Abstract
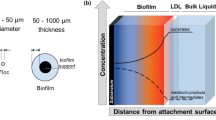
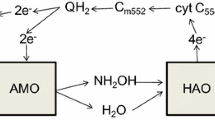
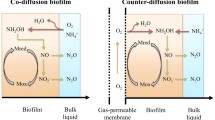
Aerobic biofilm systems are increasingly used for household wastewater treatment, but little is known about their potential to emit nitrous oxide in response to different loading conditions. We studied nitrification and nitrous oxide production in a biofilm reactor that was continuously fed with three different mixtures of household wastewater. Higher proportions of blackwater increased nitrification activity, which resulted in enhanced nitrite accumulation and nitrous oxide emissions. Applying a conceptual biofilm model together with the results of ancillary batch incubations suggested that this was caused by a higher proportion of slowly degradable compounds in blackwater. Increasing amounts of blackwater would result in less oxygen depletion by heterotrophic degradation in outer biofilm layers, leading to nitrite accumulation by enhanced ammonia oxidation as well as electron limitation of denitrification in anoxic biofilm layers. Under such conditions, nitrifier denitrification and incomplete heterotrophic denitrification would be the prevailing sources of nitrous oxide emission. These assumptions are supported by an exponential increase in the determined emission factor (nitrous oxide relative to oxidized ammonia), which accounted for 0.7 with 20 % blackwater, 1.1 with 50 % blackwater, and 8.5 with 100 % blackwater in the wastewater load.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarnink AJA, Elzing A (1998) Dynamic model for ammonia volatilization in housing with partially slatted floors, for fattening pigs. Livest Prod Sci 53:153–169. doi:10.1016/s0301-6226(97)00153-x
Andreottola G, Damiani E, Foladori P, Nardelli P, Ragazzi M (2003) Treatment of mountain refuge wastewater by fixed and moving bed biofilm systems. Water Sci Technol 48:169–177
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48:835–852
Azizi S, Valipour A, Sithebe T (2013) Evaluation of different wastewater treatment processes and development of a modified attached growth bioreactor as a decentralized approach for small communities. Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2013/156870
Beaumont HJE et al (2002) Nitrite reductase of Nitrosomonas europaea is not essential for production of gaseous nitrogen oxides and confers tolerance to nitrite. J Bacteriol 184:2557–2560. doi:10.1128/jb.184.9.2557-2560.2002
Daude D, Stephenson T (2003) Moving bed biofilm reactors: a small-scale treatment solution. Water Sci Technol 48:251–257
de Graaff MS, Zeeman G, Temmink H, van Loosdrecht MCM, Buisman CJN (2010) Long term partial nitritation of anaerobically treated black water and the emission of nitrous oxide. Water Res 44:2171–2178
Dulekgurgen E, Dogruel S, Karahan Ö, Orhon D (2006) Size distribution of wastewater COD fractions as an index for biodegradability. Water Res 40:273–282
Elenter D, Milferstedt K, Zhang W, Hausner M, Morgenroth E (2007) Influence of detachment on substrate removal and microbial ecology in a heterotrophic/autotrophic biofilm. Water Res 41:4657–4671. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.050
Fux C, Huang D, Monti A, Siegrist H (2004) Difficulties in maintaining long-term partial nitritation of ammonium-rich sludge digester liquids in a moving-bed biofilm reactor (MBBR). Water Sci Technol 49:53–60
Gujer W, Henze M, Mino T, van Loosdrecht M (1999) Activated sludge model no. 3. Water Sci Technol 39:183–193. doi:10.1016/s0273-1223(98)00785-9
Hocaoglu SM, Insel G, Cokgor EU, Baban A, Orhon D (2010) COD fractionation and biodegradation kinetics of segregated domestic wastewater: black and grey water fractions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1241–1249. doi:10.1002/jctb.2423
ICCP (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Cambridge University Press, New York
Itokawa H, Hanaki K, Matsuo T (2001) Nitrous oxide production in high-loading biological nitrogen removal process under low COD/N ratio condition. Water Res 35:657–664. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00309-2
Kampschreur MJ, Temmink H, Kleerebezem R, Jetten MSM, van Loosdrecht MCM (2009) Nitrous oxide emission during wastewater treatment. Water Res 43:4093–4103. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.001
Kindaichi T, Ito T, Okabe S (2004) Ecophysiological interaction between nitrifying bacteria and heterotrophic bacteria in autotrophic nitrifying biofilms as determined by microautoradiography-fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1641–1650. doi:10.1128/aem.70.3.1641-1650.2004
Larsen TA, Alder AC, Eggen RIL, Maurer M, Lienert J (2009) Source separation: will we see a paradigm shift in wastewater handling. Environ Sci Technol 43:6121–6125. doi:10.1021/es803001r
Law Y, Ni BJ, Lant P, Yuan ZG (2012) N2O production rate of an enriched ammonia-oxidising bacteria culture exponentially correlates to its ammonia oxidation rate. Water Res 46:3409–3419. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.043
Logan BE, Hermanowicz SW, Parker DS (1987) A fundamental model for trickling filter process design. J Water Pollut Control Fed 59:1029–1042
Molstad L, Dörsch P, Bakken LR (2007) Robotized incubation system for monitoring gases (O2, NO, N2O, N2) in denitrifying cultures. J Microbiol Methods 71:202–211. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2007.08.011
Pan YT, Ni BJ, Yuan ZG (2013) Modeling electron competition among nitrogen oxides reduction and N2O accumulation in denitrification. Environ Sci Technol 47:11083–11091. doi:10.1021/es402348n
Penn R, Hadari M, Friedler E (2012) Evaluation of the effects of greywater reuse on domestic wastewater quality and quantity. Urban Water J 9:137–148. doi:10.1080/1573062x.2011.652132
Poth M, Focht DD (1985) N-15 kinetic-analysis of N2O production by Nitrosomonas europaea—an examination of nitrifier dentrification. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1134–1141
Ravishankara AR, Daniel JS, Portmann RW (2009) Nitrous oxide (N2O): the dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. Science 326:123–125. doi:10.1126/science.1176985
Richardson D, Felgate H, Watmough N, Thomson A, Baggs E (2009) Mitigating release of the potent greenhouse gas N2O from the nitrogen cycle—could enzymic regulation hold the key? Trends Biotechnol 27:388–397. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.03.009
Rittmann BE, Regan JM, Stahl DA (1994) Nitrification as a source of soluble organic substrate in biological treatment. Water Sci Technol 30:1–8
Schmidt I (2009) Chemoorganoheterotrophic growth of Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrosomonas eutropha. Curr Microbiol 59:130–138. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9409-8
Schreiber F, Loeffler B, Polerecky L, Kuypers MMM, de Beer D (2009) Mechanisms of transient nitric oxide and nitrous oxide production in a complex biofilm. ISME J 3:1301–1313. doi:10.1038/ismej.2009.55
Schreiber F, Wunderlin P, Udert KM, Wells GF (2012) Nitric oxide and nitrous oxide turnover in natural and engineered microbial communities: biological pathways, chemical reactions, and novel technologies. Front Microbiol 3:24. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2012.00372
Todt D, Heistad A, Jenssen PD (2014) Load and distribution of organic matter and nutrients in a separated household wastewater stream. Environ Technol. doi:10.1080/09593330.2014.997300
Upadhyay AK, Hooper AB, Hendrich MP (2006) NO reductase activity of the tetraheme cytochrome c (554) of Nitrosomonas europaea. J Am Chem Soc 128:4330–4337. doi:10.1021/ja055183+
Wanner O, Reichert P (1996) Mathematical modeling of mixed-culture biofilms. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:172–184
Wanner O, Eberl HJ, Morgenroth E, Noguera DR, Picioreanu C, Rittmann BE, van Loosdrecht MCM (2006) Mathematical modeling of biofilms. IWA Publishing, London
Wunderlin P, Mohn J, Joss A, Emmenegger L, Siegrist H (2012) Mechanisms of N2O production in biological wastewater treatment under nitrifying and denitrifying conditions. Water Res 46:1027–1037. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.080
Yang JJ, Trela J, Plaza E, Tjus K (2013) N2O emissions from a one stage partial nitrification/anammox process in moving bed biofilm reactors. Water Sci Technol 68:144–152. doi:10.2166/wst.2013.232
Zhang RH, Day DL, Christianson LL, Jepson WP (1994) A computer-model for predicting ammonia release rates from swine manure pits. J Agric Eng Res 58:223–229. doi:10.1006/jaer.1994.1052
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Norwegian Research Council (Grant No skattefunn-226774). A special thanks also to Associate Prof. Arve Heistad for the support to the pilot-scale experiment setup and Olga Popovic for helping with analysis work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todt, D., Dörsch, P. Nitrous oxide emissions in a biofilm loaded with different mixtures of concentrated household wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3405–3416 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0778-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0778-1