Abstract
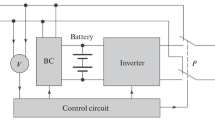
Home inverter is an important system which provides uninterrupted power supply for domestic requirements. Most of the existing systems use line frequency transformers to generate the desired sinusoidal voltage and exhibit poor load regulation and efficiency. Under spurious conditions, reliable and stable operation of the inverter is a primary requirement. In this paper, 3-stage bidirectional (boost and buck) cascaded converter topology is proposed to boost an input battery voltage from 12 to 375 V and vice-versa. DC link is connected to H-bridge converter to obtain a desired sinusoidal output voltage. In the topology, first and third stages are non-isolated boost converters and second stage is a buck derived push–pull converter. Push–pull configuration of the 2nd stage provides electrical isolation to source from high voltage DC bus. Cascaded DC–DC converter outputs are regulated by designing an average current mode control and instantaneous voltage control is designed for H-bridge inverter. Hardware is designed and developed using digital signal controllers to supply 700 W domestic load. Experiments are conducted for different linear, nonlinear and dynamic load variations.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, R., & Ferdowsi, M. (2012). Controller design method for a cascaded converter system comprised of two DC–DC converters considering the effects of mutual interactions. In 2012 Twenty-seventh annual IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC), (pp. 1838–1844). doi:10.1109/APEC.2012.6166072
Ahmadi, R., & Ferdowsi, M. (2013). Improving performance of a DC–DC cascaded converter system using an extra feedback loop. In 2013 IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition (pp. 5511–5517). doi:10.1109/ECCE.2013.6647449
Ardi, H., Ajami, A., Kardan, F., & Nikpour, S. (2016). Analysis and implementation of a non-isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter with high voltage gain. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, PP(99), 1–1. doi:10.1109/TIE.2016.2552139
Baek, J. B., Choi, W. I., & Cho, B. H. (2013). Digital adaptive frequency modulation for bidirectional DC–DC converter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(11), 5167–5176. doi:10.1109/TIE.2012.2224075.
Basso, C. (2008). Switch-mode power supplies: SPICE simulations and practical designs. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Bryant, B., & Kazimierczuk, M. K. (2005). Open-loop power-stage transfer functions relevant to current-mode control of boost pwm converter operating in ccm. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 52(10), 2158–2164. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2005.852919.
Choe, G. Y., Kim, J. S., Kang, H. S., & Lee, B. K. (2010). An optimal design methodology of an interleaved boost converter for fuel cell applications. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 5(2), 319–328.
Cooke, P. (2000). Modeling average current mode control [of power convertors]. In: Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, 2000. APEC 2000. Fifteenth Annual IEEE (Vol. 1, pp. 256–262). doi:10.1109/APEC.2000.826113
Datasheet. (2012). High speed 5 igbt in trenchstop technology copacked with rapid 1 fast and soft anti parallel diode. Technical report, Infineon Technologies AG.
Datasheet. (2013a). 120 khz bandwidth, high voltage isolation current sensor with integrated overcurrent detection. Technical report, Allegro MicroSystems LLC.
Datasheet. (2013b). 120v, n channel optimos3 power transistor ipp048n12n3g. Technical report, Infineon Technologies AG.
Datasheet. (2013c). 250v, n channel optimos3 power transistor ipp200n25n3. Technical report, Infineon Technologies AG.
Datasheet. (2013d). High speed 5 igbt in trenchstop5 technology copacked with rapid 1 fast and soft anti-parallel diode ikp40n65h5. Technical report, Infineon Technologies AG.
Datasheet. (2014). Mc56f84xxx: Digital signal controllers. Technical report, NXP Semiconductors.
David, B. (2012). Benefits of a multiphase buck converter. Technical report, Texas Instruments Incorporated.
Erickson, R., & Maksimovic, D. (2001). Fundamentals of power electronics. Power electronics. Berlin: Springer.
Hauke, B. (2010). Basic calculation of a boost converter’s power stage. Technical report, Texas Instruments Incorporated.
IS. (2014a). Part-i general and safety requirements for ups. Technical report, Uninterruptible Power Systems.
IS. (2014b). Part-iii method of specifying the performance and test requirements for ups. Technical report, Uninterruptible Power Systems.
Kittipeerachon, K., & Bunlaksananusorn, C. (2004). Feedback compensation design for switched mode power supplies with a right-half plane (rhp) zero. In Second international conference on power electronics, machines and drives, 2004, (PEMD 2004) (Conf. Publ. No. 498), (Vol. 1, pp. 236–241). doi:10.1049/cp:20040291
Kolluri, S., & Narasamma, N.L. (2013). Analysis, modeling, design and implementation of average current mode control for interleaved boost converter. In IEEE 10th international conference on power electronics and drive systems (PEDS), 2013 (pp. 280–285). doi:10.1109/PEDS.2013.6527029
Lee, K. Y., Hsu, H. Y., & Lai, Y. (2007). Simple digital-controlled ac/dc converter with power factor correction for universal input applications. In: 33rd annual conference of the IEEE, industrial electronics society, 2007. IECON 2007 (pp 1472–1477). doi:10.1109/IECON.2007.4460350
Lin, C., s Yang, L., & Wu, G. W. (2013). Study of a non-isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter. IET Power Electronics, 6(1), 30–37. doi:10.1049/iet-pel.2012.0338.
Milano, S. (2013). Allegro hall-effect sensor ics. Technical report, Allegro MicroSystems LLC.
Mishima, T., Hiraki, E., & Nakaoka, M. (2010). A high frequency-link bidirectional DC–DC converter for super capacitor-based automotive auxiliary electric power systems. Journal of Power Electronics, 10(1), 27–33.
Mitchell, D., & Mammano, B. (2002). Designing stable control loops. Technical report, Texas Instruments Incorporated.
Mohan, N., Undeland, T. M., & Robbins, W. P. (2003). Power electronics. Converters, applications and design (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Musavi, F., Eberle, W., & Dunford, W. G. (2011). A high-performance single-phase bridgeless interleaved pfc converter for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle battery chargers. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 47(4), 1833–1843. doi:10.1109/TIA.2011.2156753.
Ogata, K. (2010). Modern control engineering. Instrumentation and controls series. Englewood Cliffs: prentice hall.
Rabello, A. L., Sousa, G. C. D., & Vieira J. L. F. (1997). A fully protected push-pull current-fed DC–DC converter. In Industrial electronics, control and instrumentation (pp. 587–592)
Report, A. (1999). Understanding boost power stages in switching power supplies. Technical report, Texas Instruments Incorporated.
Ridley, R. (2011). Power supply design: Control. Power Supply Design, Ridley Engineering, Incorporated.
Tajuddin, M. F. N., Ghazali, N. H., Siong, T. C., & Ghazali, N. (2009). Modelling and simulation of modified unipolar pwm scheme on a single phase DC–AC converter using psim. In IEEE student conference on research and development, (SCOReD) 2009 (pp. 328–331). doi:10.1109/SCORED.2009.5443009
Talaat, Y., Hegazy, O., Amin, A., & Lataire, P. (2014). Control and analysis of multiphase interleaved DC/DC boost converter for photovoltaic systems. In Ninth international conference on ecological vehicles and renewable energies (EVER), 2014 (pp. 1–5). doi:10.1109/EVER.2014.6844009
Tzou, Y. Y., & Jung, S. L. (1998). Full control of a pwm DC–AC converter for ac voltage regulation. IEEE Transaction on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 34(4), 1218–1226.
Vishwas, K., Suryanarayana, K., Renukappa, N., & Prabhu, L. (2014). Modeling of multiphase boost converter for solar battery charging system. In: IEEE students’ conference on electrical, electronics and computer science (pp. 1–6)
Zhao, B., Abramovitz, A., & Smedley, K. (2015). Family of bridgeless buck-boost pfc rectifiers. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 30(12), 6524–6527. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2015.2445779.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to M/s HEXMOTO Controls Pvt. Ltd. for extending help during testing phase of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suryanarayana, K., Nagaraja, H.N. Cascaded Bidirectional Converter Topology for 700 W Transformerless High Frequency Inverter. J Control Autom Electr Syst 27, 542–553 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0256-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0256-0