Abstract
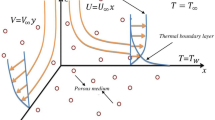
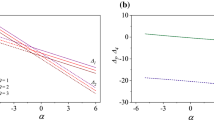
Motivated by petro-chemical geological systems, we consider the natural convection boundary layer flow from a vertical isothermal wavy surface adjacent to a saturated non-Darcian high permeability porous medium. High permeability is considered to represent geologically sparsely packed porous media. Both Darcian drag and Forchheimer inertial drag terms are included in the velocity boundary layer equation. A high permeability medium is considered. We employ a sinusoidal relation for the wavy surface. Using a set of transformations, the momentum and heat conservation equations are converted from an (x, y) coordinate system to an (\(x, \eta )\) dimensionless system. The two-point boundary value problem is then solved numerically with a pseudo-spectral method based on combining the Bellman–Kalaba quasi linearization method with the Chebyschev spectral collocation technique (SQLM). The SQLM computations are demonstrated to achieve excellent correlation with smoothed particle hydrodynamic (SPH) Lagrangian solutions. We study the effect of Darcy number (Da), Forchheimer number (Fs), amplitude wavelength (A) and Prandtl number (Pr) on the velocity and temperature distributions in the regime. Local Nusselt number is also computed for selected cases. The study finds important applications in petroleum engineering and also energy systems exploiting porous media and undulating (wavy) surface geometry. The SQLM algorithm is shown to be exceptionally robust and achieves fast convergence and excellent accuracy in nonlinear heat transfer simulations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, J., Jing, J., Jing, P., Duan, N., Cheng, W., Tan, J.: Experimental study on drag reduction of aqueous foam on heavy oil flow boundary layer in an upward vertical pipe. Pet. Sci. Eng. 146, 409–417 (2016)
Edomwonyi-Otu, L.C., Angeli, P.: Pressure drop and holdup predictions in horizontal oil–water flows for curved and wavy interfaces. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 93, 55–65 (2015)
Peet, Y., Sagaut, P., Charron, Y.: Pressure loss reduction in hydrogen pipelines by surface restructuring. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 34, 8964–8973 (2009)
Caponi, E.A., Fornberg, B., Knight, D.D., McLean, J.W., Saffman, P.G., Yuen, H.C.: Calculations of laminar viscous flow over a moving wavy surface. J. Fluid Mech. 124, 347–362 (1982)
Yao, L.S.: Natural convection along a vertical wavy surface. ASME J. Heat Transf. 105, 465–468 (1983)
Moulic, S.G., Yao, L.S.: Natural convection along a vertical wavy surface with uniform heat flux. ASME J. Heat Transf. 111, 1106–1108 (1989)
Rees, D.A.S., Pop, I.: Boundary layer flow and heat transfer on a continuous moving wavy surface. Acta Mech. 112(4), 149–158 (1995)
Hossain, M.A., Kabir, S., Rees, D.A.S.: Natural convection of fluid with variable viscosity from a heated vertical wavy surface. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 53, 48–57 (2002)
Tashtoush, B., Abu-Irshaid, E.: Heat and fluid flow from a wavy surface subjected to a variable heat flux. Acta Mech. 152, 1–8 (2001)
Bég, O.: Anwar, The Abbasi–Tajik model in thermal convection from wavy surfaces, Technical Report, Aerospace Engineering, Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, pp. 94 (2009)
Hossain, M.Z., Islam, A.K.M S.: Numerical investigation of unsteady flow and heat transfer in wavy channels. In: 15th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Sidney, Australia, pp. 13–17 (2004)
Shalini, R., Kumar, B.V.: Free convection in a thermally-stratified non-Darcian wavy porous enclosure. J. Porous Media 4, 1–18 (2004)
Rahman, S.U., Badr, H.M.: Natural convection from a vertical wavy surface embedded in saturated porous media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41(17), 4422–4429 (2002)
Chiu, C.P., Chou, H.M.: Free convection in the boundary layer flow of a micropolar fluid along a vertical wavy surface. Acta Mech. 101, 161–174 (1993)
Varol, Y., Oztop, H.F.: Buoyancy induced heat transfer and fluid flow inside a tilted wavy solar collector. Build. Environ. 42, 2062–2071 (2007)
Gawlik, K.M., Kutscher, C.F.: Wind heat loss from corrugated transpired solar collectors. ASME J. Sol. Energy Eng. 124, 256–261 (2002)
Kumar, B.V.R., Shalini, G.: Non-Darcy free convection induced by a vertical wavy surface in a thermally stratified porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 2353–2363 (2004)
Rahman, S.U.: Natural convection along vertical wavy surfaces: an experimental study. Chem. Eng. J. 84, 587–591 (2001)
Ghosh Moulic, S., Yao, L.S.: Mixed convection along a wavy surface. ASME J. Heat Transf. 111(4), 974–979 (1989)
Abdul Alim, M., Rezaul Karim, M., Miraj Akand, M.: Heat generation effects on MHD natural convection flow along a vertical wavy surface with variable thermal conductivity. Am. J. Comput. Math. 2, 42–50 (2012)
Bellman, R.E., Kalaba, R.E.: Quasilinearization and Nonlinear Boundary-Value Problems. Elsevier, NewYork (1965)
Trefethen, L.N.: Spectral Methods in MATLAB. SIAM, Philadelphia (2000)
Anwar Bég, O.: THERMO-SPH—a smoothed particle simulator for heat transfer from complex geometrical configurations, Technical Report, Gort Engovation, Bradford, UK, THERMO-D-A-154, pp. 49 (2013)
Coussy, O.: Mechanics of Porous Continua. Butterworths, France (1993)
Vafai, K., Tien, C.L.: Boundary and inertial effects on flow and heat transfer in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 24, 195–203 (1981)
Owens, R.G., Chauvière, C., Phillips, T.N.: A locally-upwinded spectral technique (LUST) for viscoelastic flows. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 108, 49–72 (2002)
Shateyi, S., Motsa, S.S.: Thermal radiation effects on heat and mass transfer over an unsteady stretching surface. Math. Probl. Eng. 2009, 1–13 (2009)
Shateyi, S., Motsa, S.S.: Variable viscosity on magnetohydrodynamic fluid flow and heat transfer over an unsteady stretching surface with Hall effect. Bound. Value Probl. 2010, 1–20 (2010)
Sibanda, P., Motsa, S., Makukula, Z.: A spectral-homotopy analysis method for heat transfer flow of a third grade fluid between parallel plates. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 22(1), 4–23 (2011)
Bég, O.A., Hameed, M., Bég, T.A.: Chebyshev spectral collocation simulation of nonlinear boundary value problems in electrohydrodynamics (EHD). Int. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Sci. Mech. 14(2), 104–115 (2013)
Hoque, M.M., Alam, M.M., Ferdows, M., Bég, O.A.: Numerical simulation of Dean number and curvature effects on magneto-biofluid flow through a curved conduit. Proc. IMECHE J. Eng. Med. 227(11), 1155–1170 (2013)
Liang, C., Chen, J., Lee, J.D.: Spectral difference solution of two-dimensional unsteady compressible micropolar equations on moving and deformable grids. In: 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Nashville, Tennessee (2012)
Bég, O.A., Motsa, S.S., Kadir, A., Bég, T.A., Islam, M.N.: Spectral quasilinear numerical simulation of micropolar convective wall plumes in high permeability porous media. J. Eng. Thermophyis. (2016) (Submitted)
Bég, O.A., Motsa, S.S., Islam, M.N., Lockwood, M.D.: Pseudo-spectral and variational iteration simulation of exothermically-reacting Rivlin–Ericksen viscoelastic flow and heat transfer in a rocket propulsion duct. Comput. Therm. Sci. 6(2), 91–102 (2014)
Gottlieb, D., Orszag, S.A.: Numerical Analysis of Spectral Methods, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. SIAM, Philadelphia (1977)
Don, W.S., Solomonoff, A.: Accuracy and speed in computing the Chebyshev collocation derivative. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 16, 1253–1268 (1995)
Canuto, C., Hussaini, M., Quarteroni, A., Zang, T.: Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (1993)
Lucy, L.B.: A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron. J. 82, 1013–1024 (1977)
Monaghan, J.J., Gingold, R.A.: Shock simulation by the particle method SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 52, 374–389 (1983)
Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30, 543–574 (1992)
Monaghan, J.J.: Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 110, 399–406 (1994)
Monaghan, J.J.: SPH without a tensile instability. J. Comput. Phys. 159, 290–311 (2000)
Morris, J.P., Fox, P.J., Zhu, Y.: Modeling low Reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 136, 214–226 (1997)
Oger, G., Doring, M., Alessandrini, B., Ferrant, P.: Two-dimensional SPH simulations of wedge water entries. J. Comput. Phys. 213, 803–822 (2006)
Comas-Cardona, S., Groenenboom, P.H.L., Binetruy, C., Krawczak, P.: A generic mixed FE-SPH method to address hydro-mechanical coupling in liquid composite moulding processes. Compos. Part A 36, 1004–1010 (2005)
Sigalotti, L.D.G., Klapp, J., Sira, E., Melean, Y., Hasmy, A.: SPH simulations of time-dependent Poiseuille flow at low Reynolds numbers. J. Comput. Phys. 191, 622–638 (2003)
Zhu, Y., Fox, P.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for diffusion through porous media. Transp. Porous Media 43, 441–471 (2001)
Cleary, P.W., Monaghan, J.J.: Conduction modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 148, 235–236 (1999)
Bég, O.A.: SPLASH—A smoothed particle hydrodynamic solver for spacecraft “splashdown” simulations in MATLAB, Technical Report for European Space Consortium- AERO-D-61-SPH, Gort Engovation-Engineering Sciences, Bradford, pp. 85 (2013)
Bég, O.A., Bég, TA.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamic simulation of magnetic field materials processing, Technical Report for Metallurgy Industry (Norway)-MANUFACT-M-14-SPH, Gort Engovation-Engineering Sciences, Bradford, pp. 64 (2013)
Liu, G.R., Liu, M.B.: Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: A Meshfree Particle Method. World Scientific Publishing Co., Singapore (2003)
Bég, O.A.: WAVY-SPH: A smoothed particle hydrodynamic solver for wavy solar collectors, Technical Report-SOLAR-E-SPH, Gort Engovation- Bradford, pp. 85 (2013)
Abdallah, M.S., Zeghmati, B.: Effects of the wavy surface on free convection–radiation along an inclined plate. WASET J. 78, 458–464 (2013)
Prasad, V.R., Gaffar, S.A., Anwar Bég, O.: Heat and mass transfer of a nanofluid from a horizontal cylinder to a micropolar fluid. AIAA J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 29, 127–139 (2015)
Uddin, M.J., Bég, O., Amin, N.S.: Hydromagnetic transport phenomena from a stretching or shrinking nonlinear nanomaterial sheet with Navier slip and convective heating: a model for bio-nano-materials processing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 368, 252–261 (2014)
Chang, T.B., Mehmood, A., Bég, O.A., Narahari, M., Islam, M.N., Ameen, F.: Numerical study of transient free convective mass transfer in a Walters-B viscoelastic flow with wall suction. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 16, 216–225 (2011)
Adesanya, S.O., Makinde, O.D.: MHD oscillatory slip flow and heat transfer in a channel filled with porous media. U.P.B Sci. Bull. A 76, 197–204 (2014)
Adesanya, S.O., Falade, J.A., Makinde, O.D.: Pulsating flow through vertical porous channel with viscous dissipation effect. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Ser. D Mech. Eng. 77(1), 25–36 (2015)
Adesanya, S.O., Falade, J.A.: Thermodynamic analysis of hydromagnetic third grade fluid flow through a channel filled with porous medium. Alex. Eng. J. 54, 615–622 (2015)
Adesanya, S.O., Oluwadare, E.O., Falade, J.A., Makinde, O.D.: Hydromagnetic natural convection flow between vertical parallel plates with time-periodic boundary conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 396, 295–303 (2015)
Adesanya, S.O., Kareem, S.O., Falade, J.A., Arekete, S.A.: Entropy generation analysis for a reactive couple stress fluid flow through a channel saturated with porous material. Energy 93, 1239–1245 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding Statement
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bég, O.A., Motsa, S.S., Bég, T.A. et al. Numerical Study of Nonlinear Heat Transfer from a Wavy Surface to a High Permeability Medium with Pseudo-Spectral and Smoothed Particle Methods. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 3, 3593–3613 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0318-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-017-0318-4