Abstract
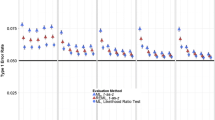
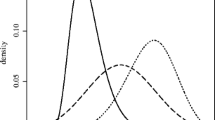
Robust automatic selection techniques for the smoothing parameter of a smoothing spline are introduced. They are based on a robust predictive error criterion and can be viewed as robust versions of C p and cross-validation. They lead to smoothing splines which are stable and reliable in terms of mean squared error over a large spectrum of model distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox D.D. 1983. Asymptotics forM-type smoothing splines. The Annals of Statistics 11: 530-551.
Cunningham J.K., Eubank R.L., and Hsing T. 1991. M-type smoothing splines with auxiliary scale estimation. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 11: 43-51.
de Boor C. 1978. A Practical Guide to Spline. Springer-Verlag, Berlin/New York.
Gasser T., Sroka L., and Jennen-Steinmetz C. 1986. Residual variance and residual pattern in nonlinear regression. Biometrika73: 625-633.
Green P.J. and Silverman B.W. 1994. Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models: A Roughness Penalty Approach. Chapman&Hall, London.
Gu C. 1992a. Cross-validating non-Gaussian data. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 1: 169-179.
Gu C. 1992b. Diagnostics for nonparametric regression models with additive terms. Journal of the American Statistical Association 87: 1051-1058.
Hampel F.R., Ronchetti E.M., Rousseeuw P.J., and Stahel W.A. 1986. Robust Statistics: The Approach Based on Influence Functions. Wiley, New York.
Härdle W. 1990. Applied Nonparametric Regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hastie T.J. and Tibshirani R.J. 1990. Generalized Additive Models. Chapman & Hall, London.
Hoaglin D.C., Mosteller F., and Tukey J.W. (Eds.) 1983. Understanding Robust and Exploratory Data Analysis. Wiley, New York.
Huber P.J. 1979. Robust smoothing. In: Launer R.L. and Wilkinson G.N. (Eds.), Robustness in Statistics. Academic Press, New York/London, pp. 33-48.
Huber P.J. 1981.Robust Statistics. Wiley, New York.
Leung D.H.Y., Marriott F.H.C., and Wu E.K.H. 1993. Bandwidth selection in robust smoothing. Journal of Nonparametric Statistics 2: 333-339.
Ronchetti E., Field C., and Blanchard W. 1997. A robust linear model selection by cross-validation. Journal of the American Statistical Association 92: 1017-1023.
Ronchetti E. and Staudte R.G. 1994. A robust version of Mallows' C p. Journal of the American Statistical Association 89: 550-559.
Utreras F.I. 1981. On computing robust splines and applications. SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 2: 153-163.
Wahba G. 1990. Spline Models for Observational Data. SIAM, Philadelphia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cantoni, E., Ronchetti, E. Resistant selection of the smoothing parameter for smoothing splines. Statistics and Computing 11, 141–146 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008975231866
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008975231866