Abstract
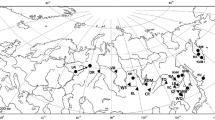
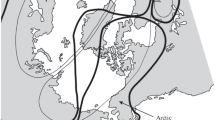
To reveal phylogeographic features of sable (Martes zibellina) in the southeast part of its range, we analyzed variability of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) cytochrome b gene, tRNA (Pro), tRNA (Thr) and control region (D-loop) sequences from 78 specimens in populations of the Russian Far East, northeast China, and Mongolia. Our results revealed the presence of 49 different haplotypes split into two major phylogenetic groups—clades A and B, the latter separated into two clades, B1 and B2. Comparative analysis of D-loop haplotypes in populations originating from the southeast (Russian Far East, China and Mongolia) and the west (northern Urals) portions of sable range indicated that all three mtDNA clades were present in different regional groups. However, highest diversity of clade B1 in northeast China and its nearly complete absence from the Urals suggest that the southeast sable range, being a refuge during Pleistocene glacial periods, can be considered the center of genetic diversification and possibly origin of this species. All divergence estimates fall within the Pleistocene suggesting that Quarternary glaciations played an important role in phylogeographic differentiation of sable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov KG (1967) The Sable in the Commercial Hunting in the Far East. Nauka, Moscow
Anderson E (1970) Quaternary evolution of the genus Martes (Carnivora, Mustelidae). Acta Zool Fenn 130: 1–132
Anderson E (1994) Evolution, prehistoric distribution, and systematics of Martes. In: Buskirk SW, Harestad AS, Raphael MG, Powell RA (eds) Martens, sables, and fishers: biology and conservation. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, pp 13–25
Aris-Brosou S, Excoffier L (1996) The impact of population expansion and mutation rate heterogeneity on DNA sequence polymorphism. Mol Biol Evol 13:494–504
Balmysheva NP, Solovenchuk LL (1999a) Genetic variation of the mitochondrial DNA gene encoding cytochrome b in the Magadan population of sable Martes zibellina L. Russ J Genet 35:1077–1081
Balmysheva NP, Solovenchuk LL (1999b) Association between mutations of mitochondrial DNA genes for citochrome b and NADH dehydrogenase 5/6 in sable Martes zibellina L. Russ J Genet 35:1447–1451
Bobkovskaya NE (2002) Large mammals of Pleistocene in low Irtish Basin. In: Kosintsev PA (ed) Pleistocene and Holocene faunas of Urals. Ural State University Press, Ekaterinburg, pp 56–61 (in Russian)
Buskirk SW, Ma YQ, Xu L, Jiang ZW (1996) Winter habitat ecology of sables (Martes zibellina) in relation to forest management in China. Ecol Appl 6:318–325
Crandall KA, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Mace GM, Wayne RK (2000) Considering evolutionary processes in conservation biology. Trends Ecol Evol 15:290–295
Davison A, Birks JDS, Brookes RC, Messenger JE, Griffiths HI (2001) Mitochondrial phylogeography and population history of pine martens Martes martes compared with polecats Mustela putorius. Mol Ecol 10:2479–2488
Deng T, Xue XX (1997) An existing countermeasure of mammals in glacian periods—a new explanation to the Bergmann's law. Acta Theriol Sin 17(4):259–265 (in Chinese)
Derevjanko AP, Shunkov MV, Agadzhanyan AK, Baryshnikov GF, Malaeva EM et al (2003) Natural environment and the man in Paleolithic of Altai Mountains. Institute of Archeology and Ethnography of Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214
Excoffier L, Lischer HE (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Harrison DJ, Fuller A, Proulx G (2004) Martens and fishers (Martes) in human-altered environments: an international perspective. Springer, New York, pp 21–76
Hewitt GM (1999) Post-glacial re-colonization of European biota. Biol J Linn Soc 68:87–112
Hosoda T, Suzuki H, Iwata MA, Hayashida M, Watanabe S, Tatara M, Tsuchiya K (1999) Genetic relationship within and between the Japanese marten Martes melampus and the sable M. zibellina, based on variation of mitochondrial DNA and nuclear ribosomal DNA. Mammal Study 24:25–33
Huelsenbeck JP, Hillis DM (1993) Success of phylogenetic methods in the four taxon case. Syst Biol 42:247–264
Inoue T, Murakami T, Abramov AV, Masuda R (2010) Mitochondrial DNA control region variations in the sable Martes zibellina of Hokkaido Island and the Eurasian continent, compared with the Japanese marten M. melampus. Mammal Study 35:145–155
Irwin DM, Kocher TD, Wilson AC (1991) Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J Mol Evol 32:128–144
Jaarola M, Tegelstrom H, Fredga K (1999) Colonization history in Fennoscandian rodents. Biol J Linn Soc 68:113–127
Koepfli KP, Deere KA, Slater GJ, Begg C, Begg K et al (2008) Multigene phylogeny of the Mustelidae: resolving relationships, tempo and biogeographic history of a mammalian adaptive radiation. BMC Biol 6:10
Kurose N, Masuda R, Siriaroonrat B, Yoshida MC (1999) Intraspecific variation of mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences of the Japanese Martes melampus and the sable Martes zibellina (Mustelidae, Carnivora, Mammalia) in Japan. Zool Sci 16:693–700
Leache AD, Reeder TW (2002) Molecular systematics of the eastern fence lizard (Sceloporus undulatus): a comparison of parsimony, likelihood, and Bayesian approaches. Syst Biol 51:44–68
Li B, Xu YC, Ma Y, Elmeros M, Lan TM, Bai SY (2011) A PCR-RFLP-based method to distinguish sable (Martes zibellina) and pine marten (Martes martes). Acta Theriol 56:283–288
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Malyarchuk BA, Petrovskaya AV, Derenko MV (2010) Intraspecific structure of sable Martes zibellina L. inferred from nucleotide variation of the mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene. Russ J Genet 46:64–68
Monakhov GI (1976) Geographic variation and taxonomic structure of the sable fauna of the USSR. Trudy VNIIOZ 26:54–86 (in Russian)
Monakhov VG (2010) Phenogeography of a cranial trait of the sable Martes zibellina L. in the species area. Dokl Biol Sci 431:94–99
Moritz C (1994) Defining ‘evolutionarily significant units’ for conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 9:373–375
Murakami T, Asano M, Ohtaishi N (2004) Mitochondrial DNA variation in the Japanese marten Martes melampus and Japanese sable, Martes zibellina. Jpn J Vet Res 51:135–142
Pavlov MP, Korsakova IB, Timofeev EV, Safonov VG (1973) Acclimation of Game Mammals and Birds in the USSR, Part 1. Volgo-Vyatskoe Publishing House, Kirov, pp 536 (in Russian)
Pawlinin WN (1966) Der Zobel. A. Ziemsen Verlag, Wittenberg Lutherstadt, Germany
Petrovskaya AV (2007) Genetic structure of the sable Martes zibellina L. populations from Magadan oblast as inferred from mitochondrial DNA variation. Russ J Genet 43:424–429
Ponomarev DV (2001) The European north-east large mammals in late Pleistocene and Holocene. Komi Science Center of Ural Division of Russian Academy of Sciences, Siktivkar (in Russian)
Ray N, Currat M, Excoffier L (2003) Intra-deme molecular diversity in spatially expanding populations. Mol Biol Evol 20:76–86
Rozhnov VV, Meschersky IG, Pishchulina SL, Simakin LV (2010) Genetic analysis of sable (Martes zibellina) and pine marten (M. martes) populations in sympatric part of distribution area in the northern Urals. Russ J Genet 4:488–492
Ruiz-Gonzalez A (2011) Phylogeography and non-invasive landscape genetics of the European pine marten (Martes martes L. 1758): insights into ancient and contemporary processes shaping genetic variation. PhD Thesis. Universidad del Pais Vasco, Vitoria-Gasteiz
Simonsen KL, Churchill GA, Aquadro CF (1995) Properties of statistical tests of neutrality for DNA polymorphism data. Genetics 141:413–429
Stone KD, Cook JA (2002) Molecular evolution of holarctic martens (genus Martes, Mammalia: Carnivora: Mustelidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 24:169–179
Taberlet P, Fumagalli L, Wust-Saucy AG, Cossons JF (1998) Comparative phylogeography and postglacial colonization routes in Europe. Mol Ecol 7:453–464
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Ternovskii DV (1977) Biology of weasel. Nauka, Moscow
Vila C, Amorim IR, Leonard JA, Posada D, Castroviejo J et al (1999) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeography and population history of the grey wolf Canis lupus. Mol Ecol 8:2089–2103
Waits L, Taberlet P, Swenson JE, Sandegren F, Franzen R (2000) Nuclear DNA microsatellite analysis of genetic diversity and gene flow in the Scandinavian brown bear (Ursus arctos). Mol Ecol 9:421–431
Walker CW, Vila C, Landa A, Linden M, Ellegren H (2001) Genetic variation and population structure in Scandinavian wolverine (Gulo gulo) populations. Mol Ecol 10:53–63
Yonezawa T, Nikaido M, Kohno N, Fukumoto Y, Okada N, Hasegawa M (2007) Molecular phylogenetic study on the origin and evolution of Mustelidae. Gene 396:1–12
Yu L, Peng D, Liu J, Luan P, Liang L et al (2011) On the phylogeny of Mustelidae subfamilies: analysis of seventeen nuclear non-coding loci and mitochondrial complete genomes. BMC Evol Biol 11:92
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Wildlife Conservation and Nature Reserve Construction Project of the State Forestry Administration of China. We are grateful to the following persons for providing tissue samples: Prof. Wei Zhang, Yanchun Xu, and Guangcai Sun at the College of Wildlife Resources, Northeast Forestry University; Dr. A.I. Antonov, Seniour Research Fellow at Khingan State Nature Reserve, Russia. The authors' thanks also go to N.S. Kashina (North-East Interdisciplinary Science Research Institute, Magadan, Russia) for figure preparation, as well as to Boyang Wang for assistance in experimental work. We also thank Thomas D. Dahmer for editing earlier versions of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Allan McDevitt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Malyarchuk, B., Ma, Z. et al. Phylogeography of sable (Martes zibellina L. 1758) in the southeast portion of its range based on mitochondrial DNA variation: highlighting the evolutionary history of the sable. Acta Theriol 58, 139–148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-012-0100-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-012-0100-2