Abstract
Background:
Infectious complications occur in most of the patients receiving high-dose therapy (HDT) and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). The objective of the study was to analyze of the type and incidence of infectious complications during neutropenia after HDT and autologous HSCT with respect to risk factors related to stem cell transplant setting in patients treated for hematological malignancies in a single center.
Patients and Methods:
A total number of 314 patients diagnosed for Hodgkin's disease (HD), non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), multiple myeloma (MM) or acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) were included in the study. Analysis of risk factors and outcome of infections after HDT and autologous HSCT was performed.
Results:
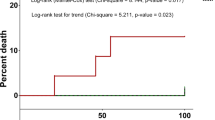
Infectious complications during neutropenia after HDT occurred in 92.3% patients. Microbiologically documented infections (MDI) accounted for 38.9% of febrile episodes, clinically documented infections (CDI) for 9.3%, and fever of unknown origin (FUO) for 51.7% cases. Median time to defervescence with antibiotic therapy was seven days for FUO and nine days for documented infections (p < 0.001). Duration of infection correlated with the length of very severe neutropenia (p < 0.001). Response to first-line antibiotic therapy was seen in 34% patients. Infections were fatal in 12 (3.8%) patients. The highest probability of infection was observed for ALL and AML patients, especially these conditioned with total body irradiation (TBI).
Conclusion:
Patients at high risk of infection after autologous HSCT were identified as those with acute leukemia and those after conditioning with TBI, all with prolonged neutropenia. We suggest that newer prophylactic strategies should be administered to these groups of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lidia Gil and Jan Styczynski contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil, L., Styczynski, J. & Komarnicki, M. Infectious Complication in 314 Patients after High-Dose Therapy and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Risk Factors Analysis and Outcome. Infection 35, 421–427 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6350-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6350-2