Abstract
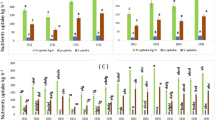
The close chemical similarity of S and Se allow for antagonistic behavior between the two elements. To determine variation for Se accumulation within onions, sixteen short-day cultivars were grown under high level (2.0 mg Na2SeO4 per litre) and no Se treatments. Selenium accumulation in bulb tissues was cultivar dependent, ranging from 60 to 113 µg Se per g dry wt. High Se fertility enhanced bulb S accumulation. Pungency was reduced in some cultivars grown under Se fertility when compared to the no Se treatment indicating that although S uptake was enhanced, S metabolism in the flavour precursor biosynthetic pathway was affected. The existing variability in onion Se uptake and accumulation have important implications for Se intake in mammalian diets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, T.A. & A. Shrift, 1982. Selenium: toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Biol Rev 57: 59–84.
Combs, G.F. Jr. & S.B. Combs, 1986. The role of selenium in nutrition. Academic Press, Orlando, Fla.
Freeman, G.G. & N. Mossadeghi, 1970. Effect of sulphate nutrition on flavour components of onion (Allium cepa). J Sci Food Agr 21(2): 610–615.
Gutenmann, W.H. & D.J. Lisk, 1996. Increasing selenium in field-grown onions by planting in peat moss pots containing fly ash. Chemosphere 32(9): 1851–1853.
Hoagland, D.R. & D.I. Arnon, 1950. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agr Expt Sta Circ 347.
Ip, C. & D.J. Lisk, 1994. Enrichment of selenium in allium vegetables for cancer prevention. Carcinogenesis 15(9): 1881–1885.
Ip, C., D.J. Lisk & G.S. Stoewsand, 1992. Mammary cancer prevention by regular garlic and selenium-enriched garlic. Nutr Cancer 17(3): 279–286.
Jones, H.A. & L.K. Mann, 1963. Onions and their allies. Botany, cultivation and utilization. Interscience Publ., NY.
Kopsell, D.A. & W.M. Randle, 1997. Selenate concentration affects selenium and sulfur uptake and accumulation by ‘Granex 33’ onions. J Am Soc Hort Sci 122: in press.
Landcaster, J.E. & M.J. Boland, 1990. Flavor biochemistry. In: H.D. Rabinowitch & J.L. Brewster (Eds.), Onions and Allied Crops, Vol. 3, pp. 33–72. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla.
Leggett, J.E. & E. Epstein, 1956. Kinetics of sulfate absorption by barley roots. Plant Physiol 31: 222–226.
Levander, O.A., 1991. Scientific rationale for the 1989 recommended dietary allowance for selenium. J Am Dietetic Assoc 91: 1572.
Mikkelsen, R.L., A.L. Page & F.T. Bingham, 1989. Factors affecting selenium accumulation by agricultural crops. In: L.W. Jacobs (Ed.), Selenium in Agriculture and the Environment, pp. 65–94. American Society of Agronomy, Inc and Soil Science Society of America, Inc, Madison, Wis.
Milchunas, D.G., W.K. Lauenroth & J.L. Dodd, 1983. The interaction of atmospheric and soil sulfur on the sulfur and selenium concentration of range plants. Plant Soil 72: 117–125.
Ng, B.H. & J.W. Anderson, 1978. Synthesis of selenocysteine by cysteine synthase from selenium accumulator and non-accumulator plants. Phytochem 17: 2069–2074.
Ng, B.H. & J.W. Anderson, 1979. Light-dependent incorporation of selenite and sulphite into selenocysteine and cysteine by isolated pea chloroplast. Phytochem 18: 573–580.
Randle, W.M., 1992. Sulfur nutrition affects nonstructural watersoluble carbohydrates in onion germplasm. HortSci 27(1): 52–55.
Randle, W.M. & M.L. Bussard, 1993a. Pungency and sugars of short-day onions as affected by sulfur nutrition. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 118(6): 766–770.
Randle, W.M. & M.L. Bussard, 1993b. Streamlining onion pungency analyses. HortSci 28(1): 60.
Randle, W.M., M.L. Bussard & D.F. Warnock, 1993. Ontogeny and sulfur fertility affect leaf sulfur in short-day onions. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 118(6): 762–765.
Randle, W.M., E.B. Block, M.H. Littlejohn, D. Putman & M.L. Bussard, 1994. Onion (Allium cepa L.) thiosulfinates respond to increasing sulfur fertility. J Agric Food Chem 42: 2085–2088.
Rennenberg, H., 1984. The fate of excess sulfur in higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 35: 121–153.
Schrauzer, G.N. & J. Sacher, 1994. Selenium in the maintenance and therapy of HIV-infected patients. Chem Biol Interactions 91: 199–205.
Shane, B.S., C.B. Littman, L.A. Essick, W.H. Gutenmann, G.J. Doss & D.J. Lisk, 1988. Uptake of selenium and mutagens by vegetables grown in fly ash containing greenhouse media. J Agr Food Chem 36: 328–333.
Vandenbrandt, P.A., R.A. Goldbohm, P. Vantveer, P. Bode, E. Dorant, R.J.J. Hermus & F. Sturmans, 1993. A prospective cohort study on selenium status and the risk of lung-cancer. Cancer Res 53: 4860–4865.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopsell, D.a., Randle, W.M. Short-day onion cultivars differ in bulb selenium and sulfur accumulation which can affect bulb pungency. Euphytica 96, 385–390 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003065618315
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003065618315