Abstract
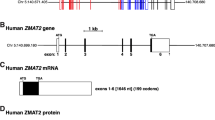
Most kelch family proteins contain two conserved domains, the BTB domain and the kelch repeat domain. Here we describe the cloning and characterization of a novel human KLHL5 gene. The 3488 bp cDNA encodes a kelch family protein homologous to the Drosophila kelch protein. It also contains the two conserved domains. Northern blot analysis reveals a single transcript. It is abundantly expressed in ovary, adrenal gland, and thyroid and less abundantly expressed in trachea, prostate, testis, lymph node, and spinal cord. KLHL5 was mapped to 4p13–4p15.1.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adams, J., Kelo, R., and Cooley, L. (2000). The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: Propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 10:17-24.
Bomont, P., Cavalier, L., Blondeau, F., Hamida, C. B., Belal, S., Tazir, M., Demir, E., Topaloglu, H., Korinthenberg, R., Tüysüz, B., Landrieu, P., Hentati, F., and Koenig, M. (2000). The gene encoding gigaxonin, a new member of the cytoskeletal BTB/kelch repeat family, is mutated in giant axonal neuropathy. Nat. Genet. 26:370-374.
Bork, P., and Doolittle, R. F. (1994). Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J. Mol. Biol. 236:1277-1282.
Cooley, L. (1998). Drosophila ring canal growth requires Src and Tec kinases. Cell 93:913-915.
DiBello, P. R., Withers, D. A., Bayer, C. A., Fristrom, J. W., and Guild, G. M. (1991). The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics 129:385-397.
Goebel, S. J., Johnson, G. P., Perkins, M. E., Davis, S. W., Winsiow, J. P., and Paoletti, E. (1990). The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology 179:247-266.
Goode, B. L., Drubin, D. G., and Barnes, G. (2000). Functional cooperation between the microtubule and actin cytoskeletons. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:63-71.
Harrison, S. D., and Travers, A. A. (1990). The tramtrack gene encodes a Drosophila finger protein that interacts with the ftz transcriptional regulatory region and shows a novel embryonic expression pattern. EMBO 9:799-812.
Hernandez, M. C., Andres-Barquin, P. J., Martinez, S., Bulfone, A., Rubenstein, J. L. R., and Israel, M. A. (1997). ENC-1: A novel mammalian kelch-related gene specifically expressed in the nervous system encodes an actin-binding protein. J. Neurosci. 17(9):3038-3051.
Joesphine, C. A., Brian S., and Jack, L. (1998). Muskelin, a novel intracellular mediator of cell adhesive and cytoskeletal responses to thrombospondin-1. EMBO 17:4964-4974.
Kim, I. F., Mohammadi, E., and Huang, R. C. C. (1999). Isolation and characterization of IPP, a novel human gene encoding an actin-binding, kelch-like protein. Gene 228:73-83.
Kim, T. A., Ota, S., Jiang, S., Pasztor, L. M., White, R. A., and Avraham, S. (2000). Genomic organization, chromosomal location and regulation of expression of the neuronal nuclear matrix protein NPR/B in human brain tumors. Gene 255:105-116.
Koonin, E. V., Senkevich, T. G., and Cheemos, V. L. (1992). A family of DNA virus genes that consists of fused portions of unrelated cellular genes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17:213-214.
Lai, F., Orelli, B. J., Till, B. G., Godley, L. A., Fernald, A. A., Pamintuan, L., and LeBeau, M. M. (2000). Molecular characterization of KLHL3, a human homologue of the Drosophila kelch gene. Genomics 66(1):65-75.
Mata, J., and Nurse, P. (1997). Teal and the microtubular cytoskeleton are important for generating global spatial order within the fission yeast cell. Cell 89:939-949.
Nemes, J. P., Benzow, K. A., and Koob, M. D. (2000). The SCA8 transcript is an antisense RNA to a brain-specific transcript encoding a novel actin-binding protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9(10):1543-1551.
Robinson, D. N., and Cooley, L. (1997). Drosophila kelch is an oligometric ring canal actin organizer. J. Cell Biol. 138:799-810.
Soltysik-Espanola, M., Rogers, R. A., Jiang, S., Kim, T. A., Gaedigk, R., White, R. A., Avraham, H., and Avraham, S. (1999). Characterization of mayven, a novel actin-binding protein predominantly expressed in brain. Mol. Biol. Cell 10(7):2361-2375.
Spence, H. J., Johnson, I., Ewart, K., Buchanan, S., Fitzgerald, U., and Ozanne, B. (2000). Krp1, a novel kelch-related protein that is involved in pseudopod elongation in transformed cells. Oncogene 19:1266-1276.
Varkey, J. P., Muhlrad, P. J., Minniti, A. N., Do, B., and Ward, S. (1995). The Caenorhabditis elegans spe-26 gene is necessary to form spermatides and encodes a protein similar to the actin-associated proteins kelch and scruin. Genes Dev. 9:1074-1086.
Xue, F., and Cooley, L. (1993). Kelch encodes a component of intercellular bridges in Drosophila egg chambers. Cell 72:681-693.
Zhao, L., Gregoire, F., and Sul, H. S. (2000). Transient induction of ENC-1, a kelch-related actin-binding protein, is required for adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:16845-16850.
Zollman, S., Godt, D., Gilbert, G., Prive, G. G., Couderc, J., and Laski, F. A. (1994). The BTB domain, found primarily in zinc finger proteins, defines an evolutionarily conserved family that includes several developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91:10717-10721.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhou, Z., Ying, K. et al. Cloning and Characterization of KLHL5, a Novel Human Gene Encoding a Kelch-Related Protein with a BTB Domain. Biochem Genet 39, 227–238 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010203114697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010203114697