Abstract
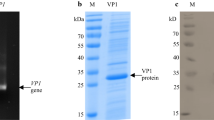
Non-structural proteins (NSPs) based diagnostics are useful for large-scale sero-surveillance of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) and to monitor viral activity as a follow up to the vaccination campaign in FMD endemic countries like India which aim at disease control through vaccination. These diagnostics are also handy in the serology of import/export of cloven-footed animals. In the present study, non-structural protein RNA polymerase (3D gene) of FMD virus (FMDV) was expressed using baculovirus expression system. Protein expression was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and confirmed by its immuno-reactivity with serum from a FMDV infected bovine, in the western blot. Recombinant 3D protein was purified and evaluated in the indirect ELISA with 1072 cattle serum samples. Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of the assay were found to be 92 and 100 %, respectively, when tested with cattle sera of known FMD status. The 3D based ELISA developed here is useful for screening the animals as an adjunct to other NSP based diagnostics available for routine serosurveillance of FMD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso Fernandez A, Auge de Melo P, Gomes I, Rosemberg F. The use of virus infection associated antigen (VIA) on the detection of cattle exposed to FMDV. Bol Cent Panam Fiebre Aftosa. 1975;17–18:17–22.
Alonso A, Gomes MPD, Martins MA, Sondahl MS. Detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus infection-associated antigen antibodies: comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and agar gel immunodiffusion tests. Prev Vet Med. 1990;9:233–40.
Anon (2004) Manual of standards for diagnostic tests and vaccines. Office Internationale des Epizooties (6th edition). Office Internationale des Epizooties, Paris, 1, p. 190–216.
Bergmann IE, Augé de Mello P, Neitzert E, Beck E, Gomes I. Diagnosis of persistent aphthovirus infection and its differentiation from vaccination response in cattle by use of enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot analysis with bioengineered nonstructural viral antigens. Am J Vet Res. 1993;6:825–31.
Bergmann I, Malirat V, Neitzert E, Beck E, Panizzutti N, Sanchez C. Improvement of a serodiagnostic strategy for foot-and-mouth Disease Virus surveillance in cattle under systematic vaccination: a combined system of an indirect ELISA-3ABC with an enzyme linked immunoelectrotransfer blot assay. Arch Virol. 2000;145:473–9.
Clavijo A, Wright P, Kitching P. Developments in diagnostic techniques for differentiating infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease. Vet J. 2004;167:9–22.
Cowan KM, Graves JG. A third antigenic component associated with foot-and-mouth disease virus infection. Virol. 1996;30:528–40.
Dekker A, Sammin D, Greiner M, Bergmann I, Paton D, Grazioli S, De Clercq K, Brocchi E. Use of continuous results to compare ELISAs for the detection of antibodies to non-structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vaccine. 2008;26:2723–32.
Frolov VG, Duque H, Palmenberg AC. Quantification of endogenous viral polymerase, 3Dpol, in preparations of meningo and encepahlomyocarditis viruses. Virology. 1999;260:148–55.
Gebauer F, La Torre JC, Gomes I, Mateu MG, Barahona H, Tiraboschi B, Bergmann I, de Mello PA, Domingo E. Rapid selection of genetic and antigenic variants of FMDV during persistence in cattle. J Virol. 1988;62:2041–9.
Hedger RS. Observations on the carrier state and related antibody titres during an outbreak of foot and mouth disease. J Hyg Camb. 1968;66:27–36.
Hoss A, Moarefi I, Scheidtmann KH, Cisek LJ, Corden JL, Dornreiter I, Arthur AK, Fanning E. Altered phosphorylation pattern of simian virus 40 T antigen expressed in insect cells by using a baculovirus vector. J Virol. 1990;64:4799–807.
Lubroth J, Brown F. Identification of native foot-and-mouth disease virus non-structural protein 2C as a serological indicator to differentiate infected from vaccinated livestock. Res Vet Sci. 1995;59:70–8.
Lubroth J, Lopez A, Ramalho AR, Meyer RF, Brown F, Darsie GC. Cattle response to foot-and-mouth disease virus non-structural proteins as antigens within vaccines produced using different concentrations. Vet Q. 1998;20:S13–7.
Mackay DKJ, Forsyth MA, Davies PR, Berlinzani A, Belsham GJ, Flint M, Ryan MD. Differentiating infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease using a panel of recombinant, non-structural proteins in ELISA. Vaccine. 1998;16:446–59.
Mohapatra JK, Pandey LK, Sanyal A, Pattnaik B. Recombinant non-structural polyprotein 3AB-based serodiagnostic strategy for FMD surveillance in bovines irrespective of vaccination. J Virol Methods. 2011;177:184–92.
Neitzert E, Beck E, Augé de Mello P, Gomes I, Bergmann IE. Expression of the aphthovirus RNA polymerase gene in E. coli and its use together with other bioengineered non-structural antigens in detection of late persistent infections. Virology 1991; 184:799–804
Newman JFE, Piatti PG, Ryan M, Brown F. Functions of minor polypeptides in foot-and-mouth disease virus and poliovirus. Trends Microbiol. 1994;2:494–7.
O’Donnell VK, Boyle DB, Sproat K, Fondevila NA, Forman A, Schudel AA, Smitsaart EN. Detection of antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus using a liquid-phase blocking sandwich ELISA (LPBE) with a bioengineered 3D protein. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1996;8:143–50.
O’Donnell VK, Smitsaart E, Cetra B, Duffy S, Finelli J, Boyle D, Draghi G, Fondevila N, Schudel AA. Detection of virus infection-associated antigen and 3D antibodies in cattle vaccinated against foot-and-mouth disease. Rev Sci Tech Off Int Epiz. 1997;16:833–40.
Pinto AA, Garland AJM. Immune response to virus-infection-associated (VIA) antigen in cattle repeatedly vaccinated with foot-and-mouth disease virus inactivated by formalin or acetylethyleneimine. J Hyg. 1979;82:41–50.
Pinto AA, Hedger RS. The detection of antibody to virus-infection-associated (VIA) antigen in various species of African wild life following natural and experimental infection with FMD virus. Arch Virol. 1978;57:307–14.
Rodriguez A, Dopazo J, Saiz JC, Sobrino F. Immunogenicity of non-structural proteins of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus differences between infected and vaccinated swine. Arch Virol. 1994;136:123–31.
Shen F, Chen PD, Walfield AM, Ye J, House J, Brown F. Differentiation of convalescent animals from vaccinated against foot-and- mouth disease by a peptide ELISA. Vaccine. 1999;17:3039–49.
Uttenthal A, Parida S, Rasmussen TB, Paton DJ, Haas B, Dundon WG. Strategies for differentiating infection in vaccinated animals (DIVA) for foot-and-mouth disease, classical swine fever and avian influenza. Expert Rev Vac. 2010;9:73–87.
Sorenson KJ, Madsen KG, Madsen ES, Salt JS, Nqindi J, Mackay DKJ. Differentiation of infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease by the detection of antibodies to the non-structural proteins 3D, 3AB and 3ABC in ELISA using antigens expressed in baculovirus. Arch. Virol. 1998;143:1461–1476.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director, Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI), Izatnagar, for facilitating this work. RK acknowledges receipt of IVRI-JRF. Authors thank Prof. M. S. Shaila, IISc, Bangalore and Dr S. E. Hasnain, CDFD, Hyderabad for providing wild strains of baculovirus. Dr Suresh Basagoudanavar is acknowledged for critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Hosamani, M., Sreenivasa, B.P. et al. Expression of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Non-Structural Protein, 3D in Insect Cells and its Application in Detection of Anti-FMDV Antibodies. Indian J. Virol. 23, 326–332 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-012-0098-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-012-0098-8