Abstract
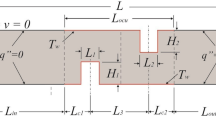
The main focus of the present paper is to apply a novel optimization algorithm called as imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA). In this algorithm the cost function being a function of input parameters has to be optimized. In the present research work, our cost function is the laminar free convection heat transfer in a horizontal cavity with adiabatic vertical and isothermally horizontal walls and adiabatic diverters. The input parameters are the diverter angle with respect to horizon varying from 0◦ to 90◦ and Rayleigh number varying from 6 × 103 to 1.2 × 104. After collecting data, the regression equation of averaged convection heat transfer is obtained as a function of the Rayleigh number and diverter angle. Subsequently, the cost function is optimized using the ICA. Results show that the proposed algorithm is powerful enough to be used for optimizing the cost function. According to the results, in order to obtain the maximum heat transfer, the diverter angle must be 27.9◦ whereas; the Rayleigh number must be 1.2 × 104.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area of the aluminum plate (m2)
- \({A'}\) :
-
Surface area of each insulator placed right and left of the aluminum plate (m2)
- C :
-
Gladstone–Dale coefficient
- e :
-
Thickness of each diverter (mm)
- H :
-
Length of the cavity (mm)
- h y :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient (W/m2 K)
- h ave :
-
Average heat transfer coefficient (W/m2 K)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of air
- L :
-
Length of each diverter (mm)
- Nu y :
-
Local Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pitch of diverters (mm)
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \({q''}\) :
-
Averaged convection heat flux (W/m2)
- \({q_{{\rm cond},\, {\rm hot\,\,wall}, \,{\rm RL}}}\) :
-
Conduction heat transfer due to the contact between the hot wall and adiabatic walls (W)
- \({q_{{\rm cond}, \, {\rm hot\,\,wall},\, {\rm FB}}}\) :
-
Conduction heat transfer due to the contacts between the hot wall and insulators placed front and back of the hot wall (W)
- \({q_{{\rm conv},\, {\rm hot\,wall}}}\) :
-
Convection heat transfer obtained from the fringe patterns of the Mach–Zehnder interferometer (W)
- \({q_{{\rm cond},\,{\rm heater}}}\) :
-
Conduction heat transfer due to the contact between the heater and insulator placed below the heater (W)
- \({q_{\rm heater}}\) :
-
Power of the heater (W)
- \({q_L }\) :
-
Overall thermal dissipation (W)
- q net :
-
Absolute value of the thermal dissipation (W)
- \({q_{{\rm rad},\,{\rm hot wall}}}\) :
-
Radiation heat transfer from the hot wall (W)
- R :
-
Gas constant (J/kg K)
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number based on the cavity side length
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- W :
-
Cavity side length (mm)
- x :
-
Direction normal to the hot surface
- y :
-
Direction along the hot surface
- \({\varepsilon }\) :
-
Fringe shift
- \({\varepsilon '}\) :
-
Emissivity of the aluminum plate
- \({\sigma }\) :
-
Stefan–Boltzmann constant (W/(m2 K4))
- \({\alpha }\) :
-
Absorption coefficient of the aluminum plate (m2/s)
- \({\lambda}\) :
-
Laser wave length (m)
- \({\theta }\) :
-
Diverter angle (°)
- \({\Delta x}\) :
-
Thickness of each adiabatic wall (m)
- \({\Delta {x}'}\) :
-
Thickness of each insulator placed front and back of the hot wall (m)
- \({\Delta {x}''}\) :
-
Thickness of the insulator placed below the heater (m)
- col:
-
Referrers to the colony
- f:
-
Film condition
- imp:
-
Referrers to the imperialist
- pop:
-
Referrers to the population
- ref:
-
Reference condition
- Sc:
-
Cold condition
- Sh:
-
Warm condition
- \({\infty}\) :
-
Ambient condition
References
Horvat, A.; Kljenak, I.; Marn, J.: Two-dimensional large-eddy simulation of turbulent natural convection due to internal heat generation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 44, 3985–3995 (2001)
Hakan, F.; Abu-Nada, E.; Varol, Y.; Chamkha, A.: Natural convection in wavy enclosures with volumetric heat sources. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50, 502–514 (2011)
Sultana, Z.; Hyder Md, N.: Non-darcy free convection inside a wavy enclosure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 34, 136–146 (2007)
Khanafer, K.; Al-Azmi, B.; Marafie, A.; Pop, I.: Non-Darcian effects on natural convection heat transfer in a wavy porous enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 1887–1896 (2009)
Yousefi, T.; Nezhad, S.M.; Bigharaz, M.; Ebrahimi, S.: An experimental study on the effect of partition angle on free-convection heat transfer in a partitioned cavity by laser interferometry method. In: 10th Biennial Conference on Engineering Systems Design and Analysis ESDA, July 12–14, Istanbul, Turkey (2010)
Mahmud S., Fraser R.A.: Magnetohydrodynamic free convection and entropy generation in a square porous cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Tranf. 47, 3245–3256 (2004)
Corcione M.: Effects of the thermal boundary conditions at the sidewalls upon natural convection in rectangular enclosures heated from below and cooled from above. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 42, 199–208 (2003)
Oztop H.F., Dagtekin I., Bahloul A.: Comparison of position of a heated thin plate located in a cavity for natural convection. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 31, 121–132 (2004)
Frederick R.L.: Natural convection in an inclined square enclosure with a partition attached to its cold wall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 32, 87–94 (1989)
Shahid H., Naylor D.: Energy performance assessment of a window with a horizontal Venetian blind. Energy Build. 37, 836–843 (2005)
Karayiannis, T.G.; Ciofalo, M.; Barbaro, G.: On natural convection in a single and two zone rectangular enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 35, 1645–57 (1992)
Safer, N.; Woloszyn, M.; Roux, J.: Three-dimensional simulation with a CFD tool of airflow phenomena in a single floor double-skin façade equipped with a venetian blind. Sol. Energy 79, 193–203 (2005)
Ganzarolli, M.M.; Milanez, L.F.: Natural convection in rectangular enclosures heated from below and symmetrically cooled from the sides. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 1063–1073 (1995)
Aydin, O.; Unal, A.; Ayhan, T.: Natural convection in rectangular enclosures heated from one side and cooled from the ceiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 5, 2345–2355 (1999)
Karami, A.; Rezaei, E.; Mahmoudinezhad, S.; Yousefi, T.: Optimization of free convection heat transfer in a horizontal cylinder beneath an adiabatic ceiling, using an Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 45, 401–407 (2012)
Rezaei, E.; Karami, A.; Shahhosseni, M.; Aghakhani, M.: The optimization of thermal performance of an air cooler equipped with butterfly inserts by the use of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 41, 214–226 (2012)
Karami, A.; Rezaei, E.; Shahhosseni, M.; Aghakhani, M.: Optimization of heat transfer in an air cooler equipped with classic twisted tape inserts using Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 38, 195–200 (2012)
Rezaei, E.; Karami, A.; Shahhosseni, M.; The use of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm for the optimization of heat transfer in an air cooler equipped with butterfly inserts. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 6, 293–301 (2012)
Karami, A.; Yousefi, T.; Ghashghaei, D.; Rezaei, E.: The application of Imperialist Competitive Algorithm in optimizing the free convection heat transfer in a vertical cavity with flow diverters. Int. J. Model. Optim. 1, 289–295 (2011)
Hauf, W.; Grigull, U.: Optical methods in heat transfer. Adv. Heat Transf. 6, 133–366 (1970)
Eckert E.R., Goldstein R.J.: Measurements in Heat Transfer, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1972)
Flack, R.D.: Mach–Zehnder interferometer errors resulting from test section misalignment. Appl. Opt. 17, 985–987 (1978)
Bever, M.B.: Encyclopedia of Materials Science And Engineering, vol. 7. Pergamon, Oxford (1986)
Gudisz, V.G.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K.: Comparison of particle swarm optimization and back propagation as training algorithms for neural networks. In: IEEE, SIS, pp. 110–117. Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. (2003)
Parsopoulos, K.E.; Vrahatis, M.N.: Particle swarm optimization method in multiobjective problems. In: ACM, SAC, pp. 603–607. (2002)
Pezzini, P.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Sudrià à-Andreu, A.: Optimization techniques to improve energy efficiency in power systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15, 2028–2041 (2011)
Chelouah, R.; Siarry, P.: Search applied to global optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 123, 256–270 (2000)
Muttil, N.; Chau, K.W.: Neural network and genetic programming for modelling coastal algal blooms. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 28, 223–238 (2006)
Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W.: A flood forecasting neural network model with genetic algorithm. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 28, 261–273 (2006)
Zhang, B.; Chen, D.; Zhao, W.: Iterative ant-colony algorithm and its application to dynamic optimization of chemical process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 29, 2078–2086 (2005)
Dorigo, M.; Blum, C.: Ant colony optimization theory: a survey. Theor. Comput. Sci. 344, 243–278 (2005)
Pham, D.T.; Soroka, A.J.; Ghanbarzadeh. A.; Koç, E.; Otri, S.; Packianather, M.: Optimising neural networks for identification of wood defects using the Bees Algorithm. In: IEEE, International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Singapore (2006)
Pham, D.T.; Ghanbarzadeh, A.; Koç, E.; Otri, S.: Application of the Bees Algorithm to the training of radial basis function networks for control chart pattern recognition. In: 5th CIRP International Seminar on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering (CIRP ICME). Ischia, Italy (2006)
Rui, X.; Ganesh, K.; Venayagamoorthy G.K.; Donald, C.: Modeling of gene regulatory networks with hybrid differential evolution and particle swarm optimization. Neural Netw. 20, 917–927 (2007)
Yanling,W.U.; Jiangang, L.U.; Youxian, S.: An improved differential evolution for optimization of chemical process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng 16, 228–234 (2008)
Atashpaz-Gargari, E.; Lucas, C.: Imperialist Competitive Algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Singapore (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karami, A., Veysi, F., Mohebbi, S. et al. Optimization of Laminar Free Convection in a Horizontal Cavity Consisting of Flow Diverters Using ICA. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 2295–2306 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0741-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0741-8