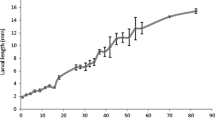
Abstract
Soldier differentiations require high juvenile hormone (JH) titers in workers and two molts via a presoldier stage. However, it is still unclear when the endogenous JH titer increases in workers, because identifying an individual before it undergoes the presoldier molt is quite difficult in natural conditions. In an incipient colony of Zootermopsis nevadensis Hagen, the oldest 3rd instar larva (Νo. 1 larva) always differentiates into a presoldier and the second 3rd instar larva (Νo. 2 larva) molts into a 4th instar larva. Consequently, by focusing on the ontogeny of the Νo. 1 larva, the timing of the increase in the JH titer can be determined. Here, we compared the expression levels of JH biosynthetic genes in the heads of Νo. 1 and Νo. 2 larvae. Most genes involved in JH biosynthesis were found in a genome database, and two candidate JH epoxidase (CYP15A1) genes were identified. Expression levels of JH acid methyltransferase (JHAMT) and one candidate CYP15A1, probably involved in the final steps of the JH biosynthesis, were specifically high in Νo. 1 larvae at 2–3 and 4–5 days after the appearance, respectively. Expression patterns of these genes may be used for the prediction of endogenous JH titer changes during presoldier differentiation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Bélles X, Martín D, Piulachs M-D (2005) The mevalonate pathway and the synthesis of juvenile hormone in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 50:181–199
Bomtorin AD, Mackert A, Rosa GCC, Moda LM, Martins JR, Bitondi MMG, Hartfelder K, Simões ZLP (2014) Juvenile hormone biosynthesis gene expression in the corpora allata of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) female castes. PLoS One 9(1):e86923
Cornette R, Gotoh H, Koshikawa S, Miura T (2008a) Juvenile hormone titers and caste differentiation in the damp-wood termite Hodotermopsis sjostedti. J Insect Physiol 54:922–930
Cornette R, Koshikawa S, Miura T (2008b) Histology of the hormone-producing glands in the damp-wood termite Hodotermopsis sjostedti (Isoptera, Termopsidae): a focus on soldier differentiation. Insect Soc 55:407–416
Cornette R, Hayashi Y, Koshikawa S, Miura T (2013) Differential gene expression in response to juvenile hormone analog treatment in the damp-wood termite Hodotermopsis sjostedti (Isoptera, Archotermopsidae). J Insect Physiol 59:509–518
Cymborowski B, Bogus M, Backage NE, Williams CM, Riddiford LM (1982) Juvenile hormone titres and metabolism during starvation-induced supernumerary larval moulting of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta L. J Insect Physiol 28:129–135
Daimon T, Kozaki T, Niwa R et al (2012) Precocious metamorphosis in the juvenile hormone—deficient mutant of the silkworm. Bombyx mori. PLoS Genet 8(3):e1002486
Deligne J, Quennedey A, Blum MS (1981) The enemies and defense mechanisms of termites. In: Hermann HR (ed) Social insects, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–76
Feyereisen R (2006) Evolution of insect P450. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1252–1255
Hartfelder K (2000) Insect juvenile hormone: from “status quo” to high society. Braz J Med Biol Res 33:157–177
Hartfelder K, Emlen DJ (2012) Endocrine control of insect polyphenism. In: Gilbert LI (ed) Insect endocrinology. Elsevier, Boston, pp 464–522
Haverty MI (1977) The proportion of soldiers in termite colonies: a list and bibliography. Sociobiology 2:199–216
Haward RW, Haverty MI (1979) Termites and juvenile hormone analogues: a review of methodology and observed effects. Sociobiology 4:269–278
Helvig C, Koener JF, Unnithan GC, Feyereisen R (2004) CYP15A1, the cytochrome P450 that catalyzes epoxidation of methyl farnesoate to juvenile hormone III in cockroach corpora allata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4024–4029
Henderson G (1998) Primer pheromones and possible soldier caste influence on the evolution of sociality in lower termites. In: Meer RKV, Breed MD, Winston ML, Espelie KE (eds) Pheromone communication in social insects. Westview Press, Boulder, pp 314–330
Itano H, Maekawa K (2008) Soldier differentiation and larval juvenile hormone sensitivity in an incipient colony of the damp-wood termite Zootermopsis nevadensis (Isoptera, Termopsidae). Sociobiology 51:1–12
Kinjoh T, Kaneko Y, Itoyama K, Mita K, Hiruma K, Shinoda T (2007) Control of juvenile hormone biosynthesis in Bombyx mori: cloning of the enzymes in the mevalonate pathway and assessment of their developmental expression in the corpora allata. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:808–818
Korb J, Hoffmann K, Hartfelder K (2009) Endocrine signatures underlying plasticity in postembryonic development of lower termite, Cryptotermes secundus (Kalotermitidae). Evol Dev 11:269–277
Koshikawa S, Cornette R, Hojo M, Maekawa K, Matsumoto T, Miura T (2005) Screening of genes expressed in developing mandibles during soldier differentiation in the termite Hodotermopsis sjostedti. FEBS Lett 579:1365–1370
Lo N, Eggeleton P (2011) Termite phylogenetics and co-cladogenesis with symbionts. In: Bignell DE, Roisin Y, Lo N (eds) Biology of termite: a modern synthesis. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 27–50
Maekawa K, Ishitani K, Gotoh H, Cornette R, Miura T (2010) Juvenile hormone titre and vitellogenin gene expression related to ovarian development in primary reproductives compared with nymphs and nymphoid reproductives of the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Physiol Entomol 35:52–58
Maekawa K, Nakamura S, Watanabe D (2012) Termite soldier differentiation in incipient colonies is related to parental proctodeal trophallactic behavior. Zool Sci 29:213–217
Maekawa K, Hayashi Y, Lee T, Lo N (2014) Presoldier differentiation of Australian termite species induced by juvenile hormone analogues. Austral Entomol 53:138–143
Marchal E, Zhang J, Badisco L, Verlinden H, Hult EF, Wielendaele PV, Yagi KJ, Tobe SS, Broeck JV (2011) Final steps in juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:219–227
Masuoka Y, Miyazaki S, Saiki R, Tsutomu T, Maekawa K (2013) High Laccase2 expression is likely involved in the formation of specific cuticular structures during soldier differentiation of the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Arthropod Struct Dev 42:469–475
Miura T (2005) Developmental regulation of caste-specific characters in social-insect polyphenism. Evol Dev 7:122–129
Miura T, Scharf ME (2011) Molecular basis underlying caste differentiation in termites. In: Bignell DE, Roisin Y, Lo N (eds) Biology of termite: a modern synthesis. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 211–253
Nijhout HF (1999) Control mechanisms of polyphenic development in insects. BioSience 49:181–192
Nijhout HF (2003) Development and evolution of adaptive polyphenisms. Evol Dev 5:9–18
Nijhout HF, Wheeler DE (1982) Juvenile hormone and the physiological basis of insect polymorphisms. Q Rev Biol 57:109–133
Noirot C, Pasteels JM (1987) Ontogenetic development and evolution of the worker caste in termites. Experientia 43:851–952
Noriega FG (2004) Nutritional regulation of JH synthesis: a mechanism to control reproductive maturation in mosquitoes? Insect Biochem Mol Biol 34:687–693
Noriega FG, Ribeiro JMC, Koener JF, Valenzuela JG, Hernandez-Martinez S, Pham VM, Feyereisen R (2006) Comparative genomics of insect hormone biosynthesis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 36:366–374
Ogino K, Hirono Y, Matsumoto T, Ishikawa H (1993) Juvenile hormone analogue, S-31183, causes a high level induction of presoldier differentiation in the Japanese damp-wood termite. Zool Sci 10:361–366
Park IY, Raina AK (2004) Juvenile hormone III titers and regulation of soldier caste in Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J Insect Physiol 50:561–566
Roisin Y (2000) Diversity and evolution of caste patterns. In: Abe T, Bignell DE, Higashi M (eds) Termites: evolution, sociality, symbioses, ecology. Kluwer Academic Press, Dortrecht, pp 95–119
Saiki R, Gotoh H, Toga K, Miura T, Maekawa K (2015) High juvenile hormone titer and abdominal activation of the JH signaling may induce reproduction of termite neotenics. Insect Mol Biol 24(4):432–441
Scharf ME, Ratliff CR, Hoteling JT, Pittendrigh BR, Bennett GW (2003) Caste differentiation responses of two sympatric Reticulitermes termite species to juvenile hormone homologs and synthetic juvenoids in two laboratory assays. Insectes Soc 50:346–354
Shinoda T, Itoyama K (2003) Juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase: a key regulatory enzyme for insect metamorphosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11986–11991
Tamura K, Peterson D, Perterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tarver MR, Coy MR, Scharf ME (2012) Cyp15F1: a novel cytochrome P450 gene linked to juvenile hormone-dependent caste differentiation in the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 80:92–108
Terrapon N, Li C, Robertson HM et al (2014) Molecular traces of alternative social organization in a termite genome. Nat Commun 5:3636
Toga K, Hojo M, Miura T, Maekawa K (2009) Presoldier induction by a juvenile hormone analog in the nasute termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis (Isoptera: Termitidae). Zool Sci 26:382–388
Toga K, Hojo M, Miura T, Maekawa K (2012) Expression and function of a limb-patterning gene Distal-less in the soldier-specific morphogenesis in the nasute termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis. Evol Dev 4:286–295
Toga K, Saiki R, Maekawa K (2013) Hox gene deformed is likely involved in mandibular regression during presoldier differentiation in the nasute termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis. J Exp Zool 9999:1–8
Treiblmayr K, Pascual N, Piulachs M-D, Keller T, Bélles X (2006) Juvenile hormone titer versus juvenile hormone synthesis in female nymphs and adults of the German cockroach (Blattella germanica). J Insect Sci 6:43
Tsuchiya M, Watanabe D, Maekawa K (2008) Effect on mandibular length of juvenile hormones and regulation of soldier differentiation in the termite Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Appl Entomol Zool 43:307–314
Tu M-P, Yin C-M, Tatar M (2005) Mutations in insulin signaling pathway alter juvenile hormone synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Gen Comp Endocrinol 142:347–356
Ueda H, Shinoda T, Hiruma K (2009) Spatial expression of the mevalonate enzymes involved in juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the corpora allata in Bombyx mori. J Insect Physiol 55:798–804
Untergasser A, Nijveen H, Rao X, Bisseling T, Geurts R, Leunissen JAM (2007) Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W71–W74
Vandesompele J, Preter KD, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Roy NV, Paepe AD, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3: research0034
Watanabe D, Maekawa K (2012) Relationships between frontal-gland formation and mandibular modification during JH III-induced presoldier differentiation in the termite Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Entomol Sci 15:56–62
Watanabe D, Gotoh H, Miura T, Maekawa K (2011) Soldier presence suppresses presoldier differentiation through a rapid decrease of JH in the termite Reticulitermes speratus. J Insect Physiol 57:791–795
Watanabe D, Gotoh H, Miura T, Maekawa K (2014) Social interactions affecting caste development through physiological actions in termites. Front Physiol 5:127
Werck-Reichhart D, Feyereisen R (2000) Cytochromes P450: a success story. Genome Biol 1(6): reviews3003.1–3009.9
Wilson EO (2000) Sociobiology: the new synthesis, Twenty-fifth anniversary. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Toru Miura and Hiroki Gotoh (Hokkaido University) for advice on and use of the HPLC–MS system. We also thank Ryota Saiki, Shutaro Hanmoto, Souichiro Kawamura and Ryutaro Suzuki (University of Toyama) for help during both the field and laboratory work. This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (nos. 24570022 and 25128705 to KM) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaguchi, H., Masuoka, Y., Inoue, T. et al. Expressions of juvenile hormone biosynthetic genes during presoldier differentiation in the incipient colony of Zootermopsis nevadensis (Isoptera: Archotermopsidae). Appl Entomol Zool 50, 497–508 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0358-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0358-3