Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of resveratrol (RVT) on sildenafil-induced relaxations of isolated corpus cavernosum in non-diabetic and diabetic aged rats.
Methods
A total of 13 male aged rats (72–80 weeks old) were randomized into two groups including non-diabetic aged rats and diabetic aged rats. Diabetes was induced in aged rats by streptozotocin (single i.p. dose of 45 mg/kg body weight) administration. At the end of the 12th week, corpus cavernosum strips of rats were suspended in an organ bath system. The corpus cavernosum relaxation was evaluated by sildenafil in the presence or absence of RVT (10−4 M) for 45 min.
Results
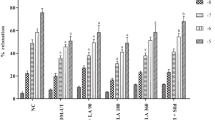
Induction of diabetes resulted in significant inhibition of sildenafil-induced corpus cavernosum relaxation in aged rats. The diminished relaxation in response to sildenafil was significantly improved by acute RVT incubation in both non-diabetic and diabetic aged rats; however, the magnitude of potentiation induced by RVT was more pronounced in diabetic aged rats. The potentiating effect of RVT was significantly inhibited by L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 10−4 M, for 30 min) incubation in both groups. After the L-NAME incubation, the relaxation response of corporal tissues evoked by sildenafil was found to be similar in diabetic and non-diabetic aged rats.
Conclusions
RVT improves sildenafil-induced relaxations of corpus cavernosum in both diabetic and non-diabetic aged rats probably by potentiating the activity of NOS, and this effect seems to be more manifest in diabetic aged group.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dashwood MR, Crump A, Shi-Wen X et al (2011) Identification of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in human penis: a potential role of reduced neuronally-derived nitric oxide in erectile dysfunction. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12:1316–1321
Costa C, Vendeira P (2008) Does erectile tissue angioarchitecture modify with aging? An immunohistological and morphometric approach. J Sex Med 5:833–840
Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF et al (2004) RhoA/Rho-kinase suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: a mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9121–9126
Angulo J, González-Corrochano R, Cuevas P et al (2010) Diabetes exacerbates the functional deficiency of NO/cGMP pathway associated with erectile dysfunction in human corpus cavernosum and penile arteries. J Sex Med 7(2 Pt 1):758–768
Toda N, Ayajiki K, Okamura T (2005) Nitric oxide and penile erectile function. Pharmacol Ther 106:233–266
Gratzke C, Angulo J, Chitaley K et al (2010) Anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 7:445–475
Nunes KP, LabaziH Webb RC (2012) New insights into hypertension-associated erectile dysfunction. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 21:163–170
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Francomano D et al (2010) Endothelial dysfunction and erectile dysfunction in the aging man. Int J Urol 17:38–47
Solomon H, Wierzbicki AS, Lumb PJ et al (2006) Cardiovascular risk factors determine erectile and arterial function response to sildenafil. Am J Hypertens 19:915–919
Rendell MS, Rajfer J, Wicker PA et al (1999) for the Sildenafil Diabetes Study Group. Sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 281:421–426
Malavige LS, Levy JC (2009) Erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Sex Med 6:1232–1247
Dalaklioglu S, Ozbey G (2013) The potent relaxant effect of resveratrol in rat corpus cavernosum and its underlying mechanisms. Int J Impot Res 25:188–193
Wu JM, Wang ZR, Hsieh TC et al (2001) Mechanism of cardioprotection by resveratrol, a phenolic antioxidant present in red wine (Review). Int J Mol Med 8:3–17
Das DK, Maulik N (2006) Resveratrol in cardioprotection: a therapeutic promise of alternative medicine. Mol Interv 6:36–47
Di Pascoli M, Diví M, Rodríguez-Vilarrupla A et al (2013) Resveratrol improves intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction and reduces hepatic fibrosis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. J Hepatol 58:904–910
Takahashi S, Nakashima Y (2012) Repeated and long-term treatment with physiological concentrations of resveratrol promotes NO production in vascular endothelial cells. Br J Nutr 107:774–780
Yu HP, Hwang TL, Hwang TL et al (2010) Resveratrol prevents endothelial dysfunction and aortic superoxide production after trauma hemorrhage through estrogen receptor-dependent hemeoxygenase-1 pathway. Crit Care Med 38:1147–1154
Bai Y, An R (2015) Resveratrol and sildenafil synergistically improve diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci 135:43–48
Park SJ, Ahmad F, Philp A et al (2012) Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases. Cell 148:421–433
Sáenz de Tejada I, Goldstein I, Azadzoi KM et al (1989) Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-mediated relaxation of penile smooth muscle from diabetic men with impotence. N Engl J Med 320:1025–1030
Toque HA, Priviero FB, Teixeira CE et al (2009) Comparative relaxing effects of sildenafil, vardenafil, and tadalafil in human corpus cavernosum: contribution of endogenous nitric oxide release. Urology 74:216–221
Soufi FG, Mohammad-Nejad D, Ahmadieh H (2012) Resveratrol improves diabetic retinopathy possibly through oxidative stress-nuclear factor κB—apoptosis pathway. Pharmacol Rep 64:1505–1514
Soner BC, Murat N, Demir O et al (2010) Evaluation of vascular smooth muscle and corpus cavernosum on hypercholesterolemia. Is resveratrol promising on erectile dysfunction? Int J Impot Res 22:227–233
Roghani M, Baluchnejadmojarad T (2010) Mechanisms underlying vascular effect of chronic resveratrol in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Phytother Res 24(Suppl 2):S148–S154
Silan C (2008) The effects of chronic resveratrol treatment on vascular responsiveness of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biol Pharm Bull 31:897–902
Babacanoglu C, Yildirim N, Sadi G et al (2013) Resveratrol prevents high-fructose corn syrup-induced vascular insulin resistance and dysfunction in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 60:160–167
Wallerath T, Deckert G, Ternes T et al (2002) Resveratrol, a polyphenolic phytoalexin present in red wine, enhances expression and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 106:1652–1658
Klinge CM, Wickramasinghe NS, Ivanova MM et al (2008) Resveratrol stimulates nitric oxide production by increasing estrogen receptor alpha-Src-caveolin-1 interaction and phosphorylation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. FASEB J 22:2185–2197
Zhang H, Zhang J, Ungvari Z et al (2009) Resveratrol improves endothelial function: role of TNFα and vascular oxidative stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1164–1171
Mattagajasingh I, Kim CS, Naqvi A et al (2007) SIRT1 promotes endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation by activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14855–14860
Su HC, Hung LM, Chen JK (2006) Resveratrol, a red wine antioxidant, possesses an insulin-like effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1339–E1346
Juan ME, González-Pons E, Munuera T et al (2005) trans-Resveratrol, a natural antioxidant from grapes, increases sperm output in healthy rats. J Nutr 135:757–760
Boydens C, Pauwels B, Vanden Daele L, Van de Voorde J (2016) Protective effect of resveratrol and quercetin on in vitro-induced diabetic mouse corpus cavernosum. Cardiovasc Diabetol 15:46
Zarzuelo MJ, López-Sepúlveda R, Sánchez M et al (2013) SIRT1 inhibits NADPH oxidase activation and protects endothelial function in the rat aorta: implications for vascular aging. Biochem Pharmacol 85:1288–1296
Buluc M, Demirel-Yilmaz E (2006) Resveratrol decreases calcium sensitivity of vascular smooth muscle and enhances cytosolic calcium increase in endothelium. Vascul Pharmacol 44:231–237
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by Akdeniz University Research Foundation and TUBITAK with 111S212 Grant Number.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of the University.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalaklioglu, S., Bayram, Z., Tasatargil, A. et al. Resveratrol reverses diabetes-related decrement in sildenafil-induced relaxation of corpus cavernosum in aged rats. Aging Clin Exp Res 29, 345–351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0582-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0582-x