Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy of insulin degludec (IDeg) relative to insulin glargine (IGlar) or insulin detemir (IDet) in glycemic control, as evaluated by continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in insulin-deficient patients with type 1 diabetes.
Methods
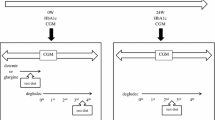
We studied 28 outpatients treated with IGlar or IDet (IGlar/IDet). Basal insulin was switched to IDeg when glycemic control was considered unstable, as judged by the dawn phenomenon or nocturnal hypoglycemia. Whole-day CGM data were also divided into daytime and nighttime data.
Results
The dawn phenomenon or nocturnal hypoglycemia under IGlar/IDet treatment was observed in all patients. Among 26 patients who completed the study, there were no significant differences in parameters representing glycemic variability, hyperglycemia, mean glycemic control, and HbA1c or insulin therapy-related quality of life at the night score. Measures of hypoglycemia [whole-day %Low and area under the curve (AUC) below 70] were significantly lower under IDeg treatment than under IGlar/IDet treatment (%Low, 9.6 ± 11.5 vs. 14.7 ± 14.9%, p = 0.045; AUC below 70, 85.5 ± 126.0 vs. 145.0 ± 178.6 mg/dl h, p = 0.030). Dividing patients into two groups according to percentage or degree of hypoglycemia under IGlar/IDet treatment, the whole-day, daytime and nighttime %Low in the high-percentage groups and AUC below 70 in the high-degree groups were significantly ameliorated, respectively (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Patients with unstable glycemic control under IGlar/IDet treatment did not improve glycemic control upon switching to IDeg, but the frequency and the degree of hypoglycemia was reduced in insulin-deficient outpatients with type 1 diabetes, especially in those suffering from severe hypoglycemia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(Suppl 1):S64–71.
Sartore G, Chilelli NC, Burlina S, Di Stefano P, Piarulli F, Fedele D, Mosca A, Lapolla A. The importance of HbA1c and glucose variability in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: outcome of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Acta Diabetol. 2012;49(Suppl 1):S153–60.
Kuenen JC, Borg R, Kuik DJ, Zheng H, Schoenfeld D, Diamant M, Nathan DM, Heine RJ, ADAG Study Group. Does glucose variability influence the relationship between mean plasma glucose and HbA1c levels in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients? Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1843–7.
UK Hypoglycaemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140–7.
Šoupal J, Škrha J Jr, Fajmon M, Horová E, Mráz M, Škrha J, Prázný M. Glycemic variability is higher in type 1 diabetes patients with microvascular complications irrespective of glycemic control. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16:198–203.
Kondos GT, Hoff JA, Sevrukov A, Daviglus ML, Garside DB, Devries SS, Chomka EV, Liu K. Electron-beam tomography coronary artery calcium and cardiac events: a 37-month follow-up of 5635 initially asymptomatic low- to intermediate-risk adults. Circulation. 2003;107:2571–6.
Snell-Bergeon JK, Roman R, Rodbard D, Garg S, Maahs DM, Schauer IE, Bergman BC, Kinney GL, Rewers M. Glycaemic variability is associated with coronary artery calcium in men with type 1 diabetes: the coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes study. Diabet Med. 2010;27:1436–42.
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2009;301:1565–72.
Lin CH, Sheu WH. Hypoglycaemic episodes and risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: 7-year follow-up study. J Intern Med. 2013;273:102–10.
Khunti K, Davies M, Majeed A, Thorsted BL, Wolden ML, Paul SK. Hypoglycemia and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in insulin-treated people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:316–22.
Lung TW, Petrie D, Herman WH, Palmer AJ, Svensson AM, Eliasson B, Clarke PM. Severe hypoglycemia and mortality after cardiovascular events for type 1 diabetic patients in Sweden. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2974–81.
McCoy RG, Van Houten HK, Ziegenfuss JY, Shah ND, Wermers RA, Smith SA. Increased mortality of patients with diabetes reporting severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1897–901.
Cox DJ, Ford D, Gonder-Frederick L, Clarke W, Mazze R, Weinger K, Ritterband L. Driving mishaps among individuals with type 1 diabetes: a prospective study. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:2177–80.
Yagasaki H, Kobayashi K, Saitou T, Nagamine K, Mitsui Y, Mochizuki M, Kobayashi K, Cho H, Ohyama K, Amemiya S, Nakazawa S. Nocturnal blood glucose and IGFBP-1 changes in type 1 diabetes: differences in the dawn phenomenon between insulin regimens. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010;118:195–9.
Frier BM. How hypoglycaemia can affect the life of a person with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24:87–92.
Jonassen I, Havelund S, Hoeg-Jensen T, Steensgaard DB, Wahlund PO, Ribel U. Design of the novel protraction mechanism of insulin degludec, an ultra-long-acting basal insulin. Pharm Res. 2012;29:2104–14.
Haahr H, Heise T. A review of the pharmacological properties of insulin degludec and their clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53:787–800.
Heise T, Hermanski L, Nosek L, Feldman A, Rasmussen S, Haahr H. Insulin degludec: four times lower pharmacodynamic variability than insulin glargine under steady-state conditions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:859–64.
Heller S, Buse J, Fisher M, Garg S, Marre M, Merker L, Renard E, Russell-Jones D, Philotheou A, Francisco AM, Pei H, Bode B, BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 1 Trial Investigators. Insulin degludec, an ultra-longacting basal insulin, versus insulin glargine in basal-bolus treatment with mealtime insulin aspart in type 1 diabetes (BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 1): a phase 3, randomised, open-label, treat-to target non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2012;379:1489–97.
Hirsch IB, Bode B, Courreges JP, Dykiel P, Franek E, Hermansen K, King A, Mersebach H, Davies M. Insulin degludec/insulin aspart administered once daily at any meal, with insulin aspart at other meals versus a standard basal-bolus regimen in patients with type 1 diabetes: a 26-week, phase 3, randomized, open-label, treat-to-target trial. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:2174–81.
Iwamoto Y, Clauson P, Nishida T, Kaku K. Insulin degludec in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes Investig. 2013;4:62–8.
Nakamura T, Sakaguchi K, So A, Nakajima S, Takabe M, Komada H, Okuno Y, Hirota Y, Nakamura T, Iida K, Kajikawa M, Nagata M, Ogawa W, Seino S. Effects of insulin degludec and insulin glargine on day-to-day fasting plasma glucose variability in individuals with type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, randomised, crossover study. Diabetologia. 2015;58:2013–9.
Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Kyaw AM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) on glucose control in diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013;5:39.
Seino Y, Nanjo K, Tajima N, Kadowaki T, Kashiwagi A, Araki E, Ito C, Inagaki N, Iwamoto Y, Kasuga M, Hanafusa T, Haneda M, Ueki K, Committee of the Japan Diabetes Society on the Diagnostic Criteria of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2010;1:212–8.
Ishii H, Furuya M, Iburi T, Yamagami K, Ishibashi R, Tsujii S. Insulin therapy related QOL at night (ITR-QOLN). J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 2008;51:593–600 (Japanese).
Yasuda H, Sanada M, Kitada K, Terashima T, Kim H, Sakaue Y, Fujitani M, Kawai H, Maeda K, Kashiwagi A. Rationale and usefulness of newly devised abbreviated diagnostic criteria and staging for diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77(Suppl 1):S178–83.
Service FJ, O’Brien PC, Rizza RA. Measurements of glucose control. Diabetes Care. 1987;10:225–37.
Service FJ, Molnar GD, Rosevear JW, Ackerman E, Gatewood LC, Taylor WF. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes. 1970;19:644–55.
Schlichtkrull J, Munck O, Jersild M. The M valve, an index of blood-sugar control in diabetics. Acta Med Scand. 1965;177:95–102.
Molnar GD, Taylor WF, Ho MM. Day-to-day variation of continuously monitored glycemia: a further measure of diabetic instability. Diabetologia. 1972;8:342–8.
Wójcicki JM. ‘‘J’’-index. A new proposition of the assessment of current glucose control in diabetic patients. Horm Metab Res. 1995;27:41–2.
McCall AL, Cox DJ, Crean J, Gloster M, Kovatchev BP. A novel analytical method for assessing glucose variability: using CGMS in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2006;8:644–53.
Kovatchev BP, Cox DJ, Gonder-Frederick LA, Young-Hyman D, Schlundt D, Clarke W. Assessment of risk for severe hypoglycemia among adults with IDDM: validation of the low blood glucose index. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1870–5.
Kashiwagi A, Kasuga M, Araki E, Oka Y, Hanafusa T, Ito H, Tominaga M, Oikawa S, Noda M, Kawamura T, Sanke T, Namba M, Hashiramoto M, Sasahara T, Nishio Y, Kuwa K, Ueki K, Takei I, Umemoto M, Murakami M, Yamakado M, Yatomi Y, Ohashi H, Committee on the Standardization of Diabetes Mellitus-Related Laboratory Testing of Japan Diabetes Society. International clinical harmonization of glycated hemoglobin in Japan: from Japan Diabetes Society to National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program values. J Diabetes Investig. 2012;3:39–40.
Kusunoki Y, Katsuno T, Miyakoshi K, Ikawa T, Nakae R, Ochi F, Tokuda M, Akagami T, Murai K, Miuchi M, Hamaguchi T, Miyagawa J, Namba M. Effects of switching from insulin glargine or detemir to insulin degludec in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2013;4:461–72.
Komuro M, Inoue G, Tabata M, Yamada Y, Atsuda K, Matsubara H, Irie J, Uchida J, Nakajima C, Izumi H, Shimada M, Yamada S. Insulin degludec requires lower bolus insulin doses than does insulin glargine in Japanese diabetic patients with insulin-dependent state. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015;9:632–8.
Schiaffini R, Ciampalini P, Fierabracci A, Spera S, Borrelli P, Bottazzo GF, Crinò A. The continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) in type 1 diabetic children is the way to reduce hypoglycemic risk. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18:324–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Shiro Fukuda (Department of Metabolic Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University) for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I.S. received honoraria from Novo Nordisk as a speaker and received research funding from Sanofi and Eli Lilly. H.I. received research funding from Novo Nordisk and belongs to the department endowed by the companies including Novo Nordisk. None of the other authors have any conflicts of interest associated with this research.
Ethical standard
This study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki of 1964 and later versions and approved by the ethics committee of Osaka University (approval no. 13089).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before enrollment.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasaki, S., Kozawa, J., Kimura, T. et al. Insulin degludec is associated with less frequent and milder hypoglycemia in insulin-deficient patients with type 1 diabetes compared with insulin glargine or detemir. Diabetol Int 8, 228–236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-017-0303-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-017-0303-5