Abstract
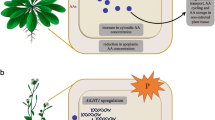
Successful colonisation of plants by pathogens requires efficient utilisation of nutrient resources available in host tissues. Several bacterial and fungal genes are specifically induced during pathogenesis and under nitrogen-limiting conditions in vitro. This suggests that a nitrogen-limiting environment may be one of the cues for disease symptom development during growth of the pathogens in planta. Here we review recent literature on the effect of nitrogen and nitrogen-regulated genes on disease development, caused by phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi. Furthermore, the potential influence of nitrogen-limitation or general nutrient limitation on several in planta-induced bacterial and fungal pathogenicity, virulence and avirulence genes will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios GN (1997) Plant Pathology. Academic Press, San Diego (USA)
Ahman J, Ek B, Rask L and Tunlid A (1996) Sequence analysis and regulation of a gene encoding a cuticle-degrading serine protease from the nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology 142: 1605–1616
Albright LM, Huala E and Ausubel FM (1989) Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genetic 23: 311–336
Anderson M, Pollitt CE, Roberts IS and Eastgate JA (1998) Identification and characterization of the Erwinia amylovora rpoS gene: RpoS is not involved in induction of fireblight disease symptoms. J Bacteriol 24: 6789–6792
Andrianopoulos A, Kourambas S, Sharp JA, Davis MA and Hynes MJ (1998) Characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans nmrA gene involved in nitrogen metabolite repression. J Bacteriol 180: 1973–1977
Balestra GM and Varvaro L (1997) Influence of nitrogen fertilization on the colonization of olive phylloplane by Pseudomonas syringae subsp. savastanoi. In: Rudolph K, Burr TJ, Mansfield JW, Stead D, Vivian A and von Kietzell J (eds) Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars and Related Pathogens (pp 88–92) Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Bender CL, Alarcon-Chaidez F and Gross DC (1999) Pseudomonas syringae phytotoxins: mode of action, regulation, and biosynthesis by peptide and polyketide synthetases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63: 266–292
Bogdanove AJ, Bauer DW and Beer SV (1998) Erwinia amylovora secretes DspE, a pathogenicity factor and functional AvrE homolog, through the Hrp (type III secretion) pathway. J Bacteriol 180: 2244–2247
Bonas U (1994) Hrp genes of phytopathogenic bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 192: 79–98
Bonas U and Van den Ackerveken G (1997) Recognition of bacterial avirulence proteins occurs inside the plant cell: a general phenomenon in resistance to bacterial diseases? Plant J 12: 1–7
Chérif M and Boubaker A (1997) Incidence of cultural practices and biological control agents on Botrytis bunch rot of grapes. 10th Congress of the Mediterranean Phytopathological Union, Montpellier, France, pp 681–687
Christensen T, Hynes MJ and Davis MA (1998) Role of the regulatory gene are A of Aspergillus oryzae in nitrogen metabolism. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 3232–3237
Coleman M, Henricot B, Arnau J and Oliver RP (1997) Starvation-induced genes of the tomato pathogen Cladosporium fulvum are also induced during growth in planta. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 9: 1106–1109
Crawford NM (1995) Nitrate: nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell 7: 859–868
Daly JM (1949) The influence of nitrogen source on the development of stem rust of wheat. Phytopathology 39: 386–394
Dangl JL (1994) The enigmatic avirulence genes of phytopathogenic bacteria. In: Dangl (ed) Bacterial Pathogenesis of Plants and Animals (pp 99–114) Springer-Verlag. Berlin, Germany
De Wit PJGM (1995) Fungal avirulence genes and plant resistance genes: unraveling the molecular basis of gene-for-gene interactions. Adv Bot Res 21: 147–185
Dixon RA and Harrison MJ (1990) Activation, structure and organization of genes involved in microbial defense in plants. Adv Genet 28: 166–234
Durbin RD and Uchytil TF (1984) The role of intercellular fluid and bacterial isolate on the in vivo production of tabtoxin and tabtoxinine-?-lactam. Physiol Plant Pathol 24: 25–31
Ellis CM (1996) Regulation of polyketide gene expression: the isolation and function of nitrogen regulatory factor NRFA from Penicillium urticae. Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, Canada
Froeliger E and Carpenter B (1996) NUT1, a major nitrogen regulatory gene in Magnaporthe grisea, is dispensable for pathogenicity. Mol Gen Genet 25: 647–656
Fu YH and Marzluf GA (1990) nit-2, the major positive-acting nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 5331–5335
Gallegly Jr ME and Walker JC (1949) Plant nutrition in relation to disease development. Am J Bot 36: 613–623
Gaudriault S, Malandrin L, Paulin JP and Barny MA (1997) DspA, an essential pathogenicity factor of Erwinia amylovora showing homology with AvrE of Pseudomonas syringae, is secreted via the Hrp secretion pathway in a DspB-dependent way. Mol Microbiol 26: 1057–1069
Gente S, Poussereau N and Fevre M (1999) Isolation and expression of a nitrogen regulatory gene, nmc, of Penicillium roqueforti. FEMS Microbiol Lett 175: 291–297
Gimeno PO, Ljungdahl PO, Styles CA and Fink GR (1992) Unipolar cell divisions in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae lead to a filamentous growth: regulation by starvation and RAS. Cell 68: 1077–1090
Groisman EA and Ochman H (1994) How Salmonella became a pathogen. Trends Microbiol 2: 289–294
Haas H, Bauer B, Redl B, Stoffler G and Marzluf GA (1995) Molecular cloning and analysis of nre, the major nitrogen regulatory gene of Penicillium chrysogenum. Curr Genet 27: 150–158
Heiskanen P, Taira S and Rhen M (1994) Role of rpoS in the regulation of Salmonella plasmid virulence (spv) genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 123: 125–130
Hensel M, Tang CM, Arst HN and Holden DW (1995) Regulation of fungal extracellular proteases and their role in mammalian pathogenesis. Can J Bot 73 (suppl 1): S1065–S1070
Hensel M, Arst Jr HN, Aufauvre-Brown A and Holden DW (1998) The role of the Aspergillus fumigatus areA gene in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mol Gen Genet 258: 553–557
Horns T and Bonas U (1996) The rpoN gene of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is not required for pathogenicity. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 9: 856–859
Huber DM and Watson RD (1974) Nitrogen form and plant disease. Annu Rev Phytopathol 12: 139–165
Huynh TV, Dahlbeck D and Staskawicz BJ (1989) Bacterial blight of soybean: regulation of a pathogen gene determining host cultivar specificity. Science 245: 1374–1377
Innes RW, Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Bisgrove SR and Staskawicz BJ (1993) Molecular analysis of avirulence gene avrRpt2 and identification of a putative regulatory sequence common to all known Pseudomonas syringae avirulence genes. J Bacteriol 175: 4859–4869
Iriarte M, Stainier I and Cornelis GR (1995) The rpoS gene from Yersinia enterocolitica and its influence on expression of virulence factors. Infect Immun 63: 1840–1847
Joosten MHAJ and De Wit PJGM (1999) The tomato-Cladosporium fulvum interaction: a versatile experimental system to study plant-pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37: 335–367
Keen NT, Tamaki S, Kobayashi D, Gerhold D, Stayton M, Shen H, Gold S, Lorang J, Thordal-Christensen H, Dahlbeck D and Staskawicz B (1990) Bacteria expressing avirulence gene avrD produce a specific elicitor of the soybean hypersensitive reaction. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 3: 112–121
Kershaw MJ and Talbot NJ (1998) Hydrophobins and repellents: proteins with fundamental roles in fungal morphogenesis. Fungal Genet Biol 23: 18–33
Knoop V, Staskawicz B and Bonas U (1991) The expression of the avirulence gene avrBs3 from Xhanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is not under control of hrp genes and is independent of plant factors. J Bacteriol 173: 7142–7150
Lam HM, Coschigano K, Oliveira IC, Melo-Oliveira R and Coruzzi G (1996) The molecular-genetics of nitrogen assimilation into amino acids in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47: 569–593
Lapwood DH and Dyson PW (1966) An effect of nitrogen on the formation of potato tubers and the incidence of common scab (Streptomyces scabies). Plant Pathol 15: 9–14
Last FT (1953) Some effects of temperature and nitrogen supply on wheat powdery mildew. Ann Appl Biol 40: 312–322
Lau GW and Hamer JE (1996) Regulatory genes controlling mpg1 expression and pathogenicity in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 8: 771–781
Lea PJ (1992) Ammonia assimilation in higher plants. In: Mengel K and Pilbeam DJ (eds) Nitrogen Metabolism of Plants (pp 153–186) Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Lindgren PB (1997) The role of hrp genes during plant-bacterial interactions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 35: 129–152
Long SR and Staskawicz BJ (1993) Prokaryotic plant parasites. Cell 73: 921–935
Lorang JM and Keen NT (1995) Characterization of avrE from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: a hrp-linked avirulence locus consisting of at least two transcriptional units Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8: 49–57
Lucas JA (1998) Plant Pathology and Plant Pathogens. Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK
Magasanik B (1996) Regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. In: Lin ECC and Lynch AS (eds) Regulation of Nitrogen Utilization (pp 1344–1356), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA
Marzluf GA (1997) Genetic regulation of nitrogen metabolism in the fungi. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61: 17–32
McCabe AP, Vanhanen S, Gelpke MDS, Van de Vondervoort PJI, Arst HN and Visser J (1998) Identification, cloning and sequence of the Aspergillus niger areAwide domain regulatory gene controlling nitrogen utilisation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1396: 163–168
McElhaney R, Alvarez AM and Kado CI (1998) Nitrogen limits Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris invasion of the host xylem. Physiol Mol Plant Path 52: 15–24
McGuire RG, Jones JB, Stanley CD and Csizinsky AA (1991) Epiphytic populations of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria and bacterial spot of tomato as influenced by nitrogen and potassium fertilization. Phytopathology 81: 656–660
McNew GL and Spencer EL (1939) Effect of nitrogen supply of sweet corn on the wilt bacterium. Phytopathology 29: 1051–1067
Mengaud J, Dramsi S, Gouin E, Vazquez-Boland JA, Milon G and Cossart P (1991) Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol 5: 2273–2283
Merrick MJ and Edwards RA (1995) Nitrogen control in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59: 604–622
Midland SL, Keen NT, Sims JJ, Midland MM, Stayton MM, Burton V, Smith MJ, Mazzola EP, Graham KJ and Clardy J (1993) The structures of syringolides 1 and 2, novel Cglycosidic elicitors from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Org Chem 58: 2940–2945
Mitchell RE (1976) Isolation and structure of chlorosis inducing toxin of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. Phytochemistry 15: 1941–1947
Mitchell RE and Bielski RL (1977) Involvement of phaseolotoxin in halo blight of beans: transport and conversion to functional toxin. Plant Physiol 60: 723–729
Moore RF, Niemezura WP, Kwok OCH and Patil SS (1984) Inhibitors of ornithine carbamoyltransferase from P. syringae pv. phaseolicola. Revised structure of phaseolotoxin. Tetrahedron Lett 25: 3931–3934
Mylona P, Pawlowski K and Bisseling T (1995) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Plant Cell 7: 869–885
Nickerson CA and Curtiss 3rd R (1997) Role of sigma factor RpoS in initial stages of Salmonella typhimurium infection. Infect Immun 65: 1814–1823
O'Neal CR, Gabriel WM, Turk AK, Libby SJ, Fang FC and Spector MP (1994) RpoS is necessary for both the positive and negative regulation of starvation survival genes during 505 phosphate, carbon, and nitrogen starvation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 176: 4610–4616
Petersen UM, Kadalayil L, Rehorn KP, Hoshizaki DK, Reuter R and Engström Y (1999) Serpent regulates Drosophila immunity genes in the larval fat body through an essential GATA motif. EMBO J 18: 4013–4022
Pérez-García A, Cánovas FM, Gallardo F, Hirel B and De Vicente A (1995) Differential expression of glutamine synthetase isoforms in tomato detached leaflets infected with Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8: 96–103
Pérez-García A, Pereira S, Pissarra J, García Gutiérrez A, Cazorla FM, Salema R, De Vicente A and Cánovas FM (1998) Cytosolic localization in tomato mesophyll cells of a novel glutamine synthtase induced in response to bacterial infection or phosphinothricin treatment. Planta 206: 426–434
Punt PJ, Strauss J, Smit R, Kinghorn JR, Van den Hondel CAMJJ and Scazzocchio C (1995) The intergenic region between divergently transcribed niiA and niaD genes of Aspergillus nidulans contains multiple NirA binding sites which act bidirectionally. Mol Cell Biol 15: 5688–5699
Rhame LG, Mindrinos MN and Panopoulos NJ (1992) Plant and environmental sensory signals control the expression of hrp genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolica. J Bact 174: 3499–3507
Rossier O, Wengelnik K, Hahn K and Bonas U (1999) The Xanthomonas Hrp type III system secretes proteins from plant and mammalian bacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 16: 9368–9373
Scazzocchio C (2000) The fungal GATA factors. Curr Opion Microbiol 3: 126–131
Screen S, Bailey A, Charnley K, Cooper R and Clarkson J (1998) Isolation of a nitrogen response regulator gene (nrr1) from Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene 221: 17–24
Segers GC, Hamada W, Oliver RP and Spanu PD (1999) Isolation and characterisation of five different hydrophobin-encoding cDNAs from the fungal tomato pathogen Cladosporium fulvum. Mol Gen Genet 261: 644–652
Shen H and Keen NT (1993) Characterization of the promoter of avirulence gene D from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Bacteriol 175: 5916–5924
Shen H, Gold SE, Tamaki SJ and Keen NT (1992) Construction of a Tn7–lux system for gene expression studies in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 122: 27–34
Showalter AM (1993) Structure and function of plant cell wall proteins. Plant Cell 5: 9–23
Skromme I, Sanchez O and Aguirre J (1995) Starvation stress modulates the expression of the Aspergillus nidulans brlA regulatory gene. Microbiology 141: 21–28
Smithson SL, Paterson IC, Bailey AM, Screen SE, Hunt BA, Cobb BD, Cooper RM, Charnley AK and Clarkson JM (1995) Cloning and characterisation of a cuticle-degrading protease from the insect pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene 166: 161–165
Snoeijers SS, Vossen P, Goosen T, Van den Broek HWJ and De Wit PJGM (1999) Transcription of the avirulence gene Avr9 of the fungal tomato pathogen Cladosporium fulvum is regulated by a GATA-type transcription factor in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 261: 653–659
Spanu P and Whiteford J (2000) Fungal raincoats as dispersal aids. Abstract book (p 140), 5th European Conference on Fungal Genetics, Arcachon, France
Spector MP (1998) The starvation-stress response (SSR) of Salmonella. Adv Microb Physiol 40: 233–279
Stephenson SA, Green JR, Manners JM and Maclean DJ (1997) Cloning and characterisation of glutamine synthetase from Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and demonstration of elevated expression during pathogenesis on Stylosanthes guianensis. Curr Genet 31: 447–54
Stephenson SA, Maclean DJ and Manners JM (1998) Disruption of the essential pathogenicity gene cgDN3 of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides results in a hypersensitive response in the host Stylosanthes guianensis. 7th International Congress of Plant Pathology, Edinburgh, Scotland, Abstract 1.8.6S
St Leger RJ (1995) The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogenesis of insects. Can J Bot 73: S1119–S1125
St Leger RJ, Frank DC, Roberts DW and Staples RC (1992) Molecular cloning and regulatory analysis of cuticle-degrading-protease structural gene from the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Eur J Biochem 204: 991–1001
Talbot NJ (1995) Having a blast: exploring the pathogenicity of Magnaporthe grisea. Trends Microbiol 3: 9–16
Talbot NJ, Ebbole DJ and Hamer JE (1993) Identification and characterization of MPG1, a gene involved in pathogenicity from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 5: 1575–1590
Talbot NJ, McCafferty HRK, Ma M, Moore K and Hamer JE (1997) Nitrogen starvation of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea may act as an environmental cue for disease symptom expression. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 50: 179–195
Teng, PS (1994) The epidemiological basis for blast management. In: Ziegler RS, Leong SA and Teng PS (eds) The Rice Blast Disease (pp 409–433) CAB International, Oxford, UK
Tomsett AB, Dunn-Coleman NS and Garrett RH (1981) The regulation of nitrate assimilation in Neurospora crassa: the isolation and genetic analysis of nmr-1 mutants. Mol Gen Genet 182: 229–233
Tudzynski B, Homann V, Feng B and Marzluf GA (1999) Isolation, characterization and disruption of the areA nitrogen regulatory gene of Gibberella fujikuroi. Mol Gen Genet 261: 106–114
Turner JG and Debbage JM (1982) Tabtoxin-induced symptoms are associated with accumulation of ammonia formed during photorespiration. Physiol Plant Pathol 20: 223–233
Valent B and Chumly FG (1991) Molecular and genetic analysis of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Annu Rev Phytopathol 29: 443–467
Van den Ackerveken GFJM, Dunn RM, Cozijnsen TJ, Vossen P, Van den Broek HWJ and De Wit PJGM (1994) Nitrogen limitation induces expression of the avirulence gene Avr9 in the tomato pathogen Cladosporium fulvum. Mol Gen Genet 243: 277–285
Van den Ackerveken GFJM, Van Kan JAL and De Wit PJGM (1992) Molecular analysis of the avirulence gene Avr9 of Cladosporium fulvum fully supports the gene-for-gene hypothesis. The Plant Journal 2: 359–366
Van Kan JAL, Van den Ackerveken, GFJM and De Wit PJGM (1991) Cloning and characterisation of cDNA of avirulence gene Avr9 of the fungal tomato pathogen Cladosporium fulvum, causal agent of tomato leaf mold. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 4: 52–59
Völksch B and Weingart H (1998) Toxin production by pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae and their antagonistic activities against epiphytic microorganisms. J Basic Microbiol 2: 135–145
Wei ZM, Sneath BJ and Beer S (1992) Expression of Erwinia amylovora hrp genes in response to environmental stimuli. J Bacteriol 174: 1875–1882
Wei YD and Mortensen CN (1992) Bioassay of toxins as a diagnostic method for Pseudomonas syringae pathovars. J Phytopathol 134: 110–116
Wessels JG (1997) Hydrophobins: proteins that change the nature of the fungal surface. Adv Microb Physiol 38: 1–45
Wilhelm S (1950) The inoculum potential of Verticillum alboatrum as affected by soil amendments. Phytopathology 40: 970–974
Williams FJ (1965) Antecedent nitrogen sources affecting virulence of Colletotrichum phomoides. Phytopathology 55: 333–335
Xiao XD and Marzluf GA (1993) Amino-acid substitutions in the zinc finger of NIT2, the nitrogen regulatory protein of Neurospora crassa, alter promoter element recognition. Curr Genet 24: 212–218
Xiao XD, Fu YH and Marzluf GA (1995) The negative-acting NMR regulatory protein of Neurospora crassa binds to and inhibits the DNA-binding activity of the positive-acting nitrogen regulatory protein NIT2. Biochemistry 34: 8861–8868
Xiao Y and Hutcheson SW (1994) A single promoter sequence recognized by a newly identified alternate sigma factor directs expression of pathogenicity and host range determinants in Pseudomonas syringae. J Bacteriol 10: 3089–3091
Xiao Y, Heu S, Yi J, Lu Y and Hutcheson SW (1994) Identification of a putative alternate sigma factor and characterization of a multicomponent regulatory cascade controlling the expression of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Pss61 hrp and hrmA genes. J Bacteriol 4: 1025–1036
Young JL, Jarai G, Fu YH and Marzluf GA (1990) Nucleotide sequence and analysis of nmr, a negative-acting regulatory gene in the nitrogen circuit of Neurospora crassa. Mol Gen Genet 222: 120–128
Yucel I, Xiao YX and Hutcheson SW (1989) Influence of Pseudomonas syringae culture conditions on initiation of the hypersensitive response of culture tobacco cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 7: 1724–1729
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snoeijers, S.S., Pérez-García, A., Joosten, M.H. et al. The Effect of Nitrogen on Disease Development and Gene Expression in Bacterial and Fungal Plant Pathogens. European Journal of Plant Pathology 106, 493–506 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008720704105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008720704105