Abstract
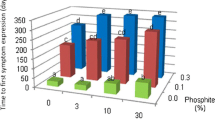
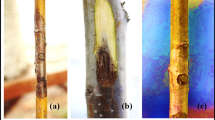
Systemic treatment of stems with injections of phosphite liquid and novel soluble capsule implants of phosphite, PHOSCAP® (phosphorous, potassium, iron, manganese, zinc, boron, copper, magnesium and molybdenum) and MEDICAP MD® (nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, iron, manganese, and zinc), were applied to Banksia grandis and Eucalyptus marginata trees to control Phytophthora cinnamomi. Four weeks after treatment application, excised branches were under-bark inoculated with P. cinnamomi. In B. grandis, phosphite implants and liquid injections significantly reduced lesion length compared to the control, and MEDICAP MD® implants; however, there was no significant difference in lesion length between trees treated with phosphite implants and liquid injections and PHOSCAP implants. In E. marginata, phosphite implants and liquid injections significantly reduced lesion length compared to the control, PHOSCAP® and MEDICAP MD® implants. In B. grandis and E. marginata, PHOSCAP® and MEDICAP MD® implants reduced the average lesion length compared to the control; however, the interactions were not significant. Results show that both liquid phosphite injections and novel phosphite implants are effective at controlling lesion extension in B. grandis and E. marginata, caused by P. cinnamomi. Further work is required to determine if nutrient application reduces Phytophthora disease through improving plant health.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JL, Murdoch EW, Cameron RL, Campana RJ (1979) Necrosis of elm tissue following chemical injection for Dutch elm disease control. Abstract Northeast Division American Phytopathological Society Nov. 17
Barrett SR, Shearer BL, Hardy GEStJ (2004) Phytotoxicity in relation to in planta concentration of the fungicide phosphite in nine Western Australian native species. Australas Plant Pathol 33:521–528
BoM (2012) Bureau of Meteorology (2012) climate Averages. Australian Commonwealth. Last Accessed:13/04/2012 from http://reg.bom.gov.au/tmp/cdio/IDCJAC0002_009240
Brasier CM, Kirk SA (2001) Comparative aggressiveness of standard and variant hybrid alder phytophthoras, Phytophthora cambivora and other Phytophthora species on bark of Alnus, Quercus, and other woody hosts. Plant Pathol 50(2):218–229
Campana RJ, Murdoch CW, Anderson JL (1979) Increased development of bacterial wetwood associated with injection holes made for the control of Dutch elm disease. Abstract Northeast Division American Phytopathological Society Nov. 23
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) ‘Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edition.’ (PRIMER-E: Plymouth)
Costonis AC (1980) The wounding effects of mauget and creative sales injections. J Arboric 6(8):204–208
Costonis AC (1981) Tree injection: perspective macro-injection/micro-injection. J Arboric 7:275–277
Day RW, Quinn GP (1989) Comparisons of treatments after an analysis of variance in ecology. Ecol Monogr 59(4):433–463
Dell B, Malajczuk N, Xu D, Grove TS (2001) ‘Nutrient disorders in plantation eucalypts.’, vol 188, 2nd edn. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, Canberra
Doccola JJ, Bristol EJ, Sifleet SD, Lojko J, Wild PM (2007) Efficacy and duration of trunk-injected imidacloprid in the management of Hemlock Wooly Adelgid (Adelges tsugae). Arboricult Urban For 33(1):12–21
Doccola JJ, Smitley DR, Davis RW, Aiken JJ, Wild PM (2011) Tree wound responses following systemic insecticide trunk injection treatments in green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica Marsh.) as determined by destructive autopsy. Arboricult Urban For 37(1):6–12
Dordas C (2008) Role of nutrients in controlling plant diseases in sustainable agriculture. Rev Agron Sust Dev 28(1):33–46
Erwin DC, Ribeiro OK (1996) ‘Phytophthora diseases worldwide.’. APS Press, St. Paul
Garas NA, Kuc J (1981) Potato lectin lyses zoospores of Phytophthora infectans and precipitates elicitors of terpenoid accumulation produced by the fungus. Physiol Plant Pathol 18:227–237
Graham RD, Webb MJ (1991) Micronutrients and disease resistance and tolerance in plants. In: Mortvedt FR, Cox JJ, Shuman LM, Welch RM (eds) Micronutrients in Agriculture, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Hardy GEStJ, Barrett SR, Shearer BL (2001) The future of phosphite as a fungicide to control the soilborne plant pathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi in natural ecosystems. Australas Plant Pathol 30:133–139
Harrell MO, Pierce PA, Mooter DP, Webster BL (1984) A comparison of treatments for treatments for chlorosis of pin oak and silver maple. J Arboric 10:246–249
Hodgkin EP, Hamilton BH (1993) Fertilizers and eutrophication in southwestern Australia: Setting the scene. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 36(2):95–103
Hüberli D, Tommerup IC, Dobrowolski MP, Calver MC, Hardy GE (2001) Phenotypic variation in a clonal lineage of two Phytophthora cinnamomi populations from Western Australia. Mycol Res 105(9):1053–1064
Hüberli D, Tommerup I, Colver M, ColquhounC I, Hardy G (2002) Temperature and inoculation method influence disease phenotypes and mortality of Eucalyptus marginata clonal lines inoculated with Phytophthora cinnamomi. Australas Plant Pathol 31(2):107–118
Lehto T, Ruuhola T, Dell B (2010) Boron in forest trees and forest ecosystems. For Ecol Manag 260(12):2053–2069
Nelson RR (1978) Genetics of horizontal resistance to plant diseases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 16(1):359–378
O’Gara E, Hardy GEStJ, McComb JA (1996) The ability of Phytophthora cinnamomi to infect through unwounded and wounded periderm tissue of Eucalyptus marginata. Plant Pathol 45(5):955–963
Scott P, Dell B, Shearer B, Barber P, Hardy GEStJ (2013) Phosphite and nutrient applications as explorative tools to identify possible factors associated with Eucalyptus gomphocephala decline in south-western Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 42:701–711
Shearer BL, Crane CE (2011) Habitat suitability of soils from a topographic gradient across the Fitzgerald River National Park for invasion by Phytophthora cinnamomi. Australas Plant Pathol 40(2):168–179 [In English]
Shearer BL, Fairman RG (2007) A stem injection of phosphite protects Banksia species and Eucalyptus marginata from Phytophthora cinnamomi for at least four years. Australas Plant Pathol 36:78–86
Shearer BL, Michaelsen BJ, Warren HJ (1987) Comparative behaviour of Phytophthora species in the secondary phloem of stems and excised roots of Banksia grandis and Eucalyptus marginata. Aust J Bot 35:103–110
Shearer BL, Michaelsen BJ, Somerford PJ (1988) Effects of isolate and time of inoculation invasion of secondary phloem of Eucalyptus spp. and Banksia grandis by Phytophthora spp. Plant Dis 72:121–126
Shearer BL, Fairman RG, Grant MJ (2006) Effective concentration of phosphite in controlling Phytophthora cinnamomi following stem injection of Banksia species and Eucalyptus marginata. For Pathol 36(2):119–135
Smith EM (1978) Responses of several species to systemic nutrient treatments in Ohio. In ‘Symposium on Systemic Chemical Treatments in Tree Culture’. Michigan State University, 67–71
Snowdon P (2000) Nutritional disorders and other abiotic stresses of eucalypts. In: Keane PJ, Kile GA, Podger FD, Brown BN (eds) ‘Diseases and Pathogens of Eucalypts.’. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne, pp 385–410
Statsoft (1999) ‘Statistica.’. Statsoft, Inc, Tulsa
Tippett J, Hill T, Shearer B (1985) Resistance of Eucalyptus spp. to invasion by Phytophthora cinnamomi. Aust J Bot 33(4):409–418
Tsao PH (1983) Factors affecting isolation and quantification of Phytophthora from soil. In: Erwin DC, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Tsao PH (eds) ‘Phytophthora, Its Biology, Taxonomy, Ecology, and Pathology.’. The American Phytopathological Society, St Paul, pp 219–236
Van Miegroet H, Johnson DW (2009) Feedbacks and synergism among biogeochemistry, basic ecology, and forest soil science. For Ecol Manag 258(10):2214–2223
Worley RE, Littrell RH (1978) Correction of pecan zinc deficiency through trunk injection. In ‘Symposium on systemic chemical treatments in tree culture’, Michigan State University, pp. 83–90
Worley RE, Littrell RL, Dutcher JD (1980) A comparison of tree trunk injection and implantation of zinc capsules for correction of zinc deficiency. J Arbicult 6:253–257
Acknowledgments
We thank Tan Dang at the University of Vietnam, for assistance and input into this study. We thank Mr Bryan Wolfe and Creative Sales Inc. for the development and supply of phosphite implants for this trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, P.M., Barber, P.A. & Hardy, G.E.S. Novel phosphite and nutrient application to control Phytophthora cinnamomi disease. Australasian Plant Pathol. 44, 431–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-015-0365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-015-0365-4