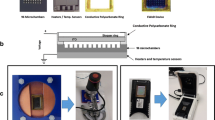
Abstract
Nowadays, microfluidic technologies have widely been employed in developing point-of-care diagnostics to address global health issues because of their potential advantages of low sample and reagent consumption, high throughput and sensitivity, large surface-to-volume ratio, and other benefits related to miniaturization. However, the fabrication of microfluidic channels is commonly costly and requires laboratory-intensive cleaning, photolithography, and etching or baking steps in cleanroom environments, making it difficult to modify. Besides, proper channel enclosure without deforming small features or without clogging of the channel during the bonding process is challenging. The present article aims to demonstrate a cheap, reliable, and rapid method for the fabrication of microfluidic channels using double-sided tapes, enabling not only highly uniform cross-sectional dimensions along the microfluidic channels but also proper adhesion in hybrid systems, composed of different layers. In other words, this technique provides a single-step integration of electrochemical sensors in a microfluidic chip, which could be useful for rapid and low-cost fabrication of microfluidic-based electrochemical sensors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hua J, Wang SQ, Wanga L, Lib F, Pingguan-Murphye B, Lub TJ, Xua F (2014) Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 54:585–597
Hawkins KR, Weigl BH (2010) Microfluidic diagnostics for low-resource settings. In: Becker H, Wang W (eds) Microfluidics, BioMEMS, and medical microsystems Viii. Proceedings of the SPIE, vol 7593, pp 75930L1–L15
Nilghaz A, Wicaksono DH, Gustiono D, Abdul Majid FA, Supriyanto E, Abdul Kadir MR (2012) Flexible microfluidic cloth-based analytical devices using a low-cost wax patterning technique. Lab Chip 12:209–218
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Gu P, Liu K, Chen H, Nishida T, Fan ZH (2011) Chemical-assisted bonding of thermoplastics/elastomer for fabricating microfluidic valves. Anal Chem 83:446–452
Mitra SK, Chakraborty S (2012) Microfluidics and nanofluidics handbook. CRC Press/Taylor and Francis, Novato
Flachsbart BR, Wong K, Iannacone JM, Abante EN, Vlach RL, Rauchfuss PA et al (2006) Design and fabrication of a multilayered polymer microfluidic chip with nanofluidic interconnects via adhesive contact printing. Lab Chip 6(5):667–674
Lin R, Burns MA (2005) Surface-modified polyolefin microfluidic devices for liquid handling. J Micromech Microeng 15:2156–2162
Zhang W, Lin S, Wang C, Hu J, Li C, Zhuang Z, Zhou Y et al (2009) PMMA/PDMS valves and pumps for disposable microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3088–3094
Sunkara V, Park DK, Hwang H, Chantiwas R, Soper SA, Cho YK (2011) Simple room temperature bonding of thermoplastics and poly(dimethylsiloxane). Lab Chip 11:962–965
Mehta G, Lee J, Cha W, Tung YC, Linderman JJ, Takayama S (2009) Hard top soft bottom microfluidic devices for cell culture and chemical analysis. Anal Chem 81:3714–3722
Steigert J, Haeberle S, Brenner T, Müller C, Steinert CP, Koltay P et al (2007) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic chips in COC. J Micromech Microeng 17(2)
Lee SW, Lee SS (2008) Shrinkage ratio of PDMS and its alignment method for the wafer level process. Microsyst Technol 14(2):205–208
Moral-Vico J, Barallat J, Abad L, Olivé-Monllau R, Xavier Muñoz-Pascual F, Galán Ortega A, del Campo FJ, Baldrich E (2015) Dual chronoamperometric detection of enzymatic biomarkers using magnetic beads and a low-cost flow cell. Biosens Bioelectron 69:328–336
Nath P, Fung D, Kunde YA, Zeytun A, Brancha B, Goddarda G (2010) Rapid prototyping of robust and versatile microfluidic components using adhesive transfer tapes. Lab Chip 10:2286–2291
Hwang JS, Kim SY, Kim YS, Song HJ, Park CY, Kim JD (2015) Implementation of PCB-based PCR chip using double-sided tape. IJCA 8(2):117–124
Khashayar P, Amoabediny Gh, Larijani B, Hosseini M, Verplancke R, Schaubroek D, De Keersmaecker M, Adriaens A, Vanfleteren J (2016) Characterization of gold nanoparticle layer deposited on gold electrode by various techniques for improved sensing abilities. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 6(4):1380–1390
Mair DA, Geiger E, Pisano AP, Frechet JMJ, Svec F (2006) Injection molded microfluidic chips featuring integrated interconnects. Lab Chip 6:1346–1354
Bartholomeusz DA, Boutté RW, Andrade JD (2005) Xurography: rapid prototyping of microstructures using a cutting plotter. J Microelectromech Syst 14(6):1364–1374
Kim J, Shin Y, Song S, Lee J, Kim J (2014) Rapid prototyping of multifunctional microfluidic cartridges for electrochemical biosensing platforms. Sens Actuators B Chem 202:60–66
Luo LW, Teo CY, Ong WL, Tang KC, Cheow LF, Yobas L (2007) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems using a laser-patterned tape. J Micromech Microeng 17:N107–N111
Patko D, Martonfalvi Z, Kovacs B, Vonderviszt F, Kellermayer M, Horvath R (2014) Microfluidic channels laser-cut in thin double-sided tapes: cost-effective biocompatible fluidics in minutes from design to final integration with optical biochips. Sens Actuators B Chem 196:352–356
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Whitesides GM, Carrilho E (2010) Diagnostics for the developing world: microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem 82:3–10
Tsao CW, DeVoe DL (2009) Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:1–16
Kim J, Surapaneni R, Gale BK (2009) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems using a PDMS/polymer tape composite. Lab Chip 9:1290–1293
Mair DA, Rolandi M, Snauko M, Noroski R, Svec F, Fréchet JMJ (2007) Room-temperature bonding for plastic high-pressure microfluidic chips. Anal Chem 79(13):5097–5102
Bruus H (2011) Basic flow solutions. In: Bruus H (ed) Theoretical microfluidics, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Hawkins KR, Steedman MR, Baldwin RR, Fu E, Ghosal S, Yager P (2007) A method for characterizing adsorption of flowing solutes to microfluidic device surfaces. Lab Chip 7(2):281–285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Estevam Las Casas.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khashayar , P., Amoabediny, G., Larijani, B. et al. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic chips using laser-cut double-sided tape for electrochemical biosensors. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 1469–1477 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0684-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0684-6