Abstract
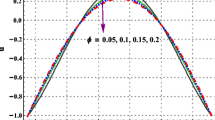
In the present paper, we have investigated peristaltic flow of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) in a curved channel with variable viscosity. The present problem is modeled and exact solutions for non-dimensional differential equation are achieved under long wavelength and low Reynolds number approximation. The features of the peristaltic motion are examined by plotting graphs and discussed in detail. Velocity tables are also incorporated for different values of volume fraction of the nano particle material and for viscosity parameter. Results showed that addition of SWCNTs decreases nano particle temperature and velocity profile near the left wall. It is found that for pure blood case, velocity for the variable viscosity fluid is greater as compared to the constant viscosity fluid. It is also found that for the case of SWCNTs, velocity for the variable viscosity fluid near the left wall decreases whereas it gets opposite behavior near the right wall.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Latham TW (1966) Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump. MS thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
Shapiro AH, Jafferin MY, Weinberg SL (1969) Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 35:669
Mekheimer KhS, Elmaboud YA (2008) The influence of heat transfer and magnetic field on peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in a vertical annulus: application of an endoscope. Phys Lett A 372:1657
Yildirim A, Sezer SA (2010) Effects of partial slip on the peristaltic flow of a MHD Newtonian fluid in an asymmetric channel. Math Comput Model 52:618
Nadeem S, Maraj EN, Akbar NS Investigation of peristaltic flow of Williamson nanofluid in a curved channel with compliant walls. Appl Nanosci. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0234-9
Elmaboud YA (2012) Influence of induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow in an annulus. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 17:685
Nadeem S, Sadaf H, Akbar NS (2014) Analysis of peristaltic flow for a Prandtl fluid model in an endoscope. J Power Tech 94:1
Khan AA, Ellahi R, Vafai K Peristaltic transport of a Jeffery fluid with variable viscosity through a porous medium in anasymmetric channel. Adv Math Phys. doi:10.1155/2012/169642
Ebaid A (2008) A new numerical solution for the MHD peristaltic flow of a bio-fluid with variable viscosity in a circular cylindrical tube via adomian decomposition method. Phys Lett A 372:5321
Nadeem S, Akbar NS (2010) Influence of temperature dependent viscosity on peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid: application of an endoscope. Appl Math Comput 216:3606
Hakeem AE, Naby AE, Misiery ME, Shamy E Hydromagnetic flow of fluid with variable viscosity in a uniform tube with peristalsis. J Phys A Math Gen 36:8535. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/36/31/314
Nadeem S, Sadaf H, Sadiq AM (2014) Analysis of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of Prandtl fluid model in an endoscopy. Curr Nanosci 10:709
Ellahi R (2013) The effects of MHD and temperature dependent viscosity on the flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a pipe. Analytical solutions. Appl Math Model 37:1451
Sheikholeslami M, Gorji BM, Ellahi R, Hassan M, Soleimani S (2014) Effects of MHD on Cu–water nanofluid flow and heat transfer by means of CVFEM. J Magn Magn Mater 349:188
Nadeem S, Maraj EN (2015) Peristaltic flow of Sutterby nano fluid in a curved channel with compliant walls. J Comput Theor Nanosci 12(2). doi:10.1166/jctn.2015.3722
Ellahi R, Razab M, Vafaia K (2012) Series solutions of non-Newtonian nanofluids with Reynolds’ model and Vogel’s model by means of the homotopy analysis method. Math Comput Model 55:1876
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, De Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297:787
Bianco A, Kostarelos K, Prato M (2005) Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 9:674
Bianco A, Prato M (2003) Can carbon nanotubes be considered useful tools for biological applications? Adv Mater 20:1765
Guo Z, Sadler PJ, Tsang SC (1998) Immobilization and visualization of DNA and proteins on carbon nanotubes. Adv Mater 10:701
Biercuk MJ, Llaguno MC, Radosavljevic M, Hyun JK, Johnson AT (2002) Carbon nanotube composites for thermal management. Appl Phys Lett 80:2767
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A, Khan AA, Gulzarb M (2015) Analysis of single and multi walled carbon nanotubes suspended in salt water solutions over a stretching cylinder. Mitt Klost 65:1
Akbar NS (2014) Peristaltic flow with Maxwell carbon nanotubes suspensions. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11:1642
Ul Haq R, Khan ZH, Khan WA (2015) Thermo physical effects of carbon nanotubes on MHD flow over a stretching surface. Physica E 63:215
Sinha N, Yeow J (2005) Carbon nano tube. IEEE Trans Nanosci 4:180
Akbar NS (2014) MHD peristaltic flow with carbon nanotubes in an asymmetric channel. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11:1323
Khan WA, Khan ZH, Rahi M Fluid flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes along a flat plate with Navier slip boundary. Appl Nanosci. doi:10.1007/s13204-013-0242-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Marcio S Carvalho.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadeem, S., Sadaf, H. Exploration of single wall carbon nanotubes for the peristaltic motion in a curved channel with variable viscosity. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 117–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0612-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0612-9