Abstract
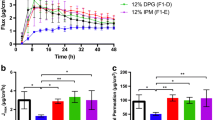
Fentanyl is a potent opioid used as an analgesic for pain therapy. Fentanyl patches have been developed using patch design technologies that use the transdermal route. The aim of this study was to compare the adhesion and dissolution properties of two fentanyl patches, Fentadur® (Pfizer Inc., USA) and Durogesic DTrans® (Janssen-Cilag, Inc., USA), which were designed as a reservoir and a matrix, respectively. For the characterization of fentanyl patches, a 180° peel adhesion test and a dissolution test were performed at 12 and 100 μg/h of fentanyl patches. Specifically, the dissolution of fentanyl patches was tested at 32 and 40 °C using the USP apparatus 6 and the released fentanyl was analyzed using LC–MS/MS. Fentadur® and Durogesic DTrans® had acceptable adhesion forces over 150 gf using 12 mm of fentanyl patches. Comparing adhesion forces of Fentadur® and Durogesic DTrans®, Fentadur® had lower adhesion force values than Durogesic DTrans®. The release of fentanyl in Fentadur® was lower than that in Durogesic DTrans®, except for 100 μg/h Fentadur® at 40 °C over 12–48 h. The results show that Fentadur® and Durogesic DTrans® had the different properties of adhesion and dissolution, which could be critical factors for the prediction of clinical use.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ah Y-C, Choi J-K, Choi Y-K, Ki H-M, Bae J-H (2010) A novel transdermal patch incorporating meloxicam: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Int J Pharm 385:12–19
Azarmi S, Roa W, Benberg RL (2007) Current perspectives in dissolution testing of conventional and novel dosage forms. Int J Pharm 328:12–21
Banerjee S, Chattopadhyay P, Ghosh A, Datta P, Veer V (2014) Aspect of adhesives in transdermal drug delivery systems. Int J Adhes Adhes 50:70–84
Cilurzo F, Gennari CG, Minghetti P (2012) Adhesive properties: a critical issue in transdermal patch development. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 9:33–45
Coopman V, Cordonnier J, Pien K, Varenbergh DV (2007) LC–MS/MS analysis of fentanyl and norfentanyl in a fatality due to application of multiple Durogesic® transdermal therapeutic systems. Forensic Sci Int 169(2–3):223–227
Ghassabian S, Moosavi SM, Valero YG, Shekar K, Fraser JF, Smith MT (2014) High-throughput assay for simultaneous quantification of the plasma concentrations of morphine, fentanyl, midazolam and their major metabolites using automated SPE coupled to LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 903:126–133
Gupta H, Babu RJ (2013) Transdermal delivery: product and patent update. Recent Patient Drug Deliv Formul 7:184–205
Lane ME (2013) The transdermal delivery of fentanyl. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 84:449–455
Nair RS, Ling TN, Abdul Shukkoor MS, Manicham B (2013) Matrix type transdermal patches of captopril: ex vivo permeation studies through excised rat skin. J Pharm Res 6:774–779
Pichayakorn W, Suksaeree J, Boonme P, Taweepreda W, Amnuaikit T, Ritthidej GC (2013) Deproteinised natural rubber used as a controlling layer membrane in reservoir-type nicotine transdermal patches. Chem Eng Res Des 91:520–529
Prodduturi S, Smith GJ, Wokovich AM, Doub WH, Westenberger BJ, Buhse L (2009) Reservoir based fentanyl transdermal drug delivery systems: effect of patch age on drug release and skin permeation. Pharm Res 26:1344–1352
Prodduturi S, Sadrieh N, Wokovich AM, Doub WH, Westenberger BJ, Buhse L (2010) Transdermal delivery of fentanyl from matrix and reservoir systems: effect of heat and compromised skin. J Pharm Sci 99:2357–2366
Ruby PK, Pathak SM, Aggarwal D (2014) Critical attributes of transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS)—a generic product development review. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 40(11):1421–1428
Schulz M, Fussnegger B, Bodmeier R (2011) Influence of adsorbents in transdermal matrix patches on the release and the physical state of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 77:240–248
Shahzad Y, Louw R, Gerber M, Du Plessis J (2015) Breaching the skin barrier through temperature modulations. J Control Release 202:1–13
Tanojo H, Bouwstra JA, Junginger HE, Bodde HE (1997) In vitro human skin barrier modulation by fatty acids: skin permeation and thermal analysis studies. Pharm Res 14:42–49
Valenta C, Auner BG (2004) The use of polymers for dermal and transdermal delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58:279–289
Wokovich AM, Prodduturi S, Doub WH, Hussain AS, Buhse LF (2006) Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 64:1–8
Yang Z, Teng Y, Wang H, Hou H (2013) Enhancement of skin permeation of bufalin by limonene via reservoir type transdermal patch: formulation design and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Int J Pharm 447:231–240
Acknowledgments
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.All authors (T.S. Kim, S.-E. Jin, B. Sun, M.-S. Kim, S.-J. Hwang) declare that they have no confolict of interest. This work was partially supported by Pfizer Inc. and also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2014R1A2A2A01005059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T.S., Jin, SE., Sun, B. et al. Comparison of adhesion and dissolution of fentanyl patches: Fentadur® and Durogesic DTrans® . Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 45, 475–480 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0195-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0195-y