Abstract
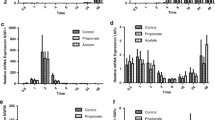
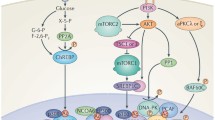
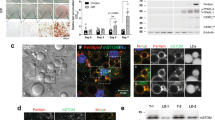
A wide number of adipocyte genes are regulated by exogenous polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) through the actions of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor. Such genes include the adipocyte lipid-binding protein (ALBP or aP2) which plays a central role in facilitating the trafficking of fatty acids within adipocytes. Work from a number of laboratories has suggested the key elements of the lipid signal transduction pathway include: (1) the transport of exogenous PUFAs across the plasma membrane, (2) metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids to second messengers including 15-deoxy Δ12,14 prostaglandin J2 (15dPGJ2), (3) trafficking of 15dPGJ2 and other second messengers from the smooth ER to the nucleus for association with peroxisome proliferator activated receptorγ (PPARγ), and (4) dimerization of PPARγ with retinoid X receptor (RXR) permitting regulation of transcription via association with any of several nuclear co-activators or repressors. In addition to the aP2 gene being a target of activation by fatty acids, at the protein level ALBP/aP2 plays a role in trafficking of fatty acids and/or their metabolises. We report here that in a heterologous system using CV-1 cells transiently transfected with PPARγ2, co-expression of ALBP/aP2 enhances the PPAR-dependent activation of gene transcription. These results suggest that ALBP/aP2 functions as a positive factor in fatty acid signalling by directly targetting and delivering fatty acids metabolises to the lipid signal transduction pathway
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernlohr DA, Simpson MA: Adipose tissue and lipid metabolism. In: D.E. Vance, J.E. Vance (eds). Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes. Elsevier Science, The Netherlands, 1996, pp 257–281
Bernlohr DA, Simpson MA, Hertzel AV, Banaszak LJ: Intracellular lipid-binding proteins and their genes. Annu Rev Nutr 17: 277–303, 1997
Keller H, Dreyer C, Medin J, Mahfoudi A, Ozato K, Wahli W: Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90: 2160–2164, 1993
Clarke SD, Jump DB: Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of gene transcription. Annu Rev Nutr 14: 83–98, 1994
Lemberger T, Desvergne B, Wahli W: Peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptors: A nuclear receptor signaling pathway in lipid physiology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12: 335–363, 1996
Forman BM, Tontonoz P, Chen J, Brun RP, Spiegelman BM, Evans RM: 15-Deoxy-delta 12, 14-prostaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR gamma. Cell 83: 803–812, 1995
Kliewer SA, Lenhard JM, Willson TM, Patel I, Morris DC, Lehmann JM: A prostaglandin J2 metabolise binds peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell 83: 813–819, 1995
Issemann I, Green S: Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature 347: 645–650, 1990
Mandrup S, Lane MD: Regulating Adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 272: 5367–5370, 1997
Kliewer SA, Forman BM, Blumberg B, Ong ES, Borgmeyer U: Differential expression and activation of a family of murine peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91: 7355–7359, 1994
Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Noonan DJ, Heyman RA, Evans RM: Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature 358: 771–774, 1992
DiRenzo J, Soderstrom M, Kurokawa R, Ogliastro M-H, Ricote M, Ingrey S, Horlein A, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors. Mol Cell Biol 17: 2166–2176, 1997
Hörlein AJ, Näär AM, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Gloss B, Kurokawa R, Ryan A, Kamei Y, Söderström M, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG: Ligandindependent repression by the thyroid hormone receptor mediated by a nuclear receptor co-repressor. Nature 377: 397–404, 1995
Yang X-J, Ogryzko VV, Nishikawa J-i, Howard BH, Nakatani Y: A p300/CBP-associated factor that competes with the adenoviral oncoprotein ETA. Nature 382: 319–324, 1996
Nagy L, Kao H-Y, Chakravarti D, Lin RJ, Hassig CA, Ayer DE, Schreiber SL, Evans RM: Nuclear receptor repression mediated by a complex containing SMRT, mSin3A, and histone deacetylase. Cell 89: 373–380, 1997
Spencer TE, Jenster G, Burcin MM, Allis CD, Zhou JX, Mizzen CA, Mckenna NJ, Onate SA, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, Omalley BW: Steroid receptor coactivator-1 is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 389: 194–198, 1997
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Devine J, Beale EG, Spiegelman BM: PPARγ2 regulates adipose expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol 15: 351–357, 1995
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM: mPPAR gamma 2: Tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev 8: 1224–1234, 1994
Amri E-Z, Bertrand B, Ailhaud G, Grimaldi P: Regulation of adipose cell differentiation. I. Fatty acids are inducers of the aP2 gene expression. J Lipid Res 32: 1449–1456, 1991
Grimaldi PA, Knobel SM, Whitesell RR, Abumrad NA: Induction of aP2 gene expression by nonmetabolized long-chain fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89: 10930–10934, 1992
Simpson MA, LiCata V, Ribarik-Coe R, Bernlohr DA: Biochemical and Biophysical Analysis of the Intracellular Lipid Binding Proteins of Adipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. (in press) 1997
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 1982
Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA: An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem 270: 12953–12956, 1995
Ross SR, Graves RA, Greenstein A, Platt KA, Shyu HL: A fat-specific enhancer is the primary determinant of gene expression for adipocyte P2 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 87: 9590–9594, 1990
Kletzien RF, Foellmi LA, Harris PKW, Wyse BM, Clarke SD: Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein: Regulation of gene expression in vivo and in vitro by an insulin-sensitizing agent. Mol Pharm 42: 558–562, 1992
Harris PK, Kletzien RF: Localization of a pioglitazone response element in the adipocyte fatty acid binding protein gene. Mol Pharm 45: 439–445, 1994
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM: Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPARγ2, a lipid activated transcription factor. Cell 79: 1147–1156, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel Hertzel, A., Bernlohr, D.A. Regulation of adipocyte gene expression by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Mol Cell Biochem 188, 33–39 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006883303023
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006883303023