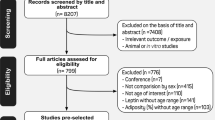
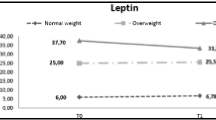
Abstract
Objective
Obesity is a growing worldwide health problem affecting both adults and children. Effective prevention and treatment modalities can be achieved by understanding the pathogenesis of obesity better. This review addresses some of the issues related to the hormones and cytokines taking part in the pathogenesis of obesity, energy balance and inflammation.
Design
We reviewed current literature on this broad subject especially concentrating on the functions of the hormones and cytokines taking part in the pathogenesis of the childhood obesity. Using the key words “obesity, children, hormones, cytokines” publications and cross references were evaluated from PubMed database between 1957 and 2009.
Results
In children, leptin and ghrelin are two hormones which have major influence on energy balance. Leptin is responsible from long term regulation of energy balance and ghrelin functions as an appetite stimulatory signal. In contrast to ghrelin, obestatin acts as an anorexigenic hormone by suppressing food intake. Adipokines secreted from adipose tissue are the key regulators of inflammation in obesity. Increased TNF-alpha and IL-6 levels but decreased levels of adiponectin and IL-10 are associated with increased inflammation, tissue injury and complications of obesity.
Conclusions
Development, pathogenesis and complications of childhood obesity consist of complex mechanisms including numerous cytokines and hormones. New treatment modalities depend on understanding these complex mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organisation. Childhood overweight and obesity. 2008. www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood/en/index.html. Accessed on August 15, 2010.
Devi S. Progress on childhood obesity patchy in the USA. Lancet 2008; 371: 105–106.
Agirbasli M, Cakir S, Ozme S, Ciliv G. Metabolic syndrome in Turkish children and adolescents. Metabolism 2006; 55: 1002–1006.
Olds TS, Tomkinson GR, Ferrar KE, Maher CA. Trends in the prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Australia between 1985 and 2008. Int J Obes (Lond) 2009; Oct 13: [Epub ahead of print].
Ji CY, Cheng TO. Epidemic increase in overweight and obesity in Chinese children from 1985 to 2005. Int J Cardiol 2009; 132: 1–10.
Branca F, Nikogosian H, Lobstein T (eds). The Challenge of Obesity in the WHO European Region and the Strategies for Response. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe 2007.
Greydanus DE, Bhave S. Obesity and adolescents; time for increased physical activity. Indian Pediatr 2004; 41: 545–550.
Aziz S, Noorulain W, Zaidi UE, Hossain K, Siddiqui IA. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents of affluent schools in Karachi. J Pak Med Assoc 2009; 59: 35–38.
Ziraba AK, Fotso JC, Ochako R. Overweight and obesity in urban Africa: A problem of the rich or the poor? BMC Public Health 2009; 9: 465–473.
Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Adipocyte stress: the endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. J Lipid Res 2007; 48: 1905–1914.
Trayhurn P. Adipocyte biology. Obes Rev 2007; 8: 41–44.
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999; 402: 656–660.
Klok MD, Jakobsdottir S, Drent ML. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: a review. Obes Rev 2007; 8: 21–34.
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1714–1719.
Foster CM, Barkan A, Kasa-Vubu JZ, Jaffe C. Ghrelin concentrations reflect body mass index rather than feeding status in obese girls. Pediatr Res 2007; 6: 731–733.
Zou CC, Liang L, Wang CL, Fu JF, Zhao ZY. The change in ghrelin and obestatin levels in obese children after weight reduction. Acta Paediatr 2009; 98: 159–165.
Stylianou C, Galli-Tsinopoulou A, Farmakiotis D, Rousso I, Karamouzis M, Koliakos G, et al. Ghrelin and leptin levels in obese adolescents. Relationship with body fat and insulin resistance. Hormones (Athens) 2007; 6: 295–303.
Galli-Tsinopoulou A, Stylianou C, Farmakiotis D, Rousso I, Karamouzis M, Nousia-Arvanitakis S. Ghrelin serum levels during oral glucose tolerance test in prepubertal obese children with insulin resistance. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2007; 20: 1085–1092.
Maffeis C, Bonadonna C, Consolaro A, Vettor R, Banzato C, Silvagni D, et al. Ghrelin, insulin sensitivity and postprandial glucose disposal in overweight and obese children. Eur J Endocrinol 2006; 154: 61–68.
Iñiguez G, Ong K, Peña V, Avila A, Dunger D, Mericq V. F Fasting and post-glucose ghrelin levels in SGA infants: relationships with size and weight gain at one year of age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 5830–5833
Krohn K, Boczan C, Otto B, Heldwein W, Landgraf R, Bauer CP, Koletzko B. Regulation of ghrelin is related to estimated insulin sensitivity in obese children. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 1482–1487.
Bellone S, Rapa A, Vivenza D, Castellino N, Petri A, Bellone J, et al. Circulating ghrelin levels as function of gender, pubertal status and adiposity in childhood. J Endocrinol Invest 2002; 25: 13–15.
Xiu-Min Wang, You-Jun Jiang, Li Liang, Li-Zhong Du. Changes of ghrelin following oral glucose tolerance test in obese children with insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 1919–1924.
Chao-Chun Zou, Li Liang, Zheng-Yan Zhao. Factors associated with fasting plasma ghrelin levels in children and adolescents. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 790–794.
Okamatsu Y, Matsuda K, Hiramoto I, Tani H, Kimura K, Yada Y, et al. Ghrelin and leptin modulate immunity and liver function in overweight children. Pediatr Int 2009; 51: 9–13.
Zhao CM, Furnes MW, Stenström B, Kulseng B, Chen D. Characterization of obestatin- and ghrelinproducing cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas of rats: an immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 2008; 331: 575–587.
Furnes WM, Stenstrom B, Tommeras K, Skoglund T, Dickson SL, Kulseng B, et al. Feeding behaviour in rats subjected to gastrectomy or gastric bypass surgery. Eur Surg Res 2008; 40: 279–288.
Huda MS, Durham BH, Wong SP, Deepak D, Kerrigan D, McCulloch P, et al. Plasma obestatin levels are lower in obese and post-gastrectomy subjects, but do not change in response to a meal. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32: 129–135.
Guo ZF, Zheng X, Qin YW, Hu JQ, Chen SP, Zhang Z. Circulating preprandial ghrelin to obestatin ratio is increased in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 1875–1880.
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Roth CL. Obestatin and ghrelin levels in obese children and adolescents before and after reduction of overweight. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2008; 68: 304–310.
Antunes H, Santos C, Carvalho S. Serum leptin levels in overweight children and adolescents. Br J Nutr 2008; 28: 1–5.
Holm JC, Gamborg M, Kaas-Ibsen K, Gammeltoft S, Ward L, Heitmann BL, et al. Time course and determinants of leptin decline during weight loss in obese boys and girls. Int J Pediatr Obes 2007; 2: 2–10.
Haqq AM, Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S, Stadler DD, Rosenfeld RG, Pratt KL, et al. Serum ghrelin levels are inversely correlated with body mass index, age, and insulin concentrations in normal children and are markedly increased in Prader-Willi syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 174–178.
Yoshinaga M, Sameshima K, Tanaka Y, Wada A, Hashiguchi J, Tahara H, et al. Adipokines and the prediction of the accumulation of cardio-vascular risk factors or the presence of metabolic syndrome in elementary school children. Circ J 2008; 72: 1874–1878.
Zhang S, Liu X, Brickman WJ, Christoffel KK, Zimmerman D, Tsai HJ, Wang G, et al. Association of plasma leptin concentrations with adiposity measurements in rural Chinese adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 3497–3504.
Kim IK, Kim J, Kang JH, Song J. Serum leptin as a predictor of fatty liver in 7-year-old Korean children. Ann Nutr Metab 2008; 53: 109–116.
Licinio J, Caglayan S, Ozata M, Yildiz BO, de Miranda PB, O’Kirwan F, et al. Phenotypic effects of leptin replacement on morbid obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypogonadism, and behavior in leptin-deficient adults. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 4531–4536.
Aprath-Husmann I, Rohrig K, Gottschling-Zeller H, Skurk T, Scriba D, Birgel M, et al. Effects of leptin on the differentiation and metabolism of human adipocytes. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 1465–1470.
Weigle DS, Cummings DE, Newby PD, Breen PA, Frayo RS, Matthys CC, et al. Roles of leptin and ghrelin in the loss of body weight caused by a low fat, high carbohydrate diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1577–1586.
Rosenbaum M, Goldsmith R, Bloomfield D, Magnano A, Weimer L, Heymsfield S, et al. Lowdose leptin reverses skeletal muscle, autonomic, and neuroendocrine adaptations to maintenance of reduced weight. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 3579–3586.
Cambuli VM, Musiu MC, Incani M, Paderi M, Serpe R, Marras V, et al. Assessment of adiponectin and leptin as biomarkers of positive metabolic outcomes after lifestyle intervention in overweight and obese children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 3051–3057.
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Verdich C, Pedersen SB, Toubro S, Astrup A, et al. Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: In vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003; 285: E527–533.
Panagopoulou P, Galli-Tsinopoulou A, Fleva A, Pavlitou-Tsiontsi E, Vavatsi-Christaki N, Nousia-Arvanitakis S. Adiponectin and insulin resistance in childhood obesity. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2008; 47: 356–362.
Jeffery AN, Murphy MJ, Metcalf BS, Hosking J, Voss LD, English P, et al. Adiponectin in childhood. Int J Pediatr Obes 2008; 3: 130–140.
Murphy MJ, Hosking J, Metcalf BS, Voss LD, Jeffery AN, Sattar N, et al. Distribution of adiponectin, leptin, and metabolic correlates of insulin resistance: a longitudinal study in British children; 1: Prepuberty (EarlyBird 15). Clin Chem 2008; 54: 1298–1306.
Eyzaguirre F, Mericq V. Insulin resistance markers in children. Horm Res 2009; 71: 65–74.
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr Rev 2005; 26: 439–451.
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto, et al. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin acts as a platelet-derived growth factor- BB-binding protein and regulates growth factor-induced common postreceptor signal in vascular smooth muscle cell. Circulation 2002; 105: 2893–2898.
Arnaiz P, Acevedo M, Barja S, Aglony M, Guzman B, Cassis B, et al. Adiponectin levels, cardiometabolic risk factors and markers of subclinical atherosclerosis in children. Int J Cardiol 2008; Sep 5: [Epub ahead of print].
Koistinen HA, Bastard JP, Dusserre E, Ebeling P, Zegari N, Andreelli F, et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha is not associated with whole body insulin resistance in obese nondiabetic or in type-2 diabetic subjects. Eur J Clin Invest 2000; 30: 302–310.
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993; 259: 87–91.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM. Tumor necrosis factor: A key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994; 43: 1271–1278.
Greenberg, AS and McDaniel ML. Identifying the links between obesity, insulin resistance and function: Potential role of adipocyte-derived cytokines in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest 2002; 32: 24–34.
Angin Y, Kuralay F, Arslan N. Evoluation of metabolic, antioxidant and oxidant systemic determinants in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease relevant to pediatric obesity. In: Sahin MF, Zefirov NS, editors, 1st Turkish-Russian Joint Meeting on Organic and Medicinal Chemistry; 2009 October 14–17; Antalya, Turkey, p. 64.
Lyon CJ, Law RE, Hsueh VA. Minireview: Adiposity, inflammation, and atherogenesis. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 2195–2200.
Gtowinska B, Urban M. Selected cytokines (Il-6, Il- 8, Il-10, MCP-1, TNF-alpha) in children and adolescents with atherosclerosis risk factors: obesity, hypertension, diabetes. Wiad Lek 2003; 56: 109–116.
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS, et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 4196–4200.
Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 847–850.
Fernandez-Real JM, Vayreda M, Richart C, Gutierrez C, Broch M, Vendrell J, et al. Circulating interleukin 6 levels, blood pressure and insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1154–1159.
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol 2001; 280: 745–751.
Yeste D, Vendrell J, Tomasini R, Broch M, Gussinyé M, Megia A, et al. Interleukin-6 in obese children and adolescents with and without glucose intolerance. Diabetes Care 2007; 30: 1892–1894.
Vozarova B, Weyer C, Hanson K, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. Circulating interleukin-6 in relation to adiposity, insulin action, and insulin secretion. Obes Res 2001; 9: 414–417.
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH. Plasma concentration of interleukin-6 and the risk of future myocardial infarction among apparently healthy men. Circulation 2000; 101: 1767–1772.
Tsigos C, Papanicolaou DA, Kyrou I, Defensor R, Mitsiadis CS, Chrousos GP. Dose-dependent effects of recombinant human interleukin-6 on glucose regulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 4167–4170.
Fasshauer M, Kralisch S, Klier M, Lossner U, Bluher M, Klein J, et al. Adiponectin gene expression and secretion is inhibited by interleukin-6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 301: 1045–1050.
Boden G, Shulman G I. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Eur J Clin Invest 2002; 32: 14–23.
Sacheck J. Pediatric obesity: an inflammatory condition? J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2008; 32: 633–637.
Bhagat K, Balance P. Inflammatory cytokines impair endothelium dependent dilatation in human veins in vivo. Circulation 1997; 96: 3042–3047.
Gunnett CA, Heistad DD, Faraci FM. Interleukin-10 protects nitric oxide-dependent relaxation during diabetes: Role of superoxide. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1931–1937.
Esposito K, Giugliano D, Nappo F, Marfella L. Regression of carotid atherosclerosis by control of postprandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Campanian Postprandial Hyperglycemia Study Group. Circulation 2004; 110: 214–219.
Waters AK, Mast BT, Vella S, De La Eva R, O’Brien LM, Bailey S, et al. Structural equation modeling of sleep apnea, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction in children. J Sleep Res 2007; 16: 388–395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arslan, N., Erdur, B. & Aydin, A. Hormones and cytokines in childhood obesity. Indian Pediatr 47, 829–839 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-010-0142-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-010-0142-y