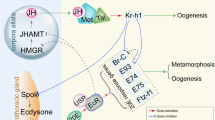
Abstract
Methoprene-tolerant (Met) is a bHLH-PAS transcription factor that functions as a core component of juvenile hormone (JH) receptors in insects. The genome of the silkworm, Bombyx mori (L.), encodes two Met paralogs, BmMet1 and BmMet2. We have previously proposed that BmMet2 forms a functional complex with steroid receptor co-activator (BmSRC) in the presence of JH and induces Krüppel-homolog 1 (BmKr-h1). In this study, we characterized BmMet2 domains and examined the role of BmMet1. A series of reporter and two-hybrid assays on BmMet2 revealed that the bHLH domain played a critical role in the binding to the JH response element of BmKr-h1 (kJHRE), the PAS-A in the transcriptional activation, and the PAS-B in the JH recognition. Furthermore, we confirmed that the BmMet2/BmSRC complex recognizes the core kJHRE (GGCCTCCACGTG). BmMet1 was found to interact with BmSRC and weakly activated the kJHRE reporter in a JH-dependent manner. The BmMet1 transcript level was much higher than the BmMet2 transcript level in the epidermis during the larval and pupal stages. By contrast, the BmMet2 transcript was hardly detected during the larval stage, but was abundant in the adult stage. These results suggest that BmMet1 is involved in the JH-dependent induction of BmKr-h1 in larvae, whereas BmMet2 is involved in adults.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou MA, He QY, Wen D, Zyaan O, Wang J, Xu JJ, Baumann AA, Joseph J, Wilson TG, Li S, Wang J (2011) Drosophila Met and Gce are partially redundant in transducing juvenile hormone action. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:938–945
Ashok M, Turner C, Wilson TG (1998) Insect juvenile hormone resistance gene homology with the bHLH-PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2761–2766
Baumann A, Fujiwara Y, Wilson TG (2010) Evolutionary divergence of the paralogs Methoprene tolerant (Met) and germ cell expressed (gce) within the genus Drosophila. J Insect Physiol 56:1445–1455
Charles JP, Iwema T, Epa VC, Takaki K, Rynes J, Jindra M (2011) Ligand-binding properties of a juvenile hormone receptor, methoprene-tolerant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:21128–21133
Cheng DJ, Meng M, Peng J, Qian WL, Kang LX, Xia QY (2014) Genome-wide comparison of genes involved in the biosynthesis, metabolism, and signaling of juvenile hormone between silkworm and other insects. Genet Mol Biol 37:444–459
Cui Y, Sui Y, Xu J, Zhu F, Palli SR (2014) Juvenile hormone regulates Aedes aegypti Krüppel homolog 1 through a conserved E box motif. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 52:23–32
Daimon T, Kozaki T, Niwa R, Kobayashi I, Furuta K, Namiki T, Uchino K, Banno Y, Katsuma S, Tamura T, Mita K, Sezutsu H, Nakayama M, Itoyama K, Shimada T, Shinoda T (2012) Precocious metamorphosis in the juvenile hormone-deficient mutant of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS Genet 8:e1002486
Dubrovsky EB, Bernardo TJ (2014) The juvenile hormone receptor and molecular mechanisms of juvenile hormone action. Adv Insect Physiol 46:305–388
Dubrovsky EB, Dubrovskaya VA, Bernardo T, Otte V, DiFilippo R, Bryan H (2011) The Drosophila FTZ-F1 nuclear receptor mediates juvenile hormone activation of E75A gene expression through an intracellular pathway. J Biol Chem 286:33689–33700
Furness SGB, Lees MJ, Whitelaw ML (2007) The dioxin (aryl hydrocarbon) receptor as a model for adaptive responses of bHLH/PAS transcription factors. FEBS Lett 581:3616–3625
Furuta K, Ichikawa A, Murata M, Kuwano E, ShinodaT Shiotsuki T (2013) Determination by LC-MS of juvenile hormone titers in hemolymph of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:988–991
Guo EE, He QY, Liu SM, Tian L, Sheng ZT, Peng Q, Guan JM, Shi MA, Li K, Gilbert LI, Wang J, Cao Y, Li S (2012) Met is required for the maximal action of 20-hydroxyecdysone during Bombyx metamorphosis. PLoS One 7:e53256
He QY, Wen D, Jia QQ, Cui CL, Wang J, Palli SR, Li S (2014) Heat shock protein 83 (Hsp83) facilitates methoprene-tolerant (Met) nuclear import to modulate uuvenile hormone signaling. J Biol Chem 289:27874–27885
Jindra M, Palli SR, Riddiford LM (2013) The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu Rev Entomol 58:181–204
Jouraku A, Yamamoto K, Kuwazaki S, Urio M, Suetsugu Y, Narukawa J, Miyamoto K, Kurita K, Kanamori H, Katayose Y, Matsumoto T, Noda H (2013) KONAGAbase: a genomic and transcriptomic database for the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. BMC Genom 14:464
Kamimura M, Matsumoto H, Kiuchi M, Ito Y, Fujiwara H, Shinoda T (2014) Development of a cell-based assay for ecdysteroid quantification using an early ecdysteroid-inducible gene promoter. Appl Entomol Zool 49:443–452
Kanamori Y, Hayakawa Y, Matsumoto H, Yasukochi Y, Shimura S, Nakahara Y, Kiuchi M, Kamimura M (2010) A eukaryotic (insect) tricistronic mRNA encodes three proteins selected by context-dependent scanning. J Biol Chem 285:36933–36944
Kayukawa T, Minakuchi C, Namiki T, Togawa T, Yoshiyama M, Kamimura M, Mita K, Imanishi S, Kiuchi M, Ishikawa Y, Shinoda T (2012) Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Krüppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11729–11734
Kayukawa T, Tateishi K, Shinoda T (2013) Establishment of a versatile cell line for juvenile hormone signaling analysis in Tribolium castaneum. Sci Rep 3:1570
Kayukawa T, Murata M, Kobayashi I, Muramatsu D, Okada C, Uchino K, Sezutsu H, Kiuchi M, Tamura T, Hiruma K, Ishikawa Y, Shinoda T (2014) Hormonal regulation and developmental role of Krüppel homolog 1, a repressor of metamorphosis, in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Dev Biol 388:48–56
Konopova B, Jindra M (2007) Juvenile hormone resistance gene Methoprene-tolerant controls entry into metamorphosis in the beetle Tribolium castaneum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10488–10493
Konopova B, Smykal V, Jindra M (2011) Common and distinct roles of juvenile hormone signaling genes in metamorphosis of holometabolous and hemimetabolous insects. PLoS One 6:e28728
Li YP, Zhang ZL, Robinson GE, Palli SR (2007) Identification and characterization of a juvenile hormone response element and its binding proteins. J Biol Chem 282:37605–37617
Li M, Mead EA, Zhu J (2011) Heterodimer of two bHLH-PAS proteins mediates juvenile hormone-induced gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:638–643
Li M, Liu PC, Wiley JD, Ojani R, Bevan DR, Li JY, Zhu JS (2014) A steroid receptor coactivator acts as the DNA-binding partner of the methoprene-tolerant protein in regulating juvenile hormone response genes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 394:47–58
Lozano J, Belles X (2011) Conserved repressive function of Krüppel homolog 1 on insect metamorphosis in hemimetabolous and holometabolous species. Sci Rep 1:163
Lozano J, Belles X (2014) Role of Methoprene-tolerant (Met) in adult morphogenesis and in adult ecdysis of Blattella germanica. PLoS One 9:e103614
Lozano J, Kayukawa T, Shinoda T, Belles X (2014) A role for taiman in insect metamorphosis. PLoS Genet 10:e1004769
Marchal E, Hult EF, Huang J, Pang Z, Stay B, Tobe SS (2014) Methoprene-tolerant (Met) knockdown in the adult female cockroach, Diploptera punctata completely inhibits ovarian development. PLoS One 9:e106737
Minakuchi C, Zhou X, Riddiford LM (2008) Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) mediates juvenile hormone action during metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Dev 125:91–105
Minakuchi C, Namiki T, Shinoda T (2009) Krüppel homolog 1, an early juvenile hormone-response gene downstream of Methoprene-tolerant, mediates its anti-metamorphic action in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Dev Biol 325:341–350
Miura K, Oda M, Makita S, Chinzei Y (2005) Characterization of the Drosophila Methoprene-tolerant gene product. Juvenile hormone binding and ligand-dependent gene regulation. FEBS J 272:1169–1178
Moglich A, Ayers RA, Moffat K (2009) Structure and signaling mechanism of Per-ARNT-Sim domains. Structure 17:1282–1294
Partch CL, Gardner KH (2010) Coactivator recruitment: a new role for PAS domains in transcriptional regulation by the bHLH-PAS family. J Cell Physiol 223:553–557
Parthasarathy R, Tan A, Palli SR (2008) bHLH-PAS family transcription factor methoprene-tolerant plays a key role in JH action in preventing the premature development of adult structures during larval-pupal metamorphosis. Mech Dev 125:601–616
Parthasarathy R, Tan A, Sun Chen Z, Rankin M, Palli SR (2009) Juvenile hormone regulation of male accessory gland activity in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Mech Dev 126:563–579
Riddiford LM (2012) How does juvenile hormone regulate insect metamorphosis and reproduction? Gen Com Endocrinol 179:477–484
Sailsbery JK, Atchley WR, Dean RA (2012) Phylogenetic analysis and classification of the fungal bHLH domain. Mol Biol Evol 29:1301–1318
Shin SW, Zou Z, Saha TT, Raikhel AS (2012) bHLH-PAS heterodimer of methoprene-tolerant and cycle mediates circadian expression of juvenile hormone-induced mosquito genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:16576–16581
Smykal V, Bajgar A, Provaznik J, Fexova S, Buricova M, Takaki K, Hodkova M, Jindra M, Dolezel D (2014) Juvenile hormone signaling during reproduction and development of the linden bug, Pyrrhocoris apterus. Insect Biochem Mol Boil 45:69–76
Wilson TG, Fabian J (1986) A Drosophila melanogaster mutant resistant to a chemical analog of juvenile hormone. Dev Biol 118:190–201
Wyatt GR (1997) Juvenile hormone in insect reproduction—a paradox? Eur J Entomol 94:323–333
Zhang Z, Xu J, Sheng Z, Sui Y, Palli SR (2011) Steroid receptor co-activator is required for juvenile hormone signal transduction through a bHLH-PAS transcription factor, methoprene tolerant. J Biol Chem 286:8437–8447
Zhao WL, Liu CY, Liu W, Wang D, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2014) Methoprene-tolerant 1 regulates gene transcription to maintain insect larval status. J Mol Endocrinol 53:93–104
Zou Z, Saha TT, Roy S, Shin SW, Backman TW, Girke T, White KP, Raikhel AS (2013) Juvenile hormone and its receptor, methoprene-tolerant, control the dynamics of mosquito gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E2173–E2181
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Program for the Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences (PROBRAIN), JSPS KAKENHI grant nos. 25850230 and 25252059, and the NIAS Strategic Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13355_2015_345_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1. Interaction of BmMet1 and BmSRC with kJHRE in S2 cells. S2 cells were cotransfected with a kJHRE reporter carrying firefly luciferase (pGL4.14), a reference reporter plasmid carrying Renilla luciferase (pRL-TK), and an expression plasmid carrying native BmMet1 and/or BmSRC. Transfected cells were treated with 10 μM methoprene (JHA) for 24 h, and reporter activities were measured using a Dual-Luciferase reporter assay system. The activity of the firefly luciferase reporter was normalized to that of the Renilla luciferase reporter in the same samples. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Data were analyzed using Student’s t tests (***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; not indicated, p > 0.05) (TIFF 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kayukawa, T., Shinoda, T. Functional characterization of two paralogous JH receptors, methoprene-tolerant 1 and 2, in the silkworm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Appl Entomol Zool 50, 383–391 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0345-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0345-8