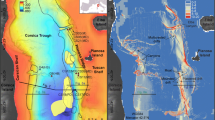
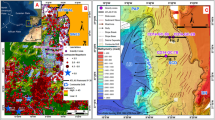
Abstract
Geotechnical characteristics of contouritic deposition often lead to preconditioning slope instabilities and failures along glaciated and formerly glaciated continental margins. However, internal depositional geometry is also an important factor in triggering instabilities. This work highlights the importance of the tectonic and oceanographic evolution of the Northwestern (NW) Svalbard margin in determining the buildup and the internal structure of contourite drifts and the subsequent type of slope instability. The analysis of seismic reflection data reveals that the presence of two contourite drifts on the flank of an active spreading ridge in the Fram Strait—NW Svalbard margin—in an area of extensive slope instability had a major impact on the evolution of slope failure. The presence of a slope sheeted drift (or plastered drift) led to the development of rotational/translational mass movement at water depth < 2500 ms, whereas at water depth > 2500 ms the presence of sediment waves facilitated the formation of planes of shear that led to internal deformation of the lower slope through a process of slump/creep. The well-documented high seismicity of the area might have provided the necessary energy to trigger the slope instability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stow D, Hunter S, Wilkinson D, Hernández-Molina F (2008) The nature of contourite deposition. Dev Sedimentol 60:143–156
Stow D, Lovell J (1979) Contourites: their recognition in modern and ancient sediments. Earth Sci Rev 14(3):251–291
Faugères J-C, Stow D (2008) Contourite drifts: nature, evolution and controls. Dev Sedimentol 60:257–288
Eiken O, Hinz K (1993) Contourites in the Fram Strait. Sed Geol 82(1):15–32
Birgel D, Hass HC (2004) Oceanic and atmospheric variations during the last deglaciation in the Fram Strait (Arctic Ocean): a coupled high-resolution organic-geochemical and sedimentological study. Quatern Sci Rev 23(1):29–47
García M, Hernández-Molina FJ, Alonso B, Vázquez JT, Ercilla G, Llave E, Casas D (2016) Erosive sub-circular depressions on the Guadalquivir Bank (Gulf of Cadiz): interaction between bottom current, mass-wasting and tectonic processes. Mar Geol 378:5–19
Faugères J-C, Stow DA, Imbert P, Viana A (1999) Seismic features diagnostic of contourite drifts. Mar Geol 162(1):1–38
Esentia I, Stow D, Smillie Z (2018) Contourite drifts and associated bedforms. In: Micallef A, Krastel S, Savini A (eds) Submarine geomorphology. Springer, Cham, pp 301–333
King EL, Bøe R, Bellec VK, Rise L, Skarðhamar J, Ferré B, Dolan MF (2014) Contour current driven continental slope-situated sandwaves with effects from secondary current processes on the Barents Sea margin offshore Norway. Mar Geol 353:108–127
Flood RD (1988) A lee wave model for deep-sea mudwave activity. Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Pap 35(6):973–983
Bulat J, Long D (2001) Images of the seabed in the Faroe–Shetland channel from commercial 3D seismic data. Mar Geophys Res 22(5):345–367
Stow D, Faugères J-C (2008) Contourite facies and the facies model. Dev Sedimentol 60:223–256
Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A (2008) Contourites, vol 60. Elsevier, New York
Stow DA, Faugères J-C, Howe JA, Pudsey CJ, Viana AR (2002) Bottom currents, contourites and deep-sea sediment drifts: current state-of-the-art. Geol Soc Lond Mem 22(1):7–20
Bryn P, Berg K, Stoker M, Solheim A (2005) Contouritic deposition and its relevance for the mass wasting record along the Mid-Norwegian Margin. Mar Pet Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.10.012
Solheim A, Berg K, Forsberg C, Bryn P (2005) The Storegga Slide Complex: repetitive large scale sliding with similar cause and development. Mar Pet Geol 22(1):97–107
Laberg J, Vorren T (2000) The Trænadjupet slide, offshore Norway—morphology, evacuation and triggering mechanisms. Mar Geol 171(2000):95–114
Laberg J, Baeten NJ, Vanneste M, Forsberg CF, Forwick M, Haflidason H (2016) Sediment failure affecting muddy contourites on the continental slope Offshore Northern Norway: lessons learned and some outstanding issues. In: Submarine mass movements and their consequences. Springer, pp 281–289
Laberg J, Camerlenghi A (2008) The significance of contourites for submarine slope stability. Dev Sedimentol 60:537–556
Vanneste M, Sultan N, Garziglia S, Forsberg CF, L’Heureux J-S (2014) Seafloor instabilities and sediment deformation processes: the need for integrated, multi-disciplinary investigations. Mar Geol 352:183–214
Miramontes E, Cattaneo A, Jouet G, Garziglia S, Thereau E, Gaillot A, Roubi A, Rovere M (2014) The Pianosa Contourite Depositional System (Corsica Trough, North Tyrrhenian Sea): stratigraphic evolution and possible role in slope instability. In: Van Rooij D, Rüggeberg A (eds) 2014. Book of abstracts. 2nd deep‐water circulation congress: the contourite log‐book. Ghent, Belgium, 10–12 Sept 2014, vol 69. VLIZ Special Publication, pp 15–16
Cattaneo A, Jouet G, Charrier S, Théreau E, Riboulot V (2014) Submarine landslides and contourite drifts along the Pianosa Ridge (Corsica Trough, Mediterranean Sea). In: Krastel S, Behrmann JH, Völker D, Stipp M, Berndt C, Urgeles R, Chaytor J, Huhn K, Strasser M, Harbitz CB (eds) Submarine mass movements and their consequences. Springer, Berlin, pp 435–445
Elger J, Berndt C, Krastel S, Piper DJ, Gross F, Geissler WH (2016) Chronology of the Fram Slide Complex offshore NW Svalbard and its implications for local and regional slope stability. Mar Geol 393:141–155
Lee HJ, Locat J, Desgagnés P, Parsons JD, McAdoo BG, Orange DL, Puig P, Wong FL, Dartnell P, Boulanger E (2007) Chapter 5: Submarine mass movements on continental margins. In: Nittrouer CA, Austin JA, Field ME, Kravitz JH, Syvitski JPM, Wiberg PL (eds) Continental-margin sedimentation: from sediment transport to sequence stratigraphy, vol 37. IAS special publication. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Oxford, pp 213–274
Mienert J, Vanneste M, Bünz S, Andreassen K, Haflidason H, Sejrup HP (2005) Ocean warming and gas hydrate stability on the mid-Norwegian margin at the Storegga Slide. Mar Pet Geol 22(1):233–244
Sloan ED (1991) Natural gas hydrates. J Pet Technol 43(12):1414–1417
Shipley T, Houston H, Buffler R (1979) Widespread occurrence of possible gas-hydrate horizons from continental slopes as identified on seismic reflection profiles. In: Offshore technology conference. Offshore Technology Conference (1979)
Nimblett J, Ruppel C (2003) Permeability evolution during the formation of gas hydrates in marine sediments. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB001650
Holbrook WS, Hoskins H, Wood WT, Stephen RA, Lizarralde D (1996) Methane hydrate and free gas on the Blake Ridge from vertical seismic profiling. Science 273(5283):1840
Mienert J, Bünz S (2016) Bottom simulating seismic reflectors (BSR). In: Harff J (ed) Encyclopedia of Marine Geosciences. Springer, Berlin, pp 62–67
Geissler WH, Pulm PV, Jokat W, Gebhardt AC (2014) Indications for the occurrence of gas hydrates in the Fram Strait from heat flow and multichannel seismic reflection data. J Geol Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/582424
Aagaard K, Foldvik A, Hillman SR (1987) The West Spitsbergen current: disposition and water mass transformation. J Geophys Res Oceans 92(C4):3778–3784. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC092iC04p03778
Jónsson S, Foldvik A, Aagaard K (1992) The structure and atmospheric forcing of the mesoscale velocity field in Fram Strait. J Geophys Res Oceans 97(C8):12585–12600
Bauerfeind E, Beszczynska-Möller A, von Appen W-J, Soltwedel T, Sablotny B, Lochthofen N (2015) Physical oceanography and current meter data from mooring FEVI9 at Hausgarten South. Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research, PANGAEA, Bremerhaven. https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.845603
Rebesco M, Wåhlin A, Laberg JS, Schauer U, Beszczynska-Möller A, Lucchi RG, Noormets R, Accettella D, Zarayskaya Y, Diviacco P (2013) Quaternary contourite drifts of the Western Spitsbergen margin. Deep Sea Res Part I 79:156–168
Beszczynska-Möller A, Fahrbach E, Schauer U, Hansen E (2012) Variability in Atlantic water temperature and transport at the entrance to the Arctic Ocean, 1997–2010. ICES J Mar Sci 69:852–863. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fss056
Forwick M, Laberg JS, Hass HC, Osti G (2015) The Kongsfjorden channel system offshore NW Svalbard: downslope sedimentary processes in a contour-current-dominated setting. Arktos 1(1):1–16
Quadfasel D, Rudels B, Kurz K (1988) Outflow of dense water from a Svalbard fjord into the Fram Strait. Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Pap 35(7):1143–1150
Schauer U, Fahrbach E (1999) A dense bottom water plume in the western Barents Sea: downstream modification and interannual variability. Deep Sea Res Part I 46(12):2095–2108
Skogseth R, Haugan P, Jakobsson M (2005) Watermass transformations in Storfjorden. Cont Shelf Res 25(5–6):667–695
Honjo S, Manganini SJ, Wefer G (1988) Annual particle flux and a winter outburst of sedimentation in the northern Norwegian Sea. Deep Sea Res Part A Oceanogr Res Pap 35(8):1223–1234
Jakobsson M, Backman J, Rudels B, Nycander J, Frank M, Mayer L, Jokat W, Sangiorgi F, O’Regan M, Brinkhuis H (2007) The early Miocene onset of a ventilated circulation regime in the Arctic Ocean. Nature 447(7147):986–990
Geissler W, Jokat W, Brekke H (2011) The Yermak Plateau in the Arctic Ocean in the light of reflection seismic data-implication for its tectonic and sedimentary evolution. Geophys J Int 187(3):1334–1362
Myhre AM, Thiede J, Firth JV et al (1995) Proc. ODP, Init Repts [CD-ROM], 151. Available: Ocean Drilling Program, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX
Mattingsdal R, Knies J, Andreassen K, Fabian K, Husum K, Grøsfjeld K, De Schepper S (2014) A new 6 Myr stratigraphic framework for the Atlantic-Arctic Gateway. Quat Sci Rev 92:170–178
Knies J, Daszinnies M, Plaza-Faverola A, Chand S, Sylta Ø, Bünz S, Johnson JE, Mattingsdal R, Mienert J (2018) Modelling persistent methane seepage offshore western Svalbard since early Pleistocene. Mar Pet Geol 91:800–811
Petersen CJ, Bünz S, Hustoft S, Mienert J, Klaeschen D (2010) High-resolution P-Cable 3D seismic imaging of gas chimney structures in gas hydrated sediments of an Arctic sediment drift. Mar Pet Geol 27(9):1981–1994
Knies J, Matthiessen J, Vogt C, Laberg JS, Hjelstuen BO, Smelror M, Larsen E, Andreassen K, Eidvin T, Vorren TO (2009) The Plio-Pleistocene glaciation of the Barents Sea-Svalbard region: a new model based on revised chronostratigraphy. Quat Sci Rev 28(9–10):812–829
Lu H, Fulthorpe CS, Mann P (2003) Three-dimensional architecture of shelf-building sediment drifts in the offshore Canterbury Basin, New Zealand. Mar Geol 193(1):19–47
Rodriguez M, Bourget J, Chamot-Rooke N, Huchon P, Fournier M, Delescluse M, Zaragosi S (2016) The Sawqirah contourite drift system in the Arabian Sea (NW Indian Ocean): a case study of interactions between margin reactivation and contouritic processes. Mar Geol 381:1–16
Osti G, Franek P, Forwick M, Laberg JS (2017) Controlling factors for slope instability in a seismically active region: the NW-Svalbard continental margin. Mar Geol 390:131–146
Waghorn KA, Bünz S, Plaza-Faverola A, Johnson JE (2018) 3D seismic investigation of a gas hydrate and fluid flow system on an active mid-ocean ridge; Svyatogor ridge, Fram Strait. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 19:2328–2341
Hornbach MJ, Saffer DM, Holbrook WS (2004) Critically pressured free-gas reservoirs below gas-hydrate provinces. Nature 427(6970):142
Plaza-Faverola A, Westbrook GK, Ker S, Exley RJ, Gailler A, Minshull TA, Broto K (2010) Evidence from three-dimensional seismic tomography for a substantial accumulation of gas hydrate in a fluid-escape chimney in the Nyegga pockmark field, offshore Norway. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB007078
Henrich R, Baumann K-H (1994) Evolution of the Norwegian current and the Scandinavian ice sheets during the past 2.6 my: evidence from ODP leg 104 biogenic carbonate and terrigenous records. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 108(1):75–94
Rebesco M, Stow D (2001) Seismic expression of contourites and related deposits: a preface. Mar Geophys Res 22(5–6):303–308
Stevenson A (1991) Miller (Sheet 61 °N–02° W), Quaternary Geology (1: 250,000 Offshore Map Series). British Geological Survey
Hill P, Moran K, Blasco S (1982) Creep deformation of slope sediments in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Geomar Lett 2(3–4):163
Geissler WH, Gebhardt AC, Gross F, Wollenburg J, Jensen L, Schmidt-Aursch MC, Krastel S, Elger J, Osti G (2016) Arctic megaslide at presumed rest. Sci Rep 6:38529
Jakobsson M, Mayer L, Coakley B, Dowdeswell JA, Forbes S, Fridman B, Hodnesdal H, Noormets R, Pedersen R, Rebesco M 2012) The international bathymetric chart of the Arctic Ocean (IBCAO) version 3.0. Geophys Res Lett 39(12)
Elger J, Berndt C, Krastel S, Piper DJ, Gross F, Spielhagen RF, Meyer S (2014) The Fram Slide off Svalbard: a submarine landslide on a low-sedimentation-rate glacial continental margin. J Geol Soc 172:153–156
Acknowledgements
We thank the captain and crew of R/V Helmer Hanssen (former R/V Jan Mayen) for their excellent support during the acquisition of geophysical data. Steinar Iversen and Bjørn Runar Olsen are especially thanked for their professional technical assistance during our cruises. We thank Jürgen Mienert and Stefan Bünz for fruitful and constructive suggestions and discussion, and Sunil Vadakkepuliyambatta for the precious help during the early phases of the work. The work was supported by the Research Council of Norway through its Center of Excellence funding scheme, project number 223259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osti, G., Waghorn, K.A., Waage, M. et al. Evolution of contourite drifts in regions of slope failures at eastern Fram Strait. Arktos 5, 105–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41063-019-00070-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41063-019-00070-y