Abstract
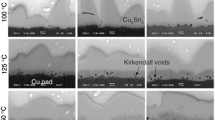
The paper deals with the research and development of lead-free solder for microelectronics in consideration of the environmental, economic, and qualitative aspects. The main aim of this paper is to study the influence of In additives to the complex properties of solder joints. The SnCu0.67In2.0 solder alloys were used for the research. They had been confronted with the most commonly used SnAg3.0Cu0.5 solder in the electronics industry in terms of melting temperatures, wetting properties, microstructures, and costs. Thermo-Calc software was used for phase’s composition prediction. The solder joint reliability was assessed to evaluate the thermal cycling test in the range from −40 to 150 °C. Altogether, 1,500 cycles were carried out. Solder joints were exposed to the thermal cycling due to practice requirement. Optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (EDX microanalysis), and shear strength test were used for the evolution of microstructure, structural integrity, and mechanical strength of thermal-cycled solder joints. Designed SnCu0.67In2.0 solder alloys reached the most suitable result for microelectronic.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Metal Prices all metal prices [online]. [cit. 2010-01-10]. http://www.metalprices.com/
Laurila T (2010) Impurity and alloying effects on interfacial reaction layers in Pb-free soldering. Mater Sci Eng. R: Reports, Corrected Proof
Rizvi JM (2005) Effect of alloying elements on properties and microstructures of SnAgCu solders. J Electron Mater 34:1115–1122. [cit. 20.01.2011]. Dostupné na internete http://www.scopus.com/
Šebo P (2008) Influence of thermal cycling on shear strength of Cu–Sn3.5AgIn–Cu joints with various content of indium. J Alloys Compd 463(1–2):168–172, Elsevier Science
Cheng MD (2004) Intermetallic compounds formed during the reflow and aging of Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu and Sn-20ln-2Ag-0.5Cu solder ball grid array packages. J Electron Mater 33(3):71–180 [cit. 20.05.2011]. http://www.scopus.com/. ISSN 03615235
Satyanarayan, Prabhu KN (2011) Reactive wetting, evolution of interfacial and bulk IMCs and their effect on mechanical properties of eutectic Sn-Cu solder alloy. Adv Colloid Interf Sci, In Press, Corrected Proof, Available online 17 May 2011, [cit. 20.06.2011].http://www.scopus.com/. ISSN 0001–8686
Niwat M, Kannachai K (2012) Evolution of intermetallic compounds between Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu low-silver lead-free solder and Cu substrate during thermal aging original research article. J Mater Sci Technol 28(1):53–59
El-Daly AA, Hammad AE (2012) Enhancement of creep resistance and thermal behavior of eutectic Sn–Cu lead-free solder alloy by Ag and In-additions original research article. Mater Des 40:292–298
Yang SC, Ho CE, Chang CW, Kao CR (2006) Rapid communication: strong concentration effect on the soldering reactions between Sn-based solders and Cu. J Mater Res 21:2436–2439
Zhao J, Qi L, Wang X-M, Wang L (2004) Influence of Bi on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solder. J Alloys Compd 375:196–201
Yen YW, Chou WT, Tseng YU, Lee C, Hsu CL (2008) Investigation of dissolution behavior of metallic substrates and intermetallic compound in molten lead-free solders. J Electron Mater 37:73–83
Chandra Rao BSS, Kumar KM, Zeng KY, Tay AAO, Kripesh V (2009) Effect of strain rate and temperature on tensile flow behaviour of SnAgCu nanocomposite solders. 11th Electronic Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC). p 272–277
Yu DQ a kol (2004) Improvement on the microstructure stability, mechanical and wetting properties of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder with the addition of rare earth elements. J Alloys Compd 376 (1–2):170–175, [cit. 20.01.2011]. Dostupné na internete http://www.scopus.com/. ISSN 0925–8388
PAN JJ, XQ a kol (2007) Development of new lead-free solder. Weld Technol 36:55–56. [cit. 20.01.2011]. Dostupné na internete http://www.scopus.com/
Yoon JW, Kim SW, Jung SB (2005) IMC morphology, interfacial reaction and joint reliability of Pb-free Sn–Ag–Cu solder on electrolytic Ni BGA substrate. J Alloys Compd 392:247–252
Tian Y, Wang C, Liu D (2004) Thermomechanical behaviour of PBGA package during laser and hot air reflow soldering. Model Simul Mater Sci Eng 12:235–243
Cheng F, Gao F, Nishikawa H, Takemoto T (2009) Interaction behavior between the additives and Sn in Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu based solder alloys and the relevant joint solderability. J Alloy Compd 472:530–534
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by VEGA Grant No. 1/0455/14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Doc. IIW-2469, recommended for publication by Commission XVII “Brazing, Soldering, and Diffusion Bonding.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodúlová, E., Šimeková, B., Kovaříková, I. et al. Research and development of lead-free solder for microelectronics in consideration of the environmental and qualitative aspects. Weld World 58, 719–727 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-014-0154-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-014-0154-7