Abstract
Presenting new functions, basic displacement functions (BDFs), a novel method is introduced for the analysis of arbitrarily tapered thin plates in preference to primarily mathematically based methodologies. BDFs are obtained through applying unit load theorem and considering two orthogonal strips of unit width in tapered plates based on static deformations. It is shown that new shape functions and consequently structural matrices could be derived in terms of BDFs through a mechanical approach. On the other hand, BDFs could be used to calculate new shape functions, whereas Hermitian functions are used in several elements such as ACM and BFS. It is demonstrated that the accuracy of these new shape functions is significantly improved by considering the geometrical and mechanical properties of the plate element in the evaluation of the structural matrices. So, contrary to usual shape functions used in FE methods, they are susceptible to the thickness variation and then higher accuracy and more rapid convergence could be expected with fewer elements. In order to verify the competency of the proposed method, several numerical examples for classical boundary conditions are carried out and the results are compared with those in the literature.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
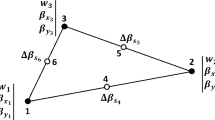
- a :
-
Length of the plate along x direction
- b :
-
Length of the plate along y direction
- b :
-
Vector of BDFs
- D(x, y):
-
Flexural rigidity of the plate at \({(x,y)=(E h^{3}(x,y)/[{12(1-\nu^{2})}])}\)
- E :
-
Young’s modulus of elasticity
- F :
-
Vector of nodal forces
- F ii :
-
Nodal flexibility matrices of i-th node
- h(x, y):
-
Thickness of the plate at (x, y)
- i, j :
-
Indices or positive integers (1, 2, 3, …)
- K :
-
Stiffness matrix of element
- l :
-
Taper factor of the plate in y direction
- M :
-
Mass matrix of element
- N :
-
Vector of shape functions
- o′:
-
A point with arbitrary coordinates (x, y)
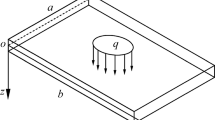
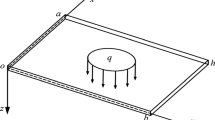
- q z (x, y):
-
External transverse load
- r :
-
Taper factor of the plate in x direction
- s :
-
Longitudinal coordinate along plate in x direction
- t :
-
Longitudinal coordinate along plate in y direction
- w :
-
Transverse displacement at (x, y)
- x :
-
Variable along longitudinal coordinate of plate element in x direction
- y :
-
Variable along longitudinal coordinate of plate element in y direction
- \({\alpha}\) :
-
Taper ratio for thickness of plate in the x direction
- \({\beta}\) :
-
Taper ratio for thickness of plate in the y direction
- \({{\bf \Delta}_i}\) :
-
Vector containing \({[w\,{\theta_x}\,{\theta_y}]_i^T}\) for node \({i (i=1,{\ldots},4)}\)
- \({\nabla^{2}}\) :
-
Two-dimensional Laplacian operator
- \({{\bf \Sigma}}\) :
-
Matrix containing nodal stiffness matrices of all nodes
- \({\theta_x}\) :
-
Rotation angle due to bending along x direction
- \({\theta_y}\) :
-
Rotation angle due to bending along y direction
- \({\nu}\) :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- \({\rho}\) :
-
Mass density per unit volume
- Ω :
-
Non-dimensional eigenfrequency \({(=\omega a^{2}\sqrt{{\rho h_1}/{D_1}})}\)
- ω :
-
Eigenfrequency (frequency of free vibration)
References
Leissa A.W.: The free vibration of rectangular plates. J. Sound Vib. 31, 257–293 (1973)
Liew K.M., Xiang Y., Kitipornchai S.: Transverse vibration of thick rectangular plates—I. Comprehensive sets of boundary conditions. Comput. Struct. 49, 1–29 (1993)
Liew K.M., Hung K.C., Lim M.K.: Vibration of Mindlin plates using boundary characteristic orthogonal polynomials. J. Sound Vib. 182, 77–90 (1995)
Liew K.M., Hung K.C., Lim M.K.: Three-dimensional vibration of rectangular plates: effects of thickness and edge constraints. J. Sound Vib. 182, 709–727 (1995)
Liew K.M., Teo T.M.: Three-dimensional vibration analysis of rectangular plates based on differential quadrature method. J. Sound Vib. 220, 577–599 (1999)
Xing Y., Liu B.: Closed form solutions for free vibrations of rectangular Mindlin plates. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 25, 689–698 (2009)
Hashemi S.H., Arsanjani M.: Exact characteristic equations for some of classical boundary conditions of vibrating moderately thick rectangular plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 819–853 (2005)
Lim C.W., Cui S., Yao W.A.: On new symplectic elasticity approach for exact bending solutions of rectangular thin plates with two opposite sides simply supported. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 5396–5411 (2007)
Yu S.N., Xiang Y., Wei G.W.: Matched interface and boundary (MIB) method for the vibration analysis of plates. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 25, 923–950 (2009)
Liu Y., Li R.: Accurate bending analysis of rectangular plates with two adjacent edges free and the others clamped or simply supported based on new symplectic approach. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 856–865 (2010)
Liu B., Xing Y.: Exact solutions for free in-plane vibrations of rectangular plates. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 24, 556–567 (2011)
Eftekhari S.A., Jafari A.A.: High accuracy mixed finite element-Ritz formulation for free vibration analysis of plates with general boundary conditions. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 1312–1344 (2012)
Al-Kaabi S.A., Aksu G.: Free vibration analysis of Mindlin plates with parabolically varying thickness. Comput. Struct. 34, 395–399 (1990)
Malhotra S.K., Ganesan N., Veluswami M.A.: Vibrations of orthotropic square plates having variable thickness (parabolic variation). J. Sound Vib. 119, 184–188 (1987)
Katsikadelis J.T., Sapountzakis E.J.: BEM solution to dynamic analysis of plates with variable thickness. Comput. Mech. 7, 369–379 (1991)
Kukreti A.R., Farsa J., Bert C.W.: Fundamental frequency of tapered plates by differential quadrature. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 118, 1221–1238 (1992)
Gutierrez R., Laura P.: Vibrations of rectangular plates with linearly varying thickness and non-uniform boundary conditions. J. Sound Vib. 178, 563–566 (1994)
Gutierrez R., Laura P.: Analysis of vibrating circular plates of non-uniform thickness by the method of differential quadrature. Ocean Eng. 22, 97–100 (1995)
Afonso S.M.B., Hinton E.: Free vibration analysis and shape optimization of variable thickness plates and shells—I. Finite element studies. Comput. Syst. Eng. 6, 27–45 (1995)
Rossi R., Belles P., Laura P.: Transverse vibration of a rectangular cantilever plates with thickness varying in a discontinuous fashion. Ocean Eng. 23, 271–276 (1996)
Bert C.W., Malik M.: Free vibration analysis of tapered rectangular plates by differential quadrature method: a semi-analytical approach. J. Sound Vib. 190, 41–63 (1996)
Barton O.: Fundamental frequency of tapered plates by method of eigensensitivity analysis. Ocean Eng. 26, 565–573 (1999)
Cheung Y.K., Zhou D.: Free vibrations of tapered rectangular plates using a new set of beam functions in Rayleigh–Ritz method. J. Sound Vib. 223, 703–722 (1999)
Bambill D.V., Rossit C.A., Laura P.A.A., Rossi R.E.: Transverse vibrations of an orthotropic rectangular plate of linearly varying thickness and with a free edge. J. Sound Vib. 235, 530–538 (2000)
Ashour A.S.: A semi-analytical solution of the flexural vibration of orthotropic plates of variable thickness. J. Sound Vib. 240, 431–445 (2001)
Ashour A.S.: Vibration of variable thickness plates with edges elastically restrained against translation and rotation. Thin Wall Struct. 42, 1–24 (2004)
Huang M., Ma X.Q., Sakiyama T., Matuda H., Morita C.: Free vibration analysis of orthotropic rectangular plates with variable thickness and general boundary conditions. J. Sound Vib. 288, 931–955 (2005)
Malekzadeh P., Shahpari S.A.: Free vibration analysis of variable thickness thin and moderately thick plates with elastically restrained edges by DQM. Thin Wall Struct. 43, 1037–1050 (2005)
Shufrin I., Eisenberger M.: Vibration of shear deformable plates with variable thickness—first-order and higher-order analyses. J. Sound Vib. 290, 465–489 (2006)
Xu Y.P., Zhou D.: Three-dimensional elasticity solution for simply supported rectangular plates with variable thickness. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 43, 165–176 (2008)
Civalek Ö.: Fundamental frequency of isotropic and orthotropic rectangular plates with linearly varying thickness by discrete singular convolution method. Appl. Math. Model. 33, 3825–3835 (2009)
Attarnejad R.: Basic displacement functions in analysis of non-prismatic beams. Eng. Comput. 27, 733–745 (2010)
Attarnejad R., Shahba A.: Basic displacement functions in analysis of centrifugally stiffened tapered beams. AJSE 36(5), 841–853 (2011)
Attarnejad R., Shahba A., Jandaghi Semnani S.: Application of differential transform in free vibration analysis of Timoshenko beams resting on two-parameter elastic foundation. AJSE 35(2), 125–132 (2010)
Attarnejad R., Shahba A., Jandaghi Semnani S.: Analysis of non-prismatic Timoshenko beams using basic displacement functions. Adv. Struct. Eng. 14, 319–332 (2011)
Attarnejad R., Shahba A., Jandaghi Semnani S.: Application of differential transform in free vibration analysis of Timoshenko beams resting on two-parameter elastic foundation. AJSE 35(2), 125–132 (2010)
Shahba A., Attarnejad R., Tavanaie Marvi M., Shahriari V.: Free vibration analysis of non-uniform thin curved arches and rings using adomian modified decomposition method. AJSE 37(4), 965–976 (2012)
Attarnejad R., Shahba A.: Dynamic basic displacement functions in free vibration analysis of centrifugally stiffened tapered beams: a mechanical solution. Meccanica 46, 1267–1281 (2011)
Pachenari, Z; Attarnejad, R.: Free vibration of tapered Mindlin plates using basic displacement functions. AJSE 39(6), 4433–4449 (2014). doi:10.1007/s13369-014-1071-1
Szilard R.: Theories and Applications of Plate Analysis: Classical, Numerical and Engineering Methods. Wiley, New Jersey (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pachenari, Z., Attarnejad, R. Analysis of Tapered Thin Plates Using Basic Displacement Functions. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 8691–8708 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1407-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1407-x