Abstract
Diverticulitis is frequently encountered in the elderly population. Because elderly patients typically have decreased physiologic reserve and other complicating comorbid conditions, treatment decisions must be carefully made. Like with younger patients, uncomplicated diverticulitis is usually treated successfully with antibiotics alone. Frequent contact with the patient is required so that worsening is promptly detected, and a treatment escalation, if needed, is not missed. Treatment of complicated diverticulitis depends on the specific complication. For perforated diverticulitis, resection with end colostomy has been the traditional operation, but in recent years, its use has been challenged by other options including resection with anastomosis and proximal diversion and laparoscopic lavage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
West L, Cole S, Goodkind D, He W. Current population reports: special studies. 65+ in America: 2010. In: Bureau USC, editor. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2014.
Boss G, Seegmiller JE. Age-related physiologic changes and their clinical significance. West J Med. 1981;135:434.
Peppas G, Bliziotis IA, Oikonomaki D, Falagas ME. Outcomes after medical and surgical treatment of diverticulitis: a systematic review of the available evidence. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22(9):1360–8.
Boles R, Jordan SM. The clinical significance of diverticulosis. Gastroenterology. 1985;35(6):579–82.
Munson K, Hensien MA, Jacob LN, Robinson AM, Liston WA. Diverticulitis: a comprehensive follow-up. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996;39(3):318–22.
Etzioni D, Mack TM, Beart Jr RW, Kaiser AM. Diverticulitis in the United States: 1998-2005: changing patterns of disease and treatment. Ann Surg. 2009;249(2):210–7.
Farrell R, Farrell JJ, Morrin MM. Diverticular disease in the elderly. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2001;30(2):475–96.
Gear J, Ware A, Fursdon P, Mann JI, Nolan DJ, Brodribb AJ, et al. Symptomless diverticular disease and intake of dietary fibre. Lancet. 1979;1(8115):511–4.
Hackford A, Veidenheimer MC. Diverticular disease of the colon. Current concepts and management. Surg Clin North Am. 1985;65(2):347–63.
Painter N, Burkitt DP. Diverticular disease of the colon, a 20th century problem. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975;4(1):3–21.
Martel J, Raskin JB. History, incidence, and epidemiology of diverticulosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;42(10):1125–7.
Shabanzadeh D, Wille-Jørgensen P. Antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14 ed2012.
Chabok A, Påhlman L, Hjern F, Haapaniemi S, Smedh K, AVOD Study Group. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotics in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. BJS. 2012;99(4):532–9.
Chow A. Appendicitis and diverticulitis. In: Hoeprich PDJM, Ronald AR, editors. Infectious disease: a treatise of infectious processes. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1994. p. 878–81.
Ferzoco L, Raptopoulos V, Silen W. Acute diverticulitis. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1521–6.
Lau K, Spilsbury K, Farooque Y, Kariyawasam SB, Owen RG, Wallace MH, et al. Is colonoscopy still mandatory after a CT diagnosis of left-sided diverticulitis: can colorectal cancer be confidently excluded? Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54(10):1265–70.
Hinchey E, Schaal PG, Richards GK. Treatment of perforated diverticular disease of the colon. Adv Surg. 1978;12:85–109.
Siewert B, Tye G, Kruskal J, Sosna J, Opelka F, Raptopoulos V, et al. Impact of CT-guided drainage in the treatment of diverticular abscesses: size matters. Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(3):680–6.
Ambrosetti P, Chautems R, Soravia C, Peiris-Waser N, Terrier F. Long-term outcome of mesocolic and pelvic diverticular abscesses of the left colon: a prospective study of 73 cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005;48:787–91.
Favuzza J, Friel JC, Kelly JJ, Perugini R, Counihan TC. Benefits of laparoscopic peritoneal lavage for complicated sigmoid diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24(7):797–801.
Singh B, May K, Coltart I, Moore NR, Cunningham C. The long-term results of percutaneous drainage of diverticula abscess. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008;90(4):297–301.
Elagili F, Stocchi L, Ozuner G, Mody R, Baker ME, Kiran RP. Predictors of postoperative outcomes for patients with diverticular abscess initially treated with percutaneous drainage. Am J Surg. 2015;209(4):703–8.
Kaiser A, Jiang JK, Lake JP, Ault G, Artinyan A, Gonzalez-Ruiz C, et al. The management of complicated diverticulitis and the role of computed tomography. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(4):910–7.
Nelson R, Ewing BM, Wengert TJ, Thorson AG. Clinical outcomes of complicated diverticulitis managed nonoperatively. Ann J Surg. 2008;196:969–74.
Gaertner W, Willis DJ, Madoff RD, Rothenberger DA, Kwaan MR, Belzer GE, et al. Percutaneous drainage of colonic diverticular abscess: is colon resection necessary? Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56(5):622–6. This article demonstrates that a conservative approach may be appropriate in certain patients including the elderly.
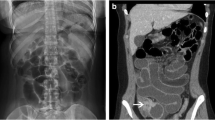
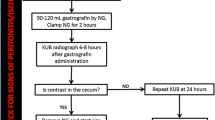
Ericksen A, Krasna MJ, Mast BA, Nosher JL, Brolin RE. Use of gastrointestinal contrast studies in obstruction of the small and large bowel. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990;33(1):56–64.
Moore F, Moore EE, Berlew CC, Coimbra R, McIntyre RC, Davis J, et al. Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: management of complicated diverticulitis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(6):1365–71.
Bordeianou L, Hodin R. Controversies in the surgical management of sigmoid diverticulitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007;11(4):542–8.
Abbas S. Resection and primary anastomosis in acute complicated diverticulitis, a systematic review of the literature. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007;22(4):351–7.
Salem L, Flum DR. Primary anastomosis or Hartmann’s procedure for patients with diverticular peritonitis? A systematic review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004;47(11):1953–64.
Salem L, Anaya DA, Roberts KE, Flum DR. Hartmann’s colectomy and reversal in diverticulitis: a population-level assessment. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005;48:5.
Oberkofler C, Rickenbacher A, Raptis DA, Lehmann K, Villiger P, Buchili C, et al. A multicenter randomized clinical trial of primary anastomosis or Hartmann’s procedure for perforated left colonic diverticulitis with purulent or fecal peritonitis. Ann Surg. 2012;256(5):826–7.
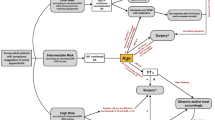
Feingold D, Steele SR, Lee S, Kaiser A, Boushey R, Buie WD, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2014;57(3):284–94. This article provides the most recent guidelines for the treatment of diverticulitis as determined by the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons.
Cirocchi R, Trastulli S, Vettoretto N, Milani D, Cavaliere D, Renzi C, et al. Laparoscopic peritoneal lavage: a definitive treatment for diverticular peritonitis or a “bridge” to elective laparoscopic sigmoidectomy?: a systematic review. Medicine. 2015;94(1), e334.
Afshar S, Kurer MA. Laparoscopic peritoneal lavage for perforated sigmoid diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis. 2012;14(2):135–42.
Vennix S, Musters GD, Mulder IM, Swank HA, Consten EC, Belgers EH, et al. Laparoscopic peritoneal lavage or sigmoidectomy for perforated diverticulitis with purulent peritonitis: a multicentre, parallel-group, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet. 2015;386(10000):1269–77. This article contains the published results from a randomized control trial comparing laparoscopic lavage and sigmoidectomy showing that a minimally invasive procedure may not be superior to the gold standard.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Elizabeth C. He declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Genevieve B. Melton declares that her spouse is an employee of St. Jude Medical and has received financial support through grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Agency for Healthcare Research Quality (AHRQ).
Joshua M. Eberhardt declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Emergency Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, E.C., Melton, G.B. & Eberhardt, J.M. Care of the Elderly Patient with Acute Diverticulitis. Curr Geri Rep 5, 49–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-016-0160-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13670-016-0160-2