Abstract
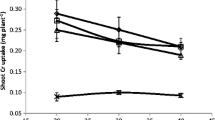
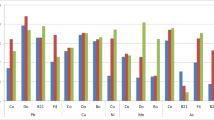
The role of rhizospheric microbes of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) in Cr uptake from hydroponic culture was investigated. The control group was exposed to Cr in range of 25–100 mg L−1 containing a control itself (with no metal addition). The experimental group received same Cr treatments, but in addition was exposed to antibiotic treatment in order to inhibit rhizospheric bacteria. The range of Cr accumulated in the roots was 3–7.65 mg L−1; in stem it ranged 2.15–42.4 mg kg−1; while in leaves, the range of Cr content was 13.7–15 mg kg−1. Overall, Cr uptake in A. donax (without rhizobacterial inhibition) was root < leaf < stem. However, the amount of Cr uptake in plants with rhizobacterial inhibition was significantly less (~4.6-folds in 100 mg L−1 Cr treatment) than those without such inhibition clearly highlighting that rhizobacterial inhibition decreased the Cr uptake. The experimental results clearly demonstrated that the inhibition of the rhizobacterial populations had great influence on the Cr uptake. However, Cr uptake could not be completely inhibited as some metal uptake was observed after the rhizobacterial inhibition although it was significantly less than the Cr uptake of plants without such inhibition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RA, Angle JS, Delorme TA, Chaney RL, van Berkum P, Moawad H, Ghanem K, Ghozlan HA (2003) Rhizobacterial effects on nickel extraction from soil and uptake by Alyssum murale. New Phytol 158:219–224
Ahemad M, Kibret M (2014) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci 26(1):1–20
Bahijri SM, Mufti AM (2002) Beneficial effects of chromium in people with type 2 diabetes, and urinary chromium response to glucose load as a possible indicator of status. Biol Trace Elem Res 85:97–109
Bar-Ness E, Chen Y, Hadar Y, Marchner H, Romheld V (1991) Siderophores of Pseudomonas putida as an iron source for dicot and monocot plants. Plant Soil 130(1–2):231–241
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37:241–250
Blaylock MJ, Salt DE, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31:860–865
Brezeanu C, de fotosinteză VP (2005) Permeabilitatea membranelor Ui conţinutul de clorofilă din frunzele de pepene galben în timpul procesului de creUtere. Lucrări Jtiinţifice Ser Hortic 48(1–2):635–638
Brígido C, Glick BR (2015) Phytoremediation using rhizobia. In: Ansari AA, Gill SS, Gill R, Lanza GR, Newman L (eds) Phytoremediation, 1st edn. Springer, Germany, pp 95–114
Caggiano R, Sabia S, D’Emilio M, Macchiato M, Anastasio A, Ragosta M, Paino S (2005) Metal levels in fodder, milk, dairy products, and tissues sampled in ovine farms of Southern Italy. Environ Res 99:48–57
Caussy D, Gochfeld M, Gurzau E, Neagu C, Ruedel H (2003) Lessons from case studies of metals: investigating exposure, bioavailability, and risk. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 56(1):45–51
Cervantes C, Campos-Garcia J, Debars S, Gutierrez-Corona F, Loza-Tavera H, Carlos-Tarres-Guzman M, Moreno-Sanchez R (2001) Interaction of chromium with microgenesis and plants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:335–347
Chaudri AM, McGrath SP, Giller KE (1992) Survival of the indigenous population of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii in soil spiked with Cd, Zn, Cu and Ni salts. Soil Biol Biochem 24(7):625–632
Chen YX, Wang YP, Lin Q, Luo YM (2005) Effect of copper-tolerant rhizosphere bacteria on mobility of copper in soil and copper accumulation by Elsholtzia splendens. Environ Int 31(6):861–866
de Souza MP, Chu D, Zhao M, Zayed AM, Ruzin SE, Schichnes D, Terry N (1999) Rhizosphere bacteria enhance selenium accumulation volatilization by Indian Mustard. Plant Physiol 119:565–573
Gadd GM (1990) Heavy metal accumulation by bacteria and other microorganisms. Experientia 46(8):834–840
Gisbert C, Ros R, de Haro A, Walker DJ, Bernal MP, Serrano R, Navarro-Avino J (2003) A plant genetically modified that accumulates Pb is especially promising for phytoremediation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:440–445
Glick BR (2015) Introduction to plant growth-promoting bacteria. In: Beneficial plant–bacterial interactions, 1st edn. Springer, Germany, pp 1–28
Hasnain S, Sabri AN (1996) Growth stimulation of Triticum Aestivum seedlings under Cr-stresses by non rhizospheric pseudomonad strains. Abstracts of the 7th international symposium on biological nitrogen fixation with non-legumes, Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, p 36
Herawati N, Suusuki S, Hayashi K, Rivai IF, Koyama H (2000) Cadmium, copper, and zinc levels in rice and soil Japan, Indonesia and China by soil type. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:33–39
Hiltner L (1904) Über neuere Erfahrungen und Probleme auf dem Gebiet der Berücksichtigung der Gründüngung und Brache. Arb Dtsch Landwirt Ges 98:59–78
Hoagland D, Arnon DI (1938) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Bull Calif Agric Stat 346:1–39
Huang Y, Tao S, Chen YJ (2005) The role of arbuscular mycorrhiza on change of heavy metal speciation in rhizosphere of maize in wastewater irrigated agriculture soil. J Environ Sci 17(2):276–280 (in Chinese)
Ianculov I, Palicica R, Butnariu M, Dumbravă D, Gergen I (2005) Obţinerea, în stare cristalină a clorofilei din cetină de brad (Abies alba) Ui de pin (Pinus sylvestris). Rev Chim 56(4):441–443
Imsande J (1998) Iron, sulfur, and chlorophyll deficiencies: a need for an integrative approach in plant physiology. Physiol Plant 103(1):139–144
Jamil M, Zeb S, Anees M, Roohi A, Ahmed I, ur Rehman S, Rha E (2014) Role of Bacillus licheniformis in phytoremediation of nickel contaminated soil cultivated with rice. Int J Phytorem 16(6):554–571
Kausar S, Mahmood Q, Raja IA, Khan A (2012) Potential of Arundo donax to treat chromium contamination. Ecol Engine 42:256–259
Kramer U, Talke IN, Hanikenne M (2007) Transition metal transport. FEBS Lett 581:2263–2272
Kumar KV, Srivastava S, Singh N, Behl HM (2009) Role of metal resistant plant growth promoting bacteria in ameliorating fly ash to the growth of Brassica juncea. J Hazard Mater 170:51–57
Liu W, Wang Q, Wang B, Hou J, Luo Y, Tang C, Franks AE (2015) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance the growth and Cd uptake of Sedum plumbizincicola in a Cd-contaminated soil. J Soil Sedim 15(5):1191–1199
McGrath SP, Zhao F-J (2003) Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids from contaminated soils. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:1–6
Mirza N, Mahmood Q, Pervez A, Ahmad R, Farooq R, Shah MM, Azim MR (2010a) Phytoremediation potential of Arundo donax in arsenic contaminated synthetic wastewater. Bioresour Technol 101:5815–5819
Mirza N, Pervez A, Mahmood Q, Ahmed SS (2010b) Phytoremediation of Arsenic (As) and Mercury (Hg) from contaminated soil. World Appl Sci J 8(1):113–118
Mirza N, Pervez A, Mahmood Q, Shah MM (2011) Ecological restoration of arsenic contaminated soil by Arundo donax L. Ecol Eng 37:1949–1956
Mukesh KR, Kumar P, Singh M, Singh A (2008) Toxic effect of heavy metals in livestock health. Veteran World 1:28–30
Plaza S, Tearall KL, Zhao FJ, Buchner P, McGrath SP, Hawkesford MJ (2007) Expression and functional analysis of metal transporter genes in two contrasting ecotypes of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. J Exp Bot 58:1717–1728
Reid CP, Szaniszlo PJ, Crowley DE (1986) Siderophore involvement in plant iron nutrition. In: Swinburne TR (ed) Iron siderophores and plant diseases. Plenum Press, New York, pp 29–42
Sabeen M, Mahmood Q, Irshad M, Fareed I, Khan A, Ullah F, Hussain J, Hayat Y, Tabassum S (2013) Cadmium phytoremediation by Arundo donax L. from contaminated soil and water. BioMed Res Int 2013:1–9
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel WW, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194
Sharma P, Goyal P, Srivastava S (2007a) Biosorption of trivalent and hexavalent chromium from aqueous systems using shelled Moringa oleifera seeds (SMOS). Chem Speciat Bioavailab 19:175–181
Sharma P, Kumari P, Srivastava MM, Srivastava S (2007b) Ternary biosorption studies of Cd (II), Cr(III) and Ni (II) on shelled Moringa oleifera seeds. Bioresour Technol 98:474–477
Shinwari KI, Shah AU, Afridi MI, Zeeshan M, Hussain H, Hussain J, Ahmad O (2015) Application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soil. Asian J Multidiscip Stud 3(4):179–185
Tak HI, Ahmad F, Babalola OO (2013) Advances in the application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metals. In: Whitacre DM (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, vol 223. Springer, New York, pp 33–52
Titah HS, Abdullah SRS, Mushrifah I, Anuar N, Basri H, Mukhlisin M (2013) Effect of applying rhizobacteria and fertilizer on the growth of Ludwigia octovalvis for arsenic uptake and accumulation in phytoremediation. Ecol Engine 58:303–313
Titah HS, Abdullah SRS, Mushrifah I, Anuar N, Basri H, Mukhlisin M (2014) Phytotoxicity and uptake of arsenic by Ludwigia octovalvis in a pilot reed bed system. Environ Engine Sci 31(2):71–79
van der Lelie D (1998) Biological interactions: the role of soil bacteria in the bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soils. In: Vangronsveld J, Cunningham SD (eds) Metal contaminated soils: in situ inactivation and phytorestoration. Springer, New York, pp 31–50 (Chapter 3)
Verbruggen N, Hermans C, Schat H (2009) Molecular mechanisms of metal hyperaccumulation in plants. New Phytol 181:759–776
Wang YJ, Liu SP, Chen XR (1993) A survey on winter birds in Shenzhen Futian Mangrove. Ecol Sci 12:74–84
Wang B, Liu L, Goa Y, Chen J (2009) Improved phytoremediation of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by Trichoderma mutant constructed by restriction enzyme-mediated integration (REMI) in cadmium polluted soil. Chemosphere 74:1400–1403
Wenzel WW, Adriano DC, Salt D, Smith R (1999) Phytoremediation: a plant–microbe-based remediation system. In: Adriano DC, Bollag J-M, Frankenberger WT Jr, Sims RC (eds) Agronomy monograph, vol 37. Madison, USA, pp 457–508
Whiting SN, de Souza MP, Terry N (2001) Rhizosphere bacteria mobilize Zn for hyperaccumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens. Environ Sci Technol 35(15):3144–3150
Wong WS, Tan SN, Ge L, Chen X, Yong JWH (2015) The importance of phytohormones and microbes in biofertilizers. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Bacterial metabolites in sustainable agroecosystem. Springer, Germany, pp 105–158
Xiong J, He Z-li, Liu D, Mahmood Q, Yang X-E (2008) The role of bacteria in the heavy metals removal and growth of Sedum alfredii Hance in an aqueous medium. Chemosphere 70:489–494
Zhao FJ, Mcgrath SP, Grossland AR (1994) Comparison of three wet digestion methods for the determination of plant sulphur by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP–AES). Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25:407–418
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of Higher Education of Pakistan Grant No. 2122 to conduct the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaheen, S., Mahmood, Q., Pervez, A. et al. Chromium uptake by giant reed under rhizobacterial inhibition. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 1581–1590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0996-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-0996-1