration. Neuroendocrinology 2000;72:341-349.
Morimoto I, Yamamoto S, Kai K, Fujihira T, Morita E, Eto S. Centrally administered murine-leptin stimulates the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis through arginine-vasopressin. Neuroendocrinology 2000;71:366-374.
Costa A, Poma A, Martignoni E, Nappi G, Ur E, Grossman A. Stimulation of corticotrophin-releasing hormone release by the obese (ob) gene product, leptin, from hypothalamic explants. Neuroreport 1997;8:1131-1134.
Pralong FP, Gomez F, Guillou L, Mosimann F, Franscella S, Gaillard RC. Food-dependent Cushing's syndrome: Possible involvement of leptin in cortisol hypersecretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:3817-3822.
Casanueva FF, Dieguez C. Neuroendocrine regulation and actions of leptin. Front Neuroendocrinol 1999;20:317-363.
Zakrewska KE, Cusin I, Sainsbury A, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Jeanrenaud B. Glucocorticoids as counterregulatory hormones of leptin. Toward an understanding of leptin resistance. Diabetes 1997;46:717-719.
De Vos P, Saladin R, Auwerx J, Staels B. Induction of ob gene expression by corticosteroids is accompanied by body weight loss and reduced food intake. J Biol Chem 1995;270: 15958-15961.
Glasow A, Haidan A, Hilbers U, Breidert M, Gillespie J, Scherbaum WA, Chrousos GP, Bornstein SR. Expression of Ob receptor in normal human adrenals: Differential regulation of adrenocortical and adrenomedullary function by leptin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:4459-4466.
Bornstein SR, Licinio J, Tauchnitz R, Engelmann L, Negrao AB, Gold P, Chrousos GP. Plasma leptin levels are increased in survivors of acute sepsis: Associated loss of diurnal rhythm, in cortisol and leptin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:280-283.
Chautard T, Spinedi E, Voirol M, Pralong F, Gaillard RC. Role of glucocorticoids in the response of the hypothalamocorticotrope immune and adipose systems to repeated endotoxin administration. Neuroendocrinol 1999;69:360-369.
Renz M, Tomlinson E, Hultgren B, Levin N, Gu Q, Shimkets RA, Lewin DA, Stewart TA. Quantitative expression analysis of genes regulated by both obesity and leptin reveals a regulatory loop between leptin and pituitary-derivedACTH. J BiolChem 2000;275:10429-10436.
Shimkets RA, Lowe DG, Tai JT, Sehl P, Jin H, Yang R, Predki PF, Rothberg BE, Murtha MT, Roth ME, Shenoy SG, Windemuth A, Simpson JW, Simons JF, Daley MP, Gold SA, McKenna MP, Hillan K, Went GT, Rothberg JM. Gene expression analysis by transcript profiling coupled to a gene database query. Nat Biotechnol 1999;17:798-803.
Frisch RE, McArthur JW. Menstrual cycles: Fatness as a determinant of minimum weight for height necessary for their maintenance or onset. Science 1974;185:949-951.
Bronson FH. Food-restricted, prepubertal, female rats: Rapid recovery of luteinizing hormone pulsing with excess food, and full recovery of pubertal development with gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Endocrinology 1986;118: 2483-2487.
Foster DL, Nagatani S. Physiological perspectives on leptin as a regulator of reproduction: Role in timing puberty. Biol Reprod 1999;60:205-215.
Chehab FF, Lim ME, Lu R. Correction of the sterility defect in homozygous obese female mice by treatment with the human recombinant leptin. Nat Genet 1996;12:318-320.
Mounzih K, Lu R, Chehab FF. Leptin treatment rescues the sterility of genetically obese ob/ob males. Endocrinology 1997;138:1190-1193.
Chehab FF, Mounzih K, Lu R, Lim ME. Early onset of reproductive function in normal female mice treated with leptin. Science 1997;275:88-90.
Ahima RS, Dushay J, Flier SN, Prabakaran D, Flier JS. Leptin accelerates the onset of puberty in normal female mice. J Clin Invest 1997;99:391-395.
Cheung CC, Thornton JE, Kuijper JL, Weigle DS, Clifton DK, Steiner RA. Leptin is a metabolic gate for the onset of puberty in the female rat. Endocrinology 1997;138:855-858.
Cheung CC, Shafeena DN, Steiner RA, Clifton DK. Leptin and sexual development in female rats and mice. The Endocrine Society's 81st Annual Meeting 1999; Abstract P1-479.
Lado-Abeal J, Lukyanenko YO, Swamy S, Hermida RC, Hutson JC, Norman RL. Short-term leptin infusion does not affect circulating levels of LH, testosterone or cortisol in food-restricted pubertal male rhesus macaques. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999;51:41-51.
Plant TM, Durrant AR. Circulating leptin does not appear to provide a signal for triggering the initiation of puberty in the male rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Endocrinology 1997;138:4505-4508.
Gruaz NM, Lalaoui M, Pierroz DD, Englaro P, Sizonenko PC, Blum WF, Aubert ML. Chronic administration of leptin into the lateral ventricle induces sexual maturation in severely food-restricted female rats. J Neuroendocrinol 1998; 10:627-633.
Cunningham MJ, Clifton DK, Steiner RA. Leptin's actions on the reproductive axis: Perspectives and mechanisms. Biol Reprod 1999;60:216-222.
Mantzoros CS, Flier JS, Rogol AD. A longitudinal assessment of hormonal and physical alterations during normal puberty in boys. V. Rising leptin levels may signal the onset of puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:1066-1070.
Clayton PE, Gill MS, Hall CM, Tillmann V, Whatmore AJ, Price DA. Serum leptin through childhood and adolescence. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1997;46:727-733.
Quinton NQ, Smith RF, Clayton PE, Gill MS, Shalet S, Justice SK, Simon SA, Walters S, Postel-Vinay M-C, Blakemore AIF, Ross RJM. Leptin binding activity changes with age: The link between leptin and puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84:2336-2341
Havel PJ, Kasim-Karakas S, Dubuc GR, Mueller W, Phinney SD. Gender differences in plasm leptin concentrations. Nature Med 1996; 2:949-950.
Quinton ND, Laird SM, Okon MA, Li TC, Smith RF, Ross RJ, Blakemore AI. Serum leptin levels during the menstrual cycle of healthy fertile women. Brit J Biomed Sci1999;56:16-19.
Hardie L, Trayhurn P, Abramovich D, Fowler P. Circulating leptin in women: A longitudinal study in the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1997;47:101-106.
Riad-Gabriel MG, Jinagouda SD, Sharma A, Boyadjian R, Saad MF. Changes in plasma leptin during the menstrual cycle. Eur J Endocrinol 1998;139:528-531.
Kopp W, Blum WF, vonPrittwitz S, Ziegler A, Lubbert H, Emons G, Herzog W, Herpertz S, Deter HC, Remschmidt H, Hebebrand J. Low leptin levels predict amenorrhea in underweight and eating disordered females. Mol Psychiatry 1997;2:267-269.
Farooqi IS, Jebb SA, Lanfmack G, Lawrence E, Cheetham CH, Prentice AM, Hughes IA, McCamish MA, O'Rahilly S. Effects of recombinant leptin therapy in a child with congenital leptin deficiency. New Engl J Med 1999;341:879-884.
Pierroz DD, Catzeflis C, Aebi AC, Rivier JE, Aubert ML.Chronic administration of neuropeptide Y into the lateral ventricle inhibits both the pituitary-testicular axis and growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I secretion in intact adult male rats. Endocrinology 1996;137:3-12.
Pralong FP, Voirol M, Giacomini M, Gaillard RC, Grouzmann E. Acceleration of pubertal development following central blockade of the Y1 subtype of neuropeptide Y receptors.Regul Pept 2000;95:47-52.
Yu WH, Kimura M, Walczewska A, Karanth S, McCann SM. Role of leptin in hypothalamic-pituitary function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:1023-1028.
Messinis IE, Milingos S, Zikopoulos K, Kollios G, Seferiadis K, Lolis D. Leptin concentrations in the follicular phase of spontaneous cycles and cycles supervulated with follicle stimulating hormone. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1152-1156.
Duggal PS, Van Der Hoek KH, Milner CR, Ryan NK, Armstrong DT, Magoffin DA, Norman RJ.The in vivo and in vitro effects of exogenous leptin on ovulation in the rat. Endocrinology 2000;141:1971-1976.
Chardonnens D, Cameo P, Aubert ML, Pralong FP, Islami D, Campana A, Gaillard RC, Bischof P. Modulation of human cytotrophoblastic leptin secretion by interleukin-1alpha and 17beta-oestradiol and its effect on HCG secretion. Mol Hum Reprod 1999;5:1077-1082.