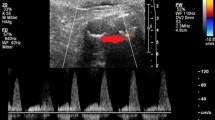
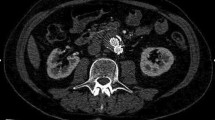
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this systematic review is to assess the accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) to computed tomography angiography (CTA) for the detection of endoleaks within EVAR surveillance program.
Material and methods
A systematic review in Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane database was performed. Articles assessing diagnostic accuracy and comparative modality (CTA vs. CEUS) for endoleaks in adult patients within surveillance programs were retrieved. Methodological assessment was performed, using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) tools. The sensitivity and specificity of data were extracted and statistical analysis was performed using MetaDiSc version 1.4.
Results
Eight articles were found eligible (n = 454 patients). The pooled sensitivity of CEUS at detecting endoleak is 0.914 (CI 0.866–0.949) and pooled specificity is 0.782 (CI 0.741–0.820).
Conclusion
The CEUS with its dynamic nature and longer scanning window demonstrated to be a highly sensitive modality for endoleak detection in comparison to CTA in delayed endoleaks type II.
Riassunto
Scopo
Scopo di questa revisione è stato valutare l'accuratezza dell'ecografia con mezzo di contrasto (CEUS) rispetto all'Agio Tomografia Computerizzata (CTA) per il rilevamento di endoleak, nell'ambito del programma di sorveglianza EVAR.
Materiali e Metodi
E' stata eseguita una revisione sistematica nei database Pubmed, Embase e Cochrane. Sono stati valutati gli articoli che prendevano in considerazione l'accuratezza diagnostica e il confronto (CTA Vs CEUS) per endoleak, in pazienti adulti nell'ambito di programmi di sorveglianza. La valutazione metodologica è stata effettuata utilizzando come strumento il Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studiesla (QUADAS). Sono state estratte sensibilità e specificità ed è stata effettuata l'analisi statistica utilizzando MetaDiSc version 1.4.
Risultati
Sono stati trovati otto articoli adatti allo studio (n = 454 pazienti). La sensibilità della CEUS nell'individuare endoleak è 0,914 (CI 0,866-0,949) e la specificità 0,782 (CI 0,741-0,820).
Conclusione
La CEUS, per la sua natura dinamica e la possibilità di scansione più lunga, ha dimostrato di essere una modalità altamente sensibile per la rilevazione di endoleak rispetto alla CTA negli endoleak di tipo II.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parodi JC, Palmaz JC, Barone HD (1991) Transfemoral intraluminal graft implantation for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg 5:491–499
Bush RL, Mureebe L, Bohannon WT, Rutherford RB (2008) The impact of recent european trials on abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: is a paradigm shift warranted? J Surg Res 48:264–271
Blankensteijn JD, de Jong SECA, Prinssen M, van der Ham AC, Buth J, van Sterkenburg SMM, Verhagen HJM, Buskens E, Grobbee DE, DREAM Trial Group (2005) Two-year outcomes after conventional or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med 352:2398–2405
Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Kwong GPS, Powel JT, Thompson SG, EVAR trial participants (2004) Comparison of endovascular aneurysm repair with open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 1), 30-day operative mortality results: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364:843–848
Lederle FA, Freischlag JA, Kyriakides TC, Padberg FT Jr, Matsumura JS, Kohler TR, Lin PH, Jean-Claude JM, Cikrit DF, Swanson KM, Peduzzi PN, OVER Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group (2009) Outcomes following endovascular vs open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. A randomized trial. JAMA 302:535–1542
Stavropoulos SW, Charagundla SR (2007) Imaging techniques for detection and management of endoleaks after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Radiology 243:641–655
Tsoumakidou G, Brountzos E (2010) Detection of complications after aortic stent grafting. Eur Cardiol 6:83–87
Carrafiello G, Recaldini C, Lagana D, Piffaretti G, Fugazzola C (2008) Endoleak detection and classification after endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm: value of CEUS over CTA. Abdom Imaging 33:357–362
Whiting P, Rutjes AWS, Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J (2004) Sources of variation and bias in studies of diagnostic accuracy: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 140:189–202
Heilberger P, Schunn C, Ritter W, Weber S, Raithel D (1997) Postoperative color flow duplex scanning in aortic endografting. J Endovasc Surg 4:262–271
Bendick PJ, Bove PG, Long GW, Zelenock GB, Brown OW, Shanley CJ (2003) Efficacy of ultrasound scan contrast agents in the noninvasive follow-up of aortic stent grafts. J Vasc Surg 37:381–385
EFSUMB Study Group (2008) Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS)—update 2008. Ultraschall Med 29:28–44
Piscaglia F, Bolondi L (2006) The safety of Sonovue in abdominal applications: retrospective analysis of 23188 investigations. Ultrasound Med Biol 33:180–186
Quaia E (2005) Detection of endoleak after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Med Radiol Contrast Media Ultrason Part 2:11–115
White GH, Yu W, May J, Chaufour X, Stephen MS (1997) Endoleak as a complication of endoluminal grafting of abdominal aortic aneurysms: classification, incidence, diagnosis, and management. J Endovasc Surg 4:152–168
Gilling-Smith G, Brennan J, Harris P, Bakran A, Gould D, McWilliams R (1999) Endotension after endovascular aneurysm repair: definition, classification, and strategies for surveillance and intervention. J Endovasc Surg 6:305–307
van Marrewijk C, Buth J, Harris PL, Norgren L, Nevelsteen A, Wyatt MG (2002) Significance of endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: the Eurostar experience. J Vasc Surg 35:461–473
Buth J, Harris PL, van Marrewijk C, Fransen G (2003) The significance and management of different types of endoleaks. Semin Vasc Surg 16(2):95–102
Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T, Amor T, Adiseshiah M, Blankensteijn JD, Buth J, Chuter TAM, Fairman RM, Gilling-Smith G, Harris PL, Hodgson KJ, Hopkinson BR, Ivancev K, Katzen BT, Lawrence-Brown M, Meier GH, Malina M, Makaroun MS, Parodi JC, Richter GM, Rubin GD, Stelter WJ, White GH, White RA, Wisselink W, Zarins CK (2002) Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg 35:1029–1035
Sternbergh WC III, Greenberg RK, Chuter TAM, Tonnessen BH (2008) Redefining postoperative surveillance after endovascular aneurysm repair: recommendations based on 5 year follow up in the US Zenith multicentre trial. J Vasc Surg 48:278–285
Schlosser FJV, Gusberg RJ, Dardik A, Lin PH, Verhagen HJM, Moll FL, Muhs BE (2009) Aneurysm rupture after EVAR: can the ultimate failure be predicted? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 37:15–22
McWilliams RG, Martin J, White D, Gould DA, Rowlands PC, Haycox A, Brennan J, Gilling-Smith GL, Harris PL (2002) Detection of endoleak with enhanced ultrasound imaging: comparison with biphasic computed tomography. J Endovasc Ther 9:170–179
Ten Bosch JA, Rouwet EV, Peters CTH, Jansen L, Verhagen HJM, Prins MH, Teijink JAW (2010) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus computed tomographic angiography for surveillance of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:638–643
McWilliams RG, Martin J, White D, Gould DA, Harris PL, Fear SC, Brennan J, Gilling-Smith GL, Bakran A, Rowlands PC (1999) Use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in follow-up after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Interv Radiol 10:1107–1114
Giannoni MF, Fanelli F, Citone M, Acconcia MC, Speziale F, Gossetti B (2007) Contrast ultrasound imaging: the best method to detect type II endoleak during endovascular aneurysm repair follow-up. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg 6:359–362
Sun Z (2006) Diagnostic value of color duplex ultrasonography in the follow-up of endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(5):759–764
Henao EA, Hodge MD, Felkai DD, McCollum CH, Noon GP, Lin PH, Lumsden AB, Bush RL (2006) Contrast-enhanced Duplex surveillance after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: improved efficacy using a continuous infusion technique. J Vasc Surg 43:259–264
Iezzi R, Basilico R, Giancristofaro D, Pascali D, Cotroneo AR, Storto ML (2009) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus color duplex ultrasound imaging in the follow-up of patients after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 49:552–560
Napoli V, Bargellini I, Sardella SG, Petruzzi P, Cioni R, Vignalli C, Ferrari M, Bartolozzi C (2004) Abdominal aortic aneurysm: contrast-enhanced US for missed endoleaks after endoluminal repair. Radiology 233:217–225
Iezzi R, Cotroneo AR, Filippone A, Di Fabio F, Quinto F, Colosimo C, Bonomo L (2006) Multidetector CT in abdominal aortic aneurysm treated with endovascular repair: are unenhanced and delayed phase enhanced images effective for endoleak detection? Radiology 241:915–921
Macari M, Chandarana H, Schmidt B, Lee J, Lamparello P, Babb J (2006) Abdominal aortic aneurysm: can the arterial phase at CT evaluation after endovascular repair be eliminated to reduce radiation dose? Radiology 241:908–914
Dill-Macky MJ, Wilson SR, Sternbach Y, Kachura J, Lindsay T (2007) Detecting endoleaks in aortic endografts using contrast-enhanced sonography. AJR 188:W262–W268
Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y (2010) Analysing and presenting results [Internet], Version 1.0. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (eds) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy, chap 10. http://srdta.cochrane.org/handbook-dta-reviews
Clevert DA, Minaifar N, Weckbach S, Kopp R, Meimarakis G, Clevert DA, Reiser M (2008) Color duplex ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound in comparison to MS-CT in the detection of endoleak following endovascular aneurysm repair. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 39:121–132
Mauro R, Maioli F, Freyrie A, Testi G, Palumbo N, Serra C, Stella A (2010) Is CEUS a valid alternative to CTA in endoleak’s detection? Ital J Vasc Endovasc Surg 17(4):253–258
Conflict of interest
The authors (J. Chung, A. Kordzadeh, I. Prionidis, Y. Panayiotopoulos, T. Browne) have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Studies
The study described in this article does not contain studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, J., Kordzadeh, A., Prionidis, I. et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) versus computed tomography angiography (CTA) in detection of endoleaks in post-EVAR patients. Are delayed type II endoleaks being missed? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ultrasound 18, 91–99 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-014-0154-x