Abstract
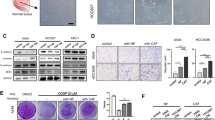
FBXO25 is a recently discovered protein that belongs to the Fbx class of the F-box family of proteins, and F-box proteins play a crucial role in tumorigenesis. However, the function of FBXO25 in cancer was not revealed so far. As measured by immunohistochemical staining, FBXO25 was highly expressed in the cytoplasm and nucleus of lung cancer samples (64.2 %, 136/212), compared with adjacent normal lung tissues (23.3 %, 7/30, p < 0.01). In addition, its expression was positively correlated with TNM staging (p < 0.001) and lymph node metastasis (p = 0.017). The overall survival of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with FBXO25-positive expression (40.646 ± 1.745 months) was significantly reduced compared with those with FBXO25-negative expression (46.548 ± 2.176 months, p = 0.023). Consistently, we found that the proliferation, invasion, and migration capacity of A549 cells transfected with FBXO25 were significantly greater than those of control cells, while interference of FBXO25 could significantly inhibit cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in H1299 cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated that FBXO25 could regulate the expression of β-catenin, YAP, some cyclins, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Collectively, these results indicate that FBXO25 may promote the tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells and might serve as a novel therapeutic target of NSCLC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassermann F, Eichner R, Pagano M. The ubiquitin proteasome system—implications for cell cycle control and the targeted treatment of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843:150–62.
Bedford L, Lowe J, Dick LR, Mayer RJ, Brownell JE. Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation and the ubiquitin-proteasome system as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:29–46.
Cenciarelli C, Chiaur DS, Guardavaccaro D, Parks W, Vidal M, Pagano M. Identification of a family of human f-box proteins. Current biology: CB. 1999;9:1177–9.
Winston JT, Koepp DM, Zhu C, Elledge SJ, Harper JW. A family of mammalian f-box proteins. Current biology: CB. 1999;9:1180–2.
Zheng N, Wang Z, Wei W. Ubiquitination-mediated degradation of cell cycle-related proteins by f-box proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;73:99–110.
Sukari A, Muqbil I, Mohammad RM, Philip PA, Azmi AS. F-box proteins in cancer cachexia and muscle wasting: emerging regulators and therapeutic opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;36:95–104.
Bochis OV, Fetica B, Vlad C, Achimas-Cadariu P, Irimie A. The importance of ubiquitin e3 ligases, scf and apc/c, in human cancers. Clujul medical. 2015;88:9–14.
Heo J, Eki R, Abbas T. Deregulation of f-box proteins and its consequence on cancer development, progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;36:33–51.
Liu Y, Mallampalli RK. Small molecule therapeutics targeting f-box proteins in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;36:105–19.
Uddin S, Bhat AA, Krishnankutty R, Mir F, Kulinski M, Mohammad RM. Involvement of f-box proteins in progression and development of human malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;36:18–32.
Hagens O, Minina E, Schweiger S, Ropers HH, Kalscheuer V. Characterization of fbx25, encoding a novel brain-expressed f-box protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:110–8.
Maragno AL, Baqui MM, Gomes MD. Fbxo25, an f-box protein homologue of atrogin-1, is not induced in atrophying muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:966–72.
Teixeira FR, Manfiolli AO, Soares CS, Baqui MM, Koide T, Gomes MD. The f-box protein fbxo25 promotes the proteasome-dependent degradation of elk-1 protein. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:28152–62.
Jang JW, Lee WY, Lee JH, Moon SH, Kim CH, Chung HM. A novel fbxo25 acts as an e3 ligase for destructing cardiac specific transcription factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;410:183–8.
Jeong HS, Jung ES, Sim YJ, Kim SJ, Jang JW, Hong KS, Lee WY, Chung HM, Park KT, Jung YS, Kim CH, Kim KS. Fbxo25 controls tbx5 and nkx2-5 transcriptional activity to regulate cardiomyocyte development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849:709–21.
Baumann U, Fernandez-Saiz V, Rudelius M, Lemeer S, Rad R, Knorn AM, Slawska J, Engel K, Jeremias I, Li Z, Tomiatti V, Illert AL, Targosz BS, Braun M, Perner S, Leitges M, Klapper W, Dreyling M, Miething C, Lenz G, Rosenwald A, Peschel C, Keller U, Kuster B, Bassermann F. Disruption of the prkcd-fbxo25-hax-1 axis attenuates the apoptotic response and drives lymphomagenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20:1401–9.
Kang G, Yun H, Sun CH, Park I, Lee S, Kwon J, Do I, Hong ME, Vrancken MV, Lee J, Park JO, Cho J, Kim KM, Sohn TS. Integrated genomic analyses identify frequent gene fusion events and vhl inactivation in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncotarget. 2015;7(6):6538–51.
Frescas D, Pagano M. Deregulated proteolysis by the f-box proteins skp2 and beta-trcp: tipping the scales of cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer. 2008;8:438–49.
Fuchs SY, Spiegelman VS, Kumar KG. The many faces of beta-trcp e3 ubiquitin ligases: reflections in the magic mirror of cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:2028–36.
Ougolkov A, Zhang B, Yamashita K, Bilim V, Mai M, Fuchs SY, Minamoto T. Associations among beta-trcp, an e3 ubiquitin ligase receptor, beta-catenin, and nf-kappab in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1161–70.
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, Hrychyk A, Schuller U, Waha A, Wharton KA, Jr., Fuchs SY, von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T: Elevated expression of wnt antagonists is a common event in hepatoblastomas. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2005;11:4295–4304.
Huang HL, Jiang Y, Wang YH, Chen T, He HJ, Liu T, Yang T, Yang LW, Chen J, Song ZQ, Yao W, Wu B, Liu G. Fbxo31 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and invasion in lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:1814–22.
Kumar R, Neilsen PM, Crawford J, McKirdy R, Lee J, Powell JA, Saif Z, Martin JM, Lombaerts M, Cornelisse CJ, Cleton-Jansen AM, Callen DF. Fbxo31 is the chromosome 16q24.3 senescence gene, a candidate breast tumor suppressor, and a component of an scf complex. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11304–13.
Huang HL, Zheng WL, Zhao R, Zhang B, Ma WL. Fbxo31 is down-regulated and may function as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2010;24:715–20.
Zhang X, Kong Y, Xu X, Xing H, Zhang Y, Han F, Li W, Yang Q, Zeng J, Jia J, Liu Z. F-box protein fbxo31 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and negatively regulated by mir-17 and mir-20a. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6178–90.
Kim M, Jho EH. Cross-talk between wnt/beta-catenin and hippo signaling pathways: a brief review. BMB Rep. 2014;47:540–5.
Stamos JL, Weis WI. The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a007898.
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V, Fassina A, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. Yap/taz incorporation in the beta-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the wnt response. Cell. 2014;158:157–70.
Zhao B, Li L, Tumaneng K, Wang CY, Guan KL. A coordinated phosphorylation by lats and ck1 regulates yap stability through scf(beta-trcp). Genes Dev. 2010;24:72–85.
Manfiolli AO, Maragno AL, Baqui MM, Yokoo S, Teixeira FR, Oliveira EB, Gomes MD. Fbxo25-associated nuclear domains: a novel subnuclear structure. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:1848–61.
Teixeira FR, Yokoo S, Gartner CA, Manfiolli AO, Baqui MM, Assmann EM, Maragno AL, Yu H, de Lanerolle P, Kobarg J, Gygi SP, Gomes MD. Identification of fbxo25-interacting proteins using an integrated proteomics approach. Proteomics. 2010;10:2746–57.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Hiroshi Kijima (Department of Pathology and Bioscience, Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan) for providing the LK2 cell line mentioned in this manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272606 to Enhua Wang, No.81302192 to Liang Wang, and No.81402369 to Guiyang Jiang) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2013021049 to Yong Zhang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, GY., Zhang, XP., Wang, L. et al. FBXO25 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of NSCLC. Tumor Biol. 37, 14311–14319 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5298-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5298-1