Abstract
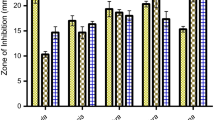
The present study explored the phytochemical screening, in vitro antimicrobial activity, in vivo antiemetic and antinociceptive potentialities of methanol extract of Erioglossum rubiginosum leaves for the first time. Crude extract of E. rubiginosum and different fractions were assayed for in vitro antimicrobial activity using disc diffusion method. The antiemetic activity was evaluated using chick emesis model; while acetic acid induced writhing test in mice was conducted to determine the antinociceptive activity. Different extracts possess carbohydrate, flavonoids, saponin, tannin, alkaloids, phenol and cardiac-glycoside in varying concentrations. Among different extractives, only the chloroform soluble fraction showed promising antimicrobial activity (zone of inhibition 6.5 to 10 mm) in comparison to positive control−ciprofloxacin, against wide range of tested microorganisms. In antiemetic assay, all the extracts showed significant (P < 0.05) activities; among them both chloroform and carbon tetrachloride extracts showed better activity (inhibition 91 and 90 % respectively) compared to the standard drug metoclopramide (inhibition 74 %). In antinociceptive assay, remarkable writhing inhibitory activity was found for the chloroform extract (53.05 %), while the standard drug diclofenac sodium inhibited 42.01 % writhing of the test animals (P < 0.05). Therefore, further studies and compound isolation are suggested to confirm the mechanism of the key compounds as the plant extracts of E. rubiginosum revealed potential biological and pharmacological activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amico-Roxas M, Caruso A, Trombadore S, Scifo R, Scapagnini U (1984) Gangliosides antinociceptive effects in rodents. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 272:103–117
Bhandari P, Andrews PLR (1991) Preliminary evidence for the involvement of the putative 5-HT4 receptor in zacopride- and copper sulfate-induced vomiting in the ferret. Eur J Pharmacol 204:273–280
Borison H, Fairbanks V (1952) Mechanism of veratrum-induced emesis in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 105:317–325
Calixto JB, Beirith A, Ferreira J, Santos ARS, Filho VC, Yunes RA (2000) Naturally occurring antinociceptive substances from plants. Phytother Res 14:401–418
Collier HO, Dinneen LC, Johnson CA, Schneider C (1968) The abdominal constriction response and its suppression by analgesic drugs in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 32:295–310
Debnath PC, Das A, Islam A, Islam MA, Hassan MM, Uddin SMG (2013) Membrane stabilization–a possible mechanism of action for the anti-inflammatory activity of a Bangladeshi medicinal plant: Erioglossum rubiginosum (Bara Harina). Pharmacogenomics J 5:104–107. doi:10.1016/j.phcgj.2013.04.001
Dewan SMR, Amin MN, Adnan T, Uddin SMN, Shahid-Ud-Daula AFM, Sarwar G, Hossain MS (2013) Investigation of analgesic potential and in vitro antioxidant activity of two plants of Asteraceae family growing in Bangladesh. J Pharm Res 6:599–603. doi:10.1016/j.jopr.2013.05.016
Fukui H, Yamamoto M, Sasaki S, Sato S (1994) Possible involvement of peripheral 5-HT4 receptors in copper sulfate-induced vomiting in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 257:47–52
Gurib-Fakim A (2006) Medicinal plants: traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol Asp Med 27:1–93
Hossain H, Jahan IA, Howlader SI, Dey SK, Hira A, Ahmed A (2013) Phytochemical screening and anti-nociceptive properties of the ethanolic leaf extract of Trema cannabina Lour. Adv Pharm Bull 3:103–108
Hossain MM, Ahamed SK, Dewan SMR, Hassan MM, Istiaq A, Islam MS, Moghal MMR (2014) In vivo antipyretic, antiemetic, in vitro membrane stabilization, antimicrobial, and cytotoxic activities of different extracts from Spilanthes paniculata leaves. Biol Res 47:45. doi:10.1186/0717-6287-47-45
Mondal H, Saha S, Awang K, Hossain H, Ablat A, Islam MK, Jahan IA (2014) Central-stimulating and analgesic activity of the ethanolic extract of Alternanthera sessilis in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:398. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-398
Rahman MA, Islam MS (2013) Antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of the phytochemicals of whole Leucas aspera extract. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:273–279
Raja DK, Jeganathan NS, Manavalan R (2013) In vitro antimicrobial activity and phytochemical analysis of Cassia auriculata Linn. Int Curr Pharm J 2:105–108
Raju GS, Moghal MMR, Dewan SMR, Amin MN, Billah M (2013) Characterization of phytoconstituents and evaluation of total phenolic content, anthelmintic, and antimicrobial activities of Solanum violaceum Ortega. (Family: Solanaceae). Avicenna J Phytomed 3:313–320
Ramzi AAM, Salah AAA, Hasson S, Althawab FMN, Alaghbari SAZ, Lindequist U (2010) Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities and phytochemical screening of some yemeni medicinal plants. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 7:323–330
Sahu MC, Padhy RN (2013) In vitro antibacterial potency of Butea monosperma Lam. against 12 clinically isolated multidrug resistant bacteria. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 3:217–226
Serrano MC, Ramírez M, Morilla D, Valverde A, Chávez M, Espinel-Ingroff A, Claro R, Fernández A, Almeida C, Martín-Mazuelos E (2004) A comparative study of the disc diffusion method with the broth microdilution and Etest methods for voriconazole susceptibility testing of Aspergillus spp. J Antimicrob Chemother 53:739–742
Triozzi PL, Laszlo J (1987) Optimum management of nausea and vomiting in cancer chemotherapy. Drugs 34:136–149
Van Wagenen BC, Larsen R, Cardellina JH, Ran dazzo D, Lidert ZC, Swithenbank C (1993) Ulosantoin, a potent insecticide from the sponge Ulosa ruetzleri. J Org Chem 58:335–337
Whittle BA (1964) The use of changes in capillary permeability in mice to distinguish between narcotic and nonnarcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 22:246–249
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Pharmacy, Noakhali Science and Technology University for giving the permission to use laboratory facilities throughout the study.
Ethical statement
All study animals received human care according to the criteria outlined in the ‘Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals’, 8th edition, prepared by the National Academy of Sciences and published by the National Institute of Health.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajib, A.I., Dewan, S.M.R., Das, A. et al. In vitro antimicrobial activity study and in vivo antiemetic, antinociceptive activity evaluation of leaves extract of Erioglossum rubiginosum using experimental animal model. Orient Pharm Exp Med 15, 135–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-015-0181-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-015-0181-y