Abstract
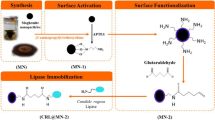
A lipase from Candida rugosa was covalently immobilized on the cellulose acetate (CA)-coated Fe2O3 nanoparticles for the biocatalysis applications. The characterization of the Fe2O3-CA particles before and after immobilization of lipase was studied. The biocatalyst was assayed for the glycerolysis of olive oil in solvent system. The effect of reaction time, temperature, molar ratio of glycerol to oil and amount of lipase on the glycerolysis reaction was investigated. Results showed that the high yield of monoglycerides (49.7 wt%) and diglycerides (17.4 wt%) was achieved at 40 °C temperature and 0.02 g of lipase with relatively low glycerol to oil molar ratio (2:1) within 4 h of reaction time. Kinetics of immobilized lipase followed Lineweaver–Burk model with lower K m and V max values when compared to the free lipase. The immobilized lipase showed higher activity, thermal stability and reusability compared to the free lipase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghamgui H., Miled N., Rebai A., Chaabouni M.K., Gargouri Y.: Production of monoolein by immobilized Staphylococcus simulans lipase in a solvent-free system: optimization by response surface methodology. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 39, 717–723 (2006)
Singh A.K., Mukhopadhyay M.: Overview of fungal lipase: a review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 166, 486–520 (2012)
Singh A.K., Mukhopadhyay M.: Response surface methodology for optimizing the glycerolysis reaction of olive oil by Candida rugosa lipase. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 20(1), 127–134 (2014)
Kaewthong W., Sirisansaneeyakul S., Prasertsan P., H-Kittikun A.: Continuous production of monoacylglycerols by glycerolysis of palm olein by immobilized lipase. Process Biochem. 40, 1525–1530 (2005)
Dalla-Vecchia R., Sebrao D., Nascimento M.G., Soldi V.: Carboxymethyl cellulose and poly (vinyl alcohol) used as a film support for lipases immobilization. Process Biochem. 40, 2677–2682 (2005)
Singh A.K., Mukhopadhyay M.: Olive oil glycerolysis with the immobilized lipase Candida antarctica in a solvent free system. Grasas Aceites 63, 202–208 (2012)
Singh A.K., Mukhopadhyay M.: Immobilization of Candida antarctica lipase onto cellulose acetate-coated Fe2O3 nanoparticles for olive oil glycerolysis. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 1225–1232 (2014)
Kim M.H., An S., Won K., Kim H.J., Lee S.H.: Entrapment of enzymes into cellulose–biopolymer composite hydrogel beads using biocompatible ionic liquid. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 75, 68–72 (2012)
Singh A.K., Mukhopadhyay M.: Optimization of lipase-catalyzed glycerolysis for mono and diglyceride production using response surface methodology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 2463–2474 (2014)
Chen Y.Z., Ching C.B., Xu R.: Lipase immobilization on modified zirconia nanoparticles: Studies on the effects of modifiers. Process Biochem. 44, 1245–1251 (2009)
Lee D.G., Ponvel K.M., Kim M., Hwang S., Ahn I.S., Lee C.H.: Immobilization of lipase on hydrophobic nano-sized magnetite particles. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 57, 62–66 (2009)
Ranjbakhsh E., Bordbar A.K., Abbasi M., Khosropour A.R., Shams E.: Enhancement of stability and catalytic activity of immobilized lipase on silica-coated modified magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 179, 272–276 (2012)
Namdeo M., Bajpai S.K.: Immobilization of α-amylase onto cellulose-coated magnetite (CCM) nanoparticles and preliminary starch degradation study. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 59, 134–139 (2009)
Wu Y., Wang Y.J., Luo G.S., Dai Y.Y.: In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4- chitosan nanoparticles for lipase immobilization by cross-linking and oxidation in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 3459–3464 (2008)
Stellmach B.: Bestimmungs Methoden Enzyme, pp. 229. Chinese Light Industry Press, Beijing (1992)
Li Y., Gao F., Wei W., Qu J.B., Ma G.H., Zhou W.Q.: Pore size of macroporous polystyrene microspheres affects lipase immobilization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 66, 182–189 (2010)
Bragger J.M., Dunn R.V., Daniel R.M.: Enzyme activity down to −100 °C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1480, 278–282 (2000)
Changa M.Y., Juangb R.S.: Activities, stabilities, and reaction kinetics of three free and chitosan–clay composite immobilized enzymes. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 36, 75–78 (2005)
Borgo C.A., Lazarin A.M., Kholin Y.V., Landers R., Gushikem Y.: The ion exchange properties and equilibrium constants of Li+, Na+ and K+ on zirconium phosphate highly dispersed on a cellulose acetate fibers surface. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 15, 50–57 (2004)
Tsioptsias C., Sakellariou K.G., Tsivintzelis I., Papadopoulou L., Panayiotou C.: Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate–Fe2O3 composite nanofibrous materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 81, 925–930 (2010)
Damstrup M.L., Jensen T., Sparsø F.V., Kiil S.Z., Jensen A.D., Xu X.: Solvent optimization for efficient enzymatic monoacylglycerol production based on a glycerolysis reaction. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 8, 559–564 (2000)
Zhong N., Li L., Xu X., Cheong L., Li B., Hu S., Zhao X.: An efficient binary solvent mixture for monoacylglycerol synthesis by enzymatic glycerolysis. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 86, 783–789 (2009)
McNeill G.P., Yamane T.: Further improvements in the yield of monoglycerides during enzymatic glycerolysis of fats and oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 68, 6–10 (1991)
Tüter M., Aksoy H.A.: Solvent-free glycerolysis of palm and palm kernel oils catalyzed by commercial1, 3-specific lipase from Humicola lanuginosa and composition of glycerolysis products. Biotechnol. Lett. 22, 31–34 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, M. Enzymatic Synthesis of Mono- and Diglyceride Using Lipase From Candida rugosa Immobilized Onto Cellulose Acetate-Coated Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 2553–2561 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2036-3