Abstract
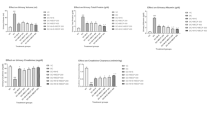
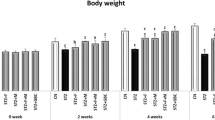
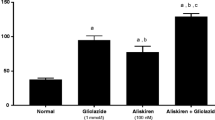
Diabetic nephropathy is a major complication of diabetes and a leading cause of end-stage renal failure in many developed countries. The study aimed to evaluate the efficiency of certain drugs and melatonin in the treatment of nephropathy secondary to diabetes. Diabetes was induced in rats by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (50 mg/kg body weight). Three days after induction of diabetes (460–500 mg/dl), rats were treated daily for 60 days with Rowatinex, melatonin, Rowatinex + melatonin, Amosar (Losartan Potassium) (LSP) and LSP + melatonin. The evaluations were made by measuring blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum uric acid, serum creatinine, urine creatinine, creatinine clearance, nitric oxide, malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, glutathione, total antioxidant capacity, kidney injury molecule-1, heat shock protein-70, caspase-3, transforming growth factor β1, and DNA degradation by comet assay and total protein contents. The histopathological picture of the kidneys and pancreases was confirmed in our results. Diabetic rats showed drastic changes in all the measured parameters. Treatment with melatonin and the selected drugs revealed amelioration levels with variable degrees. In conclusion, the combination of LSP and melatonin had the most potent effect on treating the deleterious action of diabetes on rat kidney.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schena FP, Gesualdo L. Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:S30–3.
Yoh K, Hirayama A, Ishizaki K, et al. Hyperglycemia induces oxidative and nitrosative stress and increases renal functional impairment in Nrf2-deficient mice. Genes Cells. 2008;13:1159–70.
Lewis EJ, Xu X. Abnormal glomerular permeability characteristics in diabetic nephropathy: implications for the therapeutic use of low-molecular weight heparin. Diab Care. 2008;31:S202–7.
Schaeffer V, Hansen KM, Morris DR, Abrass CK. Reductions in laminin beta2 mRNA translation are responsible for impaired IGFBP-5-mediated mesangial cell migration in the presence of high glucose. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;298:F314–22.
Yozai K, Shikata K, Sasaki M, et al. Methotrexate prevents renal injury in experimental diabetic rats via anti-inflammatory actions. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3326–38.
Seon YD, Lee TH, Lee MC. Changes of glomerular basement membrane components in Vacor-induced diabetic nephropathy. Korean J Intern Med. 1999;14:77–84.
Micah L, Thorp DO. Diabetic nephropathy: common questions. Am Fam Physician. 2005;72:96–9.
Paredes SD, Korkmaz A, Manchester LC, Tan DX, Reiter RJ. Phytomelatonin: a review. J Exp Botany. 2009;60:57–69.
Boutin JA, Audinot V, Ferry G, Delagrange P. Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and actions. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:412–9.
Hardeland R, Pandi-Perumal SR. Melatonin, a potent agent in antioxidative defense: actions as a natural food constituent, gastrointestinal factor, drug and prodrug. Nut Metab. 2005;2:22.
Reiter R, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Tan DX, Burkhardt S. Free radical-mediated molecular damage. Mechanisms for the protective actions of melatonin in the central nervous system. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2001;939:200–15.
Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Rodriguez C, Tan DX, Lopez-Burillo S, Reiter RJ. Melatonin and cell death: differential actions on apoptosis in normal and cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:1407–26.
Alvira D, Tajes M, Verdaguer E, et al. Inhibition of the cdk5/p25 fragment formation may explain the antiapoptotic effects of melatonin in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. J Pineal Res. 2006;40:251–8.
FDA Tightens up Dietary Supplement Manufacturing and Labelling. Medical News Today, 2007. Retrieved 2 Sept 2013.
Mundey K, Benloucif S, Harsanyi K, Dubocovich ML, Zee PC. Phase-dependent treatment of delayed sleep phase syndrome with melatonin. Sleep. 2005;28:1271–8.
Bach T. Preclinical and clinical overview of terpenes in the treatment of urolithiasis. European Urol. 2010;9:801–26.
Cipriani P, Mancini C. Microbiological activity of a terpen product used in the treatment of urinary diseases. Gaz Int Mede Chir. 1972;77–82.
Parving H, Lehnert H, Brochner-Mortansen J, Gomis R, Anderson S, Arner P. The effect of irbesartan on the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Eng J Med. 2001;345:870–8.
Punithavathi VR, Anuthama R, Prince SM. Combined treatment with naringin and vitamin C ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male Wistar rats. J Appl Toxicol. 2008;28:806–13.
Bhandari U, Kanojia R, Pillai KK. Effect of ethanolic extract of Zingiber officinale on dyslipidaemia in diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;97:227–30.
Yavuz O, Camb M, Bukanc N, Guvenb A, Siland F. Protective effect of melatonin on β-cell damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Acta Histochem. 2003;105:261–6.
Romics I, Siller G, Kohnen R, Mavrogenis S, Varga J, Holman E. A Special terpene combination (Rowatinex®) improves stone clearance after extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy in Urolithiasis patients: results of a placebo-controlled randomised controlled trial. Urol Int. 2011;86:102–9.
Murali B, Goyal RK. Effect of chronic treatment with losartan on streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2001;23:513–20.
Buege JA, Aust SD. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:302–10.
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B. Level of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1979;582:67–78.
Nishikimi M, Rae NA, Yagi K. The occurrence of superoxide anion in the action of reduced phenazine methosulphate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972;46:849–53.
Moshage H, Kok B, Huzenge JR, Jansen PL. Nitrite and nitrate determination in plasma: a critical evaluation. Clin Chem. 1995;41:892–6.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Karimi MM, Sani MJ, Mahmudabadi AZ, Sani AJ, Khatibi SR. Effect of acute toxicity of cadmium in mice kidney cells. Iran J Toxicol. 2012;6:691–798.
Suzuki H, Suzuki K. Rat hypoplastic kidney (hpk/hpk) induces renal anemia, hyperparathyroidism, and osteodystrophy at the end stage of renal failure. J Vet Med Sci. 1998;60:1051–8.
Atangwho IJ, Ebong PE, Eteng MU, Eyong EV, Obi AU. Effect of Vernomia amygdalina Del leaf on kidney function of diabetic rats. Int J Pharmacol. 2007;3:143–8.
Haligur M, Topsakal S, Ozmen O. Early degenerative effects of diabetes mellitus on pancreas, liver, and kidney in rats: an immunohistochemical study. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2:1–10.
Wilson GL, Leiter EH. Streptozotocin interactions with pancreatic β cells and the induction of insulin-dependent diabetes. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol. 1990;156:27–54.
Slauson DO, Cooper BJ (eds.). Pathology—the study of disease. In: Mechanisms of disease a textbook of comparative general pathology. Mosby, St. Louis; 2002, p. 1–15.
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawachi H, Fujita T. Podocyte as the target for aldosterone: roles of oxidative stress and Sgk1. Hypertension. 2007;49:355–64.
Tang J, Yan H, Zhuang S. Inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity-related glomerulopathy. Int J Nephrol. 2012;2012:e1–11.
Pan QR, Ren YL, Zhu JJ, et al. Resveratrol increases nephrin and podocin expression and alleviates renal damage in rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients. 2014;6:2619–31.
Kirkali G, Gezer S, Umur N. Nitric oxide in chronic liver disease. Turk J Med Sci. 2000;30:511–5.
El-Gengaihi SE, Hamed MA, Khalaf-Allah AM, Mohammed MA. Golden berry juice attenuates the severity of hepatorenal injury. J Diet Suppl. 2013;10:357–69.
Leonarduzzi G, Scavazza A, Biasi F, Chiarpotto E, Camandola S, Vogel S, Dargel R, Poli G. The lipid peroxidation end product 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal up-regulates transforming growth factor beta-1- expression in the macrophage lineage. A link between oxidative energy and fibrosclerosis. FASEB J. 1997;11:851–7.
Pawluczyk IZ, Harris KP. Macrophages promote prosclerotic responses in cultured rat mesangial cells: a mechanism for the initiation of glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:1525–36.
Chaudhary K, Phadke G, Nistala R, Weidmeyer CE, McFarlane SI, Whaley-Connell A. The emerging role of biomarkers in diabetic and hypertensive chronic kidney disease. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2010;10:37–42.
Carlsson AC, Calamia M, Rise’rus U, et al. Kidney injury molecule (KIM)-1 is associated with insulin resistance: results from two community-based studies of elderly individuals. Diab Resh Clin Pract. 2014;103:516–21.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and renal injury: mechanisms and implications. Am J Nephrol. 2006;26:232–44.
Riserus U, Basu S, Jovinge S, Fredrikson GN, Arnlov J, Vessby B. Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid causes isomer-dependent oxidative stress and elevated Creactive protein: a potential link to fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. Circulation. 2002;106:1925–9.
Knight SF, Imig JD. Obesity, insulin resistance, and renal function. Microcirculation. 2007;14:349–62.
Esposito K, Nappo F, Marfella R, Giugliano G, Giugliano F, Ciotola M. Inflammatory cytokine concentrations are acutely increased by hyperglycemia in humans: role of oxidative stress. Circulation. 2002;106:2067–72.
Peralta CA, Katz R, Bonventre JV, Sabbisetti V, Siscovick D. Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) with kidney function decline in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:904–11.
Vaidya VS, Niewczas MA, Ficociello LH, Johnson AC, Collings FB, Warram JH. Regression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes is associated with lower levels of urinary tubular injury biomarkers, kidney injury molecule-1, and N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminidase. Kidney Int. 2011;79:464–70.
Fink AL. Chaperone-mediated protein folding. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:425–49.
Kim HJ, Hwang NR, Lee KJ. Heat shock response for understanding diseases of protein denaturation. Moll Cell. 2007;23:123–31.
Barutta F, Pinach S, Giunti S, et al. Heat shock protein expression in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295:F1817–24.
Woo M, Hakem R, Soengas MS. Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPPp32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes. Genes Dev. 1998;12:806–19.
Maedler K, Spinas GA, Lehmann R. Glucose induces beta-cell apoptosis via upregulation of the Fas receptor in human islets. Diabetes. 2011;50:1683–90.
Brezniceanu ML, Liu F, Wei CC. Attenuation of interstitial fibrosis and tubular apoptosis in db/db transgenic mice overexpressing catalase in renal proximal tubular cells. Diabetes. 2008;57:451–9.
Liu F, Brezniceanu ML, Wei CC. Overexpression of angiotensinogen increases tubular apoptosis in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:269–80.
Frances DE, Ronco MT, Monti JA. Hyperglycemia induces apoptosis in rat liver through the increase of hydroxyl radical: new insights into the insulin effect. J Endocrinol. 2010;205:187–200.
Lannergren J, Westerblod H, Bruton SD. Dynamic vacuolation in skeletal muscle fibers after fatigue. Cell Biol Int. 2002;26:911–20.
Szkudelski T. The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res. 2001;50:536–46.
Woods JA, Young AJ, Gilmore IT. Measurement of menadione-mediated DNA damage in human lymphocytes using the Comet assay. Free Radic Res. 1997;26:113–24.
Kaneto H, Fujii J, Suzuki K. DNA cleavage induced by glycation of Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. Biochem J. 1994;304:219–25.
Shaffie NM, Morsy FA, Ali AG, Sharaf HA. Effect of craway, coriander and fennel on the structure of kidney and islets of Langerhans in alloxan-induced diabetic rats: histological and histochemical study. Researcher. 2010;2:27–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal rights
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Motawi, T.K., Ahmed, S.A., Hamed, M.A. et al. Combination of melatonin and certain drugs for treatment of diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Diabetol Int 7, 413–424 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-016-0268-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-016-0268-9