Abstract
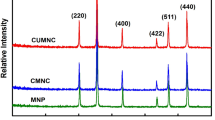
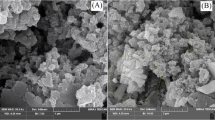
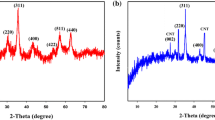
A series of new (MgO) x CuO and (MgO) x MnO2 nanocomposites were prepared and used as adsorbent for removal of As3+, Hg2+, and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution with high capacity and detection limit. These nanocomposites were synthesized with different molar ratios by sonochemical method in alkaline solution using polyvinylpyrrolidone as a capping agent and were characterized by FTIR, AAS, UV–Vis spectroscopy, and TEM and SEM imaging. The maximum heavy metal ions adsorption was achieved for (MgO)0.32CuO and (MgO)2.9MnO2 nanocomposites assisted by 3-min sonication using ultrasound. Adsorbent capacity of (MgO)0.32CuO reached 500.0 mg/g and detection limit was 0.1 ppb for As3+. Also (MgO)2.9MnO2 nanocomposite adsorbed 457.1 mg/g of Hg2+ and 461.2 mg/g of Pb2+. Extremely low detection limits of 1.5 and 2.0 ppb were obtained for Hg(II) and Pb(II) ions, respectively, which are much lower than the WHO allowable limits. So, these nanocomposites should be excellent candidate for heavy metal removal with advantage of high capacity, high sensitivity, cost effectiveness and easy preparation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Rahmani, H.Z. Mousavi, M. Fazli, Effect of nanostructure alumina on adsorption of heavy metals. Desalination 253, 94–100 (2010)
L.X. Yang, Y.J. Zhu, H. Tong, W. Wang, Submicrocubes and highly oriented assemblies of MnCO3 synthesized by ultrasound agitation method and their thermal transformation to nanoporous Mn2O3. Ultrason. Sonochem. 14, 259–265 (2007)
Q. Oua, L. Zhoua, S. Zhaob, H. Genga, J. Haoa, Y. Xua, H. Chena, X. Chena, Self-templated synthesis of bifunctional Fe3O4@MgSiO3 magnetic sub-microspheres for toxic metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 180, 121–127 (2012)
P. Mondal, C.B. Majumder, B. Mohanty, Laboratory based approaches for arsenic remediation from contaminated water: recent developments. J. Hazard. Mater. B 137, 464–479 (2006)
B.K. Mandal, K.T. Suzuki, Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58, 201–235 (2002)
Q. Li, W. Tang, S. Gao, J.K. Shang, Arsenic (III, V) removal from aqueous solution by ultrafine α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized from solvent thermal method. J. Hazard. Mater. 192, 131–138 (2011)
D. Gibicar, M. Horvat, M. Logar, V. Fajon, I. Falnoga, R. Ferrara, E. Lanzillotta, C. Ceccarini, B. Mazzolai, B. Denby, J. Pacyna, Human exposure to mercury in the vicinity of chlor-alkali plant. Environ. Res. 109, 355–367 (2009)
D. Karunasagar, M. Krishna, Y. Anjaneyulu, J. Arunachalam, Studies of mercury pollution in a lake due to a thermometer factory situated in a tourist resort: kodaikkanal, India. Environ. Pollut. 143, 153–158 (2006)
F. Zahir, S.J. Rizwi, S.K. Haq, R.H. Khan, Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 20, 5 (2005)
L. Donga, Z. Zhua, Y. Qiub, J. Zhaoa, Removal of lead from aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/magnetite composite adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 165, 827–834 (2010)
World Health Organization, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, vol. 11. (WHO Press, Switzerland, 2008), p. 1
M.J. Gonzalez Munoz, M.A. Rodriguez, S. Luque, J.R. Alvarez, Recovery of heavy metals from metal industry waste waters by chemical precipitation and nanofiltration. Desalination 200, 742–744 (2006)
H.M. Baker, A.M. Massadeh, H.A. Younes, Natural Jordanian zeolite: removal of heavy metal ions from water samples using column and batch methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 157, 319–330 (2009)
M.G. Khedr, Nanofiltration and low energy reverse osmosis for rejection of radioactive isotopes and heavy metal cations from drinking water sources. Desalin. Water. Treat. 2, 342–350 (2009)
USEPA, Arsenic occurrence in public water supplies, in EPA-815-R-00-023 (Washington, DC, 2000)
D. Mohan, C.U. Pittman, Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 142, 1–53 (2007)
M. Kobya, E. Demirbas, E.I.M. Senturk, Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from apricot stone. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 4 (2005)
J.U.K. Oubagaranadin, Z.V.P. Murthy, Adsorption of divalent lead on a montmorillonite−illite type of clay. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 10627–10636 (2009)
S. Sun, L. Wang, A. Wang, Adsorption properties of crosslinked carboxymethyl-chitosan resin with Pb(II) as template ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 136(3), 930–937 (2006)
X. Wang, Y. Zheng, A. Wang, Fast removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 168, 970–977 (2009)
C. Gao, W. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Xu, Controllable fabrication of mesoporous MgO with various morphologies and their absorption performance for toxic pollutants in water. Cryst. Growth Des. 8, 3785–3790 (2008)
J. Lee, S. Mahendra, P.J.J. Alvarez, Nanomaterials in the construction industry: A review of their applications and environmental health and safety considerations. ACS Nano 4, 3580–3590 (2010)
Z. Ren, G. Zhang, J.P. Chen, Adsorptive removal of arsenic from water by an iron–zirconium binary oxide adsorbent. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 358, 230–237 (2011)
Z. Xu, Q. Li, S. Gao, J.K. Shang, As(III) removal by hydrous titanium dioxide prepared from one-step hydrolysis of aqueous TiCl4 solution. Water Res. 44, 5713–5721 (2010)
A. Cao, J.D. Monnell, C. Matranga, J. Wu, L. Cao, D. Gao, Hierarchical nanostructured copper oxide and its application in arsenic removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 18624–18628 (2007)
W. Yantasee, C.L. Warner, T. Sangvanich, R.S. Addleman, T.G. Carter, R.J. Wiacek, G.E. Fryxell, C. Timchalk, M.G. Warner, Removal of heavy metals from aqueous systems with thiol functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 5114–5119 (2007)
K.P. Lisha, S.M. Maliyekkal, T. Pradeep, Manganese dioxide nanowhiskers: a potential adsorbent for the removal of Hg(II) from water. Chem. Eng. J. 160, 432–439 (2010)
B.Y. Song, Y. Eom, T.G. Lee, Removal and recovery of mercury from aqueous solution using magnetic silica nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 4754–4759 (2011)
S. Recillas, A. Garcia, E. Gonzalez, E. Casals, V. Puntes, X. Font, A. Sanchez, Use of CeO2, TiO2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the removal of lead from water: toxicity of nanoparticles and derived compounds. Desalination 227, 213–220 (2011)
J. Wang, S. Zheng, Y. Shao, J. Liu, D. Zhu, Z. Xu, Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 349, 293–299 (2010)
M.A. Karimi, S.H. Roozbahani, R. Asadiniya, A. HatefiMehrjardi, M.H. Mashhadizadeh, R. Behjatmanesh-Ardakani, M. Mazloum-Ardakani, H. Kargar, S.M. Zebarjad, Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles and nanocomposite of ZnO and MgO by sonochemical method and their application for zinc polycarboxylate dental cement preparation. Int. Nano Lett. 1, 43–51 (2011)
H. Chen, J. He, Facile synthesis of monodisperse manganese oxide nanostructures and their application in water treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 17540–17545 (2008)
N.N. Nassar, Rapid removal and recovery of Pb(II) from wastewater by magnetic nanoadsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 184, 9 (2010)
M. Farooq, A. Ramli, R. Subbarao, Some studies on the synthesis and surface properties of mixed oxides of alumina and magnesia. J. Chem. Environ. 15, 715–720 (2011)
A. Trass, H. Elshamy, I. Mehasseb, M. Kemary, CuO nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, optical properties and interaction with amino acids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2997–3001 (2012)
F. Davar, F. Mohandes, M. Salavati, Synthesis and characterization manganese oxide nanobundles from decomposition of manganese oxalate. Inorg. Chim. Acta 362, 3663–3668 (2009)
F. Gu, C. Li, H. Cao, W. Shao, Y. Hu, J. Chen, A. Chen, Crystallinity of Li-doped MgO: Dy3+ nanocrystals via combustion process and their photoluminescence properties. J. Alloys Compd. 453, 361–365 (2008)
S. Reddy, B.E.K. Swamy, H. Jayadevapp, CuO nanoparticle sensor for the electrochemical determination of dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 61, 78–86 (2012)
X.L. Luo, J.J. Xu, W. Zhao, H.Y. Chen, A novel glucose ENFET based on the special reactivity of MnO2 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 19, 1295–1300 (2004)
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of University of Kurdistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Askari, P., Faraji, A., Khayatian, G. et al. Effective ultrasound-assisted removal of heavy metal ions As(III), Hg(II), and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by new MgO/CuO and MgO/MnO2 nanocomposites. J IRAN CHEM SOC 14, 613–621 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-1011-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-016-1011-y