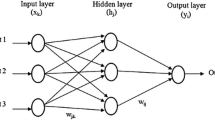
Abstract
The paper presents an endeavor to predict the percentage yarn strength utilization (% SU) in cotton woven fabrics using artificial neural network approach. Fabrics in plain, 2/2 twill, 3/1 twill and 4-end broken twill weaves having three pick densities and three weft counts in each weave have been considered. Different artificial neural network models, with different set of input parameters, have been explored. It has been found that % SU can be predicted fairly accurately by only five fabric parameters, namely the number of load bearing and transverse yarns per unit length, the yarn crimp % in the load bearing and transverse directions and the float length of the weave. Trend analysis of the artificial neural network model has also been carried out to see how the various parameters affect the % SU. The results indicate that while an increase in the number of load bearing or transverse yarns increases the % SU, an increase in the float length and the crimp % in the yarns have a detrimental effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- % SU :
-
Percentage strength utilization
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- N e :
-
English count of the yarn
- NL and NT :
-
Number of load bearing and transverse yarns per 2.5 cm in a sample
- L and T:
-
Load bearing and transverse yarns
- MAPE:
-
Mean Absolute Percentage Error
- MSE:
-
Mean Squared Error
- SL, ST :
-
Single yarn strength of load bearing and transverse yarns
- CL, CT :
-
Crimp % in load bearing and transverse yarns
- FL :
-
Float length of the weave
- p L :
-
Spacing between load bearing yarns
- VT :
-
Binding force of transverse yarns on the load bearing yarn
References
F.T. Pierce, The geometry of cloth structure. J. Text. Inst. 28(3), T45–T96 (1937)
A. Kemp, An extension of Peirce’s cloth geometry to the treatment of non-circular threads. J. Text. Inst. 49(1), T44–T48 (1958)
J.B. Hamilton, A general system of woven fabric geometry. J. Text. Inst. 55, 66 (1964)
B. Olofsson, A general model of a fabric as a geometric mechanical structure. J. Text. Inst. 55(11), T541 (1964)
G.A.V. Leaf, R.D. Anandjiwala, A generalized model of plain woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 55, 92 (1985)
R.D. Anandjiwala, G.A.V. Leaf, Large scale extension and recovery of plain woven fabrics, part-I: theoretical. Text. Res. J. 61, 619 (1991)
R.D. Anandjiwala, G.A.V. Leaf, Large scale extension and recovery of plain woven fabrics. Part-II: experimental and discussion. Text. Res. J. 61(12), 743–755 (1991)
S. Kawabata, M. Niwa, H. Kawai, The finite-deformation theory of plain weaves. Part II: the uniaxial-deformation theory. J. Text. Inst. 64(2), 47 (1973)
S. Kawabata, M. Niwa, H. Kawai, The finite-deformation theory of plain weaves. Part I: the biaxial-deformation theory. J. Text. Inst. 64(2), 21 (1973)
T.V. Sagar, P. Potluri, J.W.S. Hearle, Mesoscale modelling of interlaced fibre assemblies using energy method. Comput. Mater. Sci. 28, 49 (2003)
A.A. Shahpurwala, P. Schwartz, Modeling woven fabric tensile strength using statistical bundle theory. Text. Res. J. 59, 26 (1989)
G. Chen, X. Ding, Breaking progress simulation and strength prediction of woven fabric under uni-axial tensile loading. Text. Res. J. 76, 875 (2006)
J. Fan, L.A. Hunter, Worsted fabric expert system. Part II: an artificial neural network model for predicting the properties of worsted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 68, 763 (1998)
D. Bhattacharjee, V.K. Kothari, A neural network system for prediction of thermal resistance of textile fabrics. Text. Res. J. 77, 4 (2007)
B.K. Behera, R. Mishra, Artificial neural network-based prediction of aesthetic and functional properties of worsted suiting fabrics. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 19(5), 259 (2007)
M. Zeydan, Modelling the woven fabric strength using artificial neural network and Taguchi methodologies. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 20(2), 104 (2008)
B.K. Behera, R. Guruprasad, Predicting bending rigidity of woven fabrics using artificial neural networks. Fibers Polymers 11(8), 1187 (2010)
A. Majumdar, A. Ghosh, S.S. Saha, A. Roy, S. Barman, D. Panigrahi, A. Biswas, Empirical modelling of tensile strength of woven fabrics. Fibers Polymers 9(2), 240 (2008)
D.P. Dobnik, M. Brezocnik, Prediction of the ultraviolet protection of cotton woven fabrics dyed with reactive dystuffs. Fibers Text. East. Eur. 17(72), 55 (2009)
D.E. Rumelhart, G. Hinton, R.J. Williams, Learning Internal representations by error propagation, in Parallel Distributed Processing, vol 1, ed. by D.E. Rumelhart, J.L. McClelland (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1986), p. 318
S. Haykin, Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation, 2nd edn. (Pearson Education, Singapore, 2004), p. 161
A. Majumdar, Soft computing in fibrous materials engineering. Text. Progress 43(1), 1 (2011)
S. Rajasekaran, G.A.V. Pai, Neural networks, fuzzy logic and genetic algorithms: synthesis and applications (Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, 2003), p. 42
J.M. Zurada, Introduction to artificial neural systems (Jaico Publishing House, Mumbai, 2003), p. 175
P. Grosberg, The geometrical properties of plain cloths, in Structural Mechanics of Fibers, Yarns and Fabrics, vol. 1, ed. by J.W.S Hearle, P. Grosberg, S. Backer (Wiley Interscience, New York, 1969) p. 325
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful to Vardhaman Textiles Ltd., India for manufacturing of fabrics at C.P.D.C., Mahavir Spinning Mills—Textile Division Textiles, Baddi, H.P., India and Shahi Exports Pvt. Ltd. (Unit of Sarla Fabrics Ltd. Ghaziabad, U.P.), India for desizing and scouring of the fabrics in relaxed form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S. Prediction of Yarn Strength Utilization in Cotton Woven Fabrics using Artificial Neural Network. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. E 96, 151–157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-014-0049-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-014-0049-6