Abstract
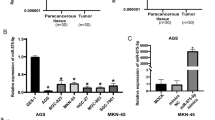
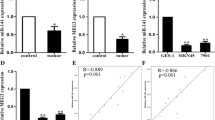
Aberrant expression of miR-137 has been reported in many kinds of cancers, but its mechanisms seem to be diversely. In the present study, we compared the expression level of miR-137 in 18 paired gastric cancer (GC) samples and surgical margin (SM) samples by RNA extraction and quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR). Then, we investigated the effects of miR-137 on cell proliferation, cell cycle, and cell migration separately by cell growth counting assay, cell cycle analysis, and transwell assay. Candidate targets of miR-137 were selected by biological information analysis from the intersection of miRDB, Pictar, and TarScan. Finally, mRNA and protein expression level of Krűppel-like factor 12 (KLF12) and Myosin 1C (MYO1C) were tested by QRT-PCR and western blotting assay, followed by the Luciferase reporter assay to investigate the direct interaction between them and miR-137. The results showed that miR-137 was down-regulated in GC samples than in SM samples. The expression level of miR-137 was significantly higher in patients without the vascular embolus than those with vascular embolus. And the overall survival time of patients with high miR-137 expression was longer than those with low miR-137 expression. Over expression of miR-137 could inhibit the cell migration, proliferation, and promote cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 stage in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cell lines. KLF12 and MYO1C might be the candidate target genes of miR-137 with direct interactions between them and miR-137. In conclusion, miR-137 plays tumor suppressor roles in gastric cancer cell lines by targeting KLF12 and MYO1C.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang TL, Fock KM. Clinical epidemiology of gastric cancer. Singap Med J. 2014;55(12):621–8.
Wu K, Li L, Li S. Circulating microRNA-21 as a biomarker for the detection of various carcinomas: an updated meta-analysis based on 36 studies. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(3):1973–81.
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, Tanaka Y, Kinoshita K, Saito S, Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, Baba Y, Baba H. Serum microRNA-21 is a novel biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106(2):188–92.
Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D, Shu Y. MiRNA-21: a biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(5):330–40.
Zhang HL, Yang LF, Zhu Y, Yao XD, Zhang SL, Dai B, Zhu YP, Shen YJ, Shi GH, Ye DW. Serum miRNA-21: elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate. 2011;71(3):326–31.
Kandalam MM, Beta M, Maheswari UK, Swaminathan S, Krishnakumar S. Oncogenic microRNA 17-92 cluster is regulated by epithelial cell adhesion molecule and could be a potential therapeutic target in retinoblastoma. Mol Vis. 2012;18:2279–87.
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Blanco M, Haz M, Medina V, Iglesias-Díaz P, Lorenzo-Patiño MJ, Reboredo M, Santamarina I, Figueroa A, Antón-Aparicio LM, Calvo L. Prognostic impact of disseminated tumor cells and microRNA-17-92 cluster deregulation in gastrointestinal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2011;39(5):1253–64.
Li Y, Xu Z, Li B, Zhang Z, Luo H, Wang Y, Lu Z, Wu X. Epigenetic silencing of miRNA-9 is correlated with promoter-proximal CpG island hypermethylation in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(6):2576–86.
Fiaschetti G, Abela L, Nonoguchi N, Dubuc AM, Remke M, Boro A, Grunder E, Siler U, Ohgaki H, Taylor MD, Baumgartner M, Shalaby T, Grotzer MA. Epigenetic silencing of miRNA-9 is associated with HES1 oncogenic activity and poor prognosis of medulloblastoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(3):636–47.
Du Y, Liu Z, Gu L, Zhou J, Zhu BD, Ji J, Deng D. Characterization of human gastric carcinoma-related methylation of 9 miRCpG islands and repression of their expressions in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:249.
Wong TS, Man OY, Tsang CM, Tsao SW, Tsang RK, Chan JY, Ho WK, Wei WI, To VS. MicroRNA let-7 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation through downregulating c-myc expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137(3):415–22.
Lee ST, Chu K, Oh HJ, Im WS, Lim JY, Kim SK, Park CK, Jung KH, Lee SK, Kim M, Roh JK. Let-7 microRNA inhibits the proliferation of human glioblastoma cells. J Neuro-Oncol. 2011;102(1):19–24.
Liang S, He L, Zhao X, Miao Y, Gu Y, Guo C, Xue Z, Dou W, Hu F, Wu K, Nie Y, Fan D. MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e18409.
Xiu Y, Liu Z, Xia S, Jin C, Yin H, Zhao W, Wu Q. MicroRNA-137 upregulation increases bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting PAQR3. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109734.
Zhang B, Liu T, Wu T, Wang Z, Rao Z, Gao J. microRNA-137 functions as a tumor suppressor in human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting SLC22A18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;74:111–8.
Li P, Ma L, Zhang Y, Ji F, Jin F. MicroRNA-137 down-regulates KIT and inhibits small cell lung cancer cell proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68(1):7–12.
Liu LL, SX L, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W, Yang YZ, Luo RZ, Zhang CZ, Yun JP. FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137 suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 2014;5(13):5113–24.
Zheng X, Dong J, Gong T, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Li Y, Shang Y, Li K, Ren G, Feng B, Li J, Tian Q, Tang S, Sun L, Li M, Zhang H, Fan D. MicroRNA library-based functional screening identified miR-137 as a suppresser of gastric cancer cell proliferation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015;141(5):785–95.
Liu S, Cui J, Liao G, Zhang Y, Ye K, Lu T, Qi J, Wan G. MiR-137 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(9):9131–8.
Cheng Y, Li Y, Liu D, Zhang R, Zhang J. miR-137 effects on gastric carcinogenesis are mediated by targeting cox-2-activated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(17):3274–81.
Minocherhomji S, Ying S, Bjerregaard VA, Bursomanno S, Aleliunaite A, Wu W, Mankouri HW, Shen H, Liu Y, Hickson ID. Replication stress activates DNA repair synthesis in mitosis. Nature. 2015;528(7581):286–90.
Giefing M, Wierzbicka M, Rydzanicz M, Cegla R, Kujawski M, Szyfter K. Chromosomal gains and losses indicate oncogene and tumor suppressor gene candidates in salivary gland tumors. Neoplasma. 55(1):55–60.
Xu M, Jin H, CX X, Sun B, Mao Z, Bi WZ, Wang Y. miR-382 inhibits tumor growth and enhance chemosensitivity in osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5(19):9472–83.
Nakamura Y, Migita T, Hosoda F, Okada N, Gotoh M, Arai Y, Fukushima M, Ohki M, Miyata S, Takeuchi K, Imoto I, Katai H, Yamaguchi T, Inazawa J, Hirohashi S, Ishikawa Y, Shibata T. Krüppel-like factor 12 plays a significant role in poorly differentiated gastric cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(8):1859–67.
Greenberg MJ, Ostap EM. Regulation and control of myosin-I by the motor and light chain-binding domains. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23(2):81–9.
Gillespie PG. Myosin I and adaptation of mechanical transduction by the inner ear. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci. 2004;359(1452):1945–51.
Hedberg Oldfors C, Dios DG, Linder A, Visuttijai K, Samuelson E, Karlsson S, Nilsson S, Behboudi A. Analysis of an independent tumor suppressor locus telomeric to Tp53 suggested Inpp5k and Myo1c as novel tumor suppressor gene candidates in this region. BMC Genet. 2015;16:80.
Ihnatovych I, Sielski NL, Hofmann WA. Selective expression of myosin IC isoform a in mouse and human cell lines and mouse prostate cancer tissues. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e108609.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Ningbo Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: 2014A610219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, F. et al. miR-137 plays tumor suppressor roles in gastric cancer cell lines by targeting KLF12 and MYO1C. Tumor Biol. 37, 13557–13569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5199-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5199-3